selumetinib
Array Biopharma To Report Top-line Results From ARRY-502 Asthma Trial
Sacramento Bee
AstraZeneca began a pivotal trial with selumetinib (an Array-invented drug) in patients with thyroid cancer in May 2013 and expects to begin a Phase 3 trial in patients with non-small cell lung cancer during the second half of 2013. Three other Array …
http://www.sacbee.com/2013/07/22/5586413/array-biopharma-to-report-top.html
Selumetinib (AZD6244) is a drug being investigated for the treatment of various types of cancer, for example non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).

The gene BRAF is part of the MAPK/ERK pathway, a chain of proteins in cells that communicates input from growth factors. Activating mutations in the BRAF gene, primarily V600E (meaning that the amino acid valine in position 600 is replaced by glutamic acid), are associated with lower survival rates in patients with papillary thyroid cancer. Another type of mutation that leads to undue activation of this pathway occurs in the gene KRAS and is found in NSCLC. A possibility of reducing the activity of the MAPK/ERK pathway is to block the enzyme MAPK kinase (MEK), immediately downstream of BRAF, with the drug selumetinib. More specifically, selumetinib blocks the subtypes MEK1 and MEK2 of this enzyme.[1]
In addition to thyroid cancer, BRAF-activating mutations are prevalent in melanoma (up to 59%), colorectal cancer (5–22%), serous ovarian cancer (up to 30%), and several other tumor types.[2]
KRAS mutations appear in 20 to 30% of NSCLC cases and about 40% of colorectal cancer.[1]
A Phase II clinical trial about selumetinib in NSCLC has been completed in September 2011;[3] one about cancers with BRAF mutations is ongoing as of June 2012[update].[4]
- Troiani, T.; Vecchione, L.; Martinelli, E.; Capasso, A.; Costantino, S.; Ciuffreda, L. P.; Morgillo, F.; Vitagliano, D. et al. (2012). “Intrinsic resistance to selumetinib, a selective inhibitor of MEK1/2, by cAMP-dependent protein kinase a activation in human lung and colorectal cancer cells”. British Journal of Cancer 106 (10): 1648–1659. doi:10.1038/bjc.2012.129. PMC 3349172. PMID 22569000.
|displayauthors= suggested (help) edit
- Davies, H.; Bignell, G. R.; Cox, C.; Stephens, P.; Edkins, S.; Clegg, S.; Teague, J.; Woffendin, H. et al. (2002). “Mutations of the BRAF gene in human cancer”. Nature 417 (6892): 949–954. doi:10.1038/nature00766. PMID 12068308.
|displayauthors= suggested (help) edit
- ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00890825 Comparison of AZD6244 in Combination With Docetaxel Versus Docetaxel Alone in KRAS Mutation Positive Non Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) Patients
- ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00888134 AZD6244 in Cancers With BRAF Mutations
more info…………………………………….
AZD-6244 (Selumetinib) is an orally-available, aminobenzimidazole-based, allosteric inhibitor of MEK1 kinase with an IC50 of 14 nM. [1] IC50 concentrations of
In cellular growth assays, AZD-6244 was more potent in cell lines containing activating B-Raf and Ras mutations, with IC50 values ranging from 59 to 473 nM. In HT-29 and Malme-3M cell studies, AZD-6244 was found to induce G1-S cell cycle arrest, inducing apoptosis after a 2-day incubation period. [1] In Colo-205 xenografts, AZD6244 induced increased levels of cleaved caspase-3, indicating apoptosis. [2]
In diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) lines, nanomolar concentration of AZD-6244 effectively downregulated MEK/ERK target substrates, including c-Myc, Mcl-1, and Bcl-2. [3]
Technical information:
| Chemical Formula: |
|
C17H15BrClFN4O3 |
| CAS #: |
|
606143-52-6 |
| Molecular Weight: |
|
457.68 |
| |
|
|
| Appearance: |
|
White |
| Chemical Name: |
|
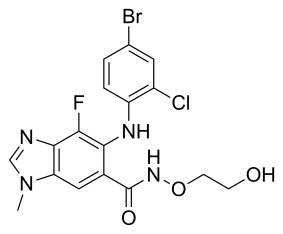
6-(4-bromo-2-chlorophenylamino)-7-fluoro-N-(2-hydroxyethoxy)-3-methyl-3H-benzo[d]imidazole-5-carboxamide |
| Solubility: |
|
Up to 100 mM in DMSO |
| Synonyms: |
|
AZD-6244, AZD 6244, AZD6244, Selumetinib, Selumetinib sulfate, NSC-748727, ARRY-142886 |
Reference:
| 1. |
Yeh et al., Biological characterization of ARRY-142886 (AZD6244), a potent, highly selective mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 1/2 inhibitor. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 1576-1583 Pubmed ID: 17332304 |
| 2. |
Davies et al., AZD6244 (ARRY-142886), a potent inhibitor of mitogen-activated protein kinase/extracellular signal-regulated kinase kinase 1/2 kinases: mechanism of action in vivo, pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic relationship, and potential for combination in preclinical models. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2007, 6, 2209-2219. Pubmed ID: 17699718 |
| 3. |
Bhalla et al., The novel anti-MEK small molecule AZD6244 induces BIM-dependent and AKT-independent apoptosis in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Blood, 2011, 118(4), 1052-1061. Pubmed ID: 21628402 |