Reslizumab
(Cinqair®) Approved Active, FDA 2016-03-23
An interleukin-5 (IL-5) antagonist used to treat severe asthma.
CAS 241473-69-8
![]()
Research Code CDP-835; CEP-38072; CTx-55700; SCH-5570; SCH-55700; TRFK-5,

Anti-interleukin-5 monoclonal antibody – Celltech/Schering-Plough
Reslizumab was approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) on March 23, 2016. It was developed and marketed as Cinqair® by Teva.
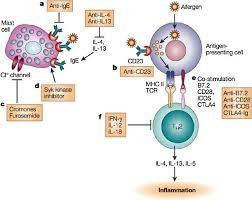
Reslizumab is an interleukin-5 antagonist, which binds to human IL-5 and prevents it from binding to the IL-5 receptor, thereby reducing eosinophilic inflammation. It is indicated for the maintenance treatment of patients with severe asthma in patients aged 18 years and older.
Cinqair® is available as injection for intravenous infusion, containing 100 mg of reslizumab in 10 mL solution in single-use vials. The recommended dose is 3 mg/kg once every four weeks.
- Originator Celltech R&D; Schering-Plough
- Developer Celltech R&D; Teva Pharmaceutical Industries
- Class Antiasthmatics; Monoclonal antibodies
- Mechanism of Action Interleukin 5 receptor antagonists
- Orphan Drug Status Yes – Oesophagitis
- 23 Mar 2016 Registered for Asthma in USA (IV) – First global approval
- 04 Mar 2016 Pooled efficacy data from two phase III trials in Asthma presented at the 2016 Annual Meeting of the American Academy of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology (AAAAI-2016)
- 10 Dec 2015 Preregistration for Asthma in Canada (IV)
Reslizumab (trade name Cinqair) is a humanized monoclonal antibody intended for the treatment of eosinophil-meditated inflammations of the airways, skin and gastrointestinal tract.[1] The FDA approved reslizumab for use with other asthma medicines for the maintenance treatment of severe asthma in patients aged 18 years and older on March 23, 2016. Cinqair is approved for patients who have a history of severe asthma attacks (exacerbations) despite receiving their current asthma medicines.[2]

Teva Announces FDA Acceptance of the Biologics License Application for Reslizumab
Investigational Biologic for the Treatment of Inadequately Controlled Asthma in Patients with Elevated Blood Eosinophils Accepted for Review
JERUSALEM–(BUSINESS WIRE)–Jun. 15, 2015– Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd., (NYSE: TEVA) announced today that the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has accepted for review the Biologics License Application (BLA) for reslizumab, the company’s investigational humanized monoclonal antibody (mAb) which targets interleukin-5 (IL-5), for the treatment of inadequately controlled asthma in adult and adolescent patients with elevated blood eosinophils, despite an inhaled corticosteroid (ICS)-based regimen.
“Despite currently available medicines, uncontrolled asthma remains a serious problem for patients, physicians and healthcare systems, highlighting the need for targeted new treatment options,” said Dr. Michael Hayden, President of Global R&D and Chief Scientific Officer at Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd. “The reslizumab BLA filing acceptance represents a significant milestone for Teva as we work toward serving a specific asthma patient population that is defined by elevated blood eosinophil levels and inadequately controlled symptoms despite standard of care therapy. In clinical trials, patients treated with reslizumab showed significant reductions in the rate of asthma exacerbations and significant improvement in lung function. If approved, we believe reslizumab will serve as an important new targeted treatment option to achieve better asthma control for patients with eosinophil-mediated disease.”
The BLA for reslizumab includes data from Teva’s Phase III BREATH clinical trial program. The program consisted of four separate placebo-controlled Phase III trials involving more than 1,700 adult and adolescent asthma patients with elevated blood eosinophils, whose symptoms were inadequately controlled with inhaled corticosteroid-based therapies. Results from these studies demonstrated that reslizumab, in comparison to placebo, reduced asthma exacerbation rates by at least half and provided significant improvement in lung function and other secondary measures of asthma control when added to an existing ICS-based therapy. Common adverse events in the reslizumab treatment group were comparable to placebo and included worsening of asthma, nasopharyngitis, upper respiratory infections, sinusitis, influenza and headache. Two anaphylactic reactions were reported and resolved following medical treatment at the study site.
Results from the reslizumab BREATH program were recently presented at the American Thoracic Society 2015 Annual Meeting and the American Academy of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology 2015 Annual Meeting, in addition to being published in The Lancet Respiratory Medicine. The BLA for reslizumab has been accepted for filing by the FDA for standard review, with FDA Regulatory Action expected in March 2016.
About Reslizumab
Reslizumab is an investigational humanized monoclonal antibody which targets interleukin-5 (IL-5). IL-5 is a key cytokine involved in the maturation, recruitment, and activation of eosinophils, which are inflammatory white blood cells implicated in a number of diseases, such as asthma. Elevated levels of blood eosinophils are a risk factor for future asthma exacerbations. Reslizumab binds circulating IL-5 thereby preventing IL-5 from binding to its receptor.
About Asthma
Asthma is a chronic (long term) disease usually characterized by airway inflammation and narrowing of the airways, which can vary over time. Asthma may cause recurring periods of wheezing (a whistling sound when you breathe), chest tightness, shortness of breath and coughing that often occurs at night or early in the morning. Without appropriate treatment, asthma symptoms may become more severe and result in an asthma attack, which can lead to hospitalization and even death.
About Eosinophils
Eosinophils are a type of white blood cell that are present at elevated levels in the lungs and blood of many asthmatics. Evidence shows that eosinophils play an active role in the pathogenesis of the disease. IL-5 has been shown to play a crucial role in maturation, growth and activation of eosinophils. Increased levels of eosinophils in the sputum and blood have been shown to correlate with severity and frequency of asthma exacerbations.
About Teva
Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd. (NYSE and TASE: TEVA) is a leading global pharmaceutical company that delivers high-quality, patient-centric healthcare solutions to millions of patients every day. Headquartered in Israel, Teva is the world’s largest generic medicines producer, leveraging its portfolio of more than 1,000 molecules to produce a wide range of generic products in nearly every therapeutic area. In specialty medicines, Teva has a world-leading position in innovative treatments for disorders of the central nervous system, including pain, as well as a strong portfolio of respiratory products. Teva integrates its generics and specialty capabilities in its global research and development division to create new ways of addressing unmet patient needs by combining drug development capabilities with devices, services and technologies. Teva’s net revenues in 2014 amounted to $20.3 billion. For more information, visit www.tevapharm.com.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration today approved Cinqair (reslizumab) for use with other asthma medicines for the maintenance treatment of severe asthma in patients aged 18 years and older. Cinqair is approved for patients who have a history of severe asthma attacks (exacerbations) despite receiving their current asthma medicines.
Asthma is a chronic disease that causes inflammation in the airways of the lungs. During an asthma attack, airways become narrow making it hard to breathe. Severe asthma attacks can lead to asthma-related hospitalizations because these attacks can be serious and even life-threatening. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, as of 2013, more than 22 million people in the U.S. have asthma, and there are more than 400,000 asthma-related hospitalizations each year.
“Health care providers and their patients with severe asthma now have another treatment option to consider when the disease is not well controlled by their current asthma therapies,” said Badrul Chowdhury, M.D., Ph.D., director of the Division of Pulmonary, Allergy, and Rheumatology Products in the FDA’s Center for Drug Evaluation and Research.
Cinqair is administered once every four weeks via intravenous infusion by a health care professional in a clinical setting prepared to manage anaphylaxis. Cinqair is a humanized interleukin-5 antagonist monoclonal antibody produced by recombinant DNA technology in murine myeloma non-secreting 0 (NS0) cells. Cinqair reduces severe asthma attacks by reducing the levels of blood eosinophils, a type of white blood cell that contributes to the development of asthma.
The safety and efficacy of Cinqair were established in four double-blind, randomized, placebo‑controlled trials in patients with severe asthma on currently available therapies. Cinqair or a placebo was administered to patients every four weeks as an add-on asthma treatment. Compared with placebo, patients with severe asthma receiving Cinqair had fewer asthma attacks, and a longer time to the first attack. In addition, treatment with Cinqair resulted in a significant improvement in lung function, as measured by the volume of air exhaled by patients in one second.
Cinqair can cause serious side effects including allergic (hypersensitivity) reactions. These reactions can be life-threatening. The most common side effects in clinical trials for Cinqair included anaphylaxis, cancer, and muscle pain.
Cinqair is made by Teva Pharmaceuticals in Frazer, Pennsylvania.

References
- 1Walsh, GM (2009). “Reslizumab, a humanized anti-IL-5 mAb for the treatment of eosinophil-mediated inflammatory conditions”. Current opinion in molecular therapeutics 11 (3): 329–36. PMID 19479666.
- 2http://www.fda.gov/NewsEvents/Newsroom/PressAnnouncements/ucm491980.htm
- http://www.fda.gov/NewsEvents/Newsroom/PressAnnouncements/ucm491980.htm
| Monoclonal antibody | |
|---|---|
| Type | Whole antibody |
| Source | Humanized (from rat) |
| Target | IL-5 |
| Clinical data | |
| Trade names | Cinquil |
| Identifiers | |
| ATC code | R03DX08 (WHO) |
| ChemSpider | none |
/////////CDP-835, CEP-38072, CTx-55700, SCH-5570, SCH-55700, TRFK-5, Reslizumab, Cinqair®, teva, interleukin-5 (IL-5) antagonist, severe asthma, FDA 2016, Orphan Drug StatuS