
PA 824
The search for a new tuberculosis drug after many decades and first time through a unique model of open drug discovery programme may finally bear fruits in near future, with India all set for the launch of the phase II clinical trial of the drug candidate.
The drug, coming through the Open Source Drug Discovery (OSDD) programme by Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR), will go for the clinical trials on drug-resistant TB patients in India very soon. The process of filing for permission from the Drug Controller General of India (DCGI) is on and public sector LRS Hospital for Respiratory and Infectious Diseases, New Delhi, has been selected for trials. This phase II trials will involve around 250-300 patients, sources said.

The drug candidate, Pa824, was synthesised in India long ago. After a series of ownership changes, the molecule was licensed to CSIR for further development now.
http://www.pharmabiz.com/NewsDetails.aspx?aid=76568&sid=1
Tuberculosis (TB) is one of the leading infectious diseases in the world, with approximately one-third of the world’s population harboring the causative agent, Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb). Though previously a disease associated with aristocratic societies, TB is now predominantly a third-world disease, particularly affecting Asian communities and sub-Saharan Africa. Mtb isolates are increasingly resistant to drug therapies: multidrug-resistant TB (MDR TB) or more severely, extensively drug-resistant TB (XDR TB). As a consequence of these emerging strains, it is becoming increasingly apparent that novel drugs are necessary to combat Mtb infections.

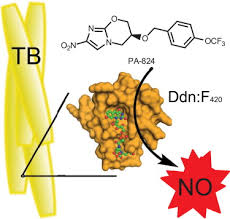
PA 824 is an experimental anti-tuberculosis drug.[1][2] The bicyclic nitroimidazole like molecule PA-824 has got a very complex mechanism of action active against both replicating and hypoxic, non-replicating Mycobacterium tuberculosis.Microarray analysis of the mode of action of PA-824 showed a puzzling mixed effect both on genes responsive to both cell wall inhibition (like isoniazid) and respiratory poisoning (like cyanide). The aerobic killing mechanism of this drug appears to involve inhibition of cell wall mycolic acid biosynthesis through an as yet unknown molecular mechanism.The respiratory poisoning through nitric oxide release seemed to be a crucial element of anaerobic activity by PA-824. The effect of PA-824 on the respiratory complex under hypoxic non-replicating conditions was also manifested in a rapid drop in intracellular ATP levels, again similar to that observed by cyanide treatment.[3]PA-824 recently was shown to be safe, well tolerated, and efficacious at doses of 100–200 mg daily in a dose-ranging study among drug-sensitive, sputum smear–positive, adult pulmonary TB patients [4]

- Ginsberg AM, Laurenzi MW, Rouse DJ, Whitney KD, Spigelman MK (September 2009). “Safety, tolerability, and pharmacokinetics of PA-824 in healthy subjects”. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 53 (9): 3720–5.doi:10.1128/AAC.00106-09. PMC 2737845. PMID 19528280.
- Stover CK, Warrener P, VanDevanter DR, et al (2000). “A small-molecule nitroimidazopyran drug candidate for the treatment of tuberculosis”. Nature 405 (6789): 962–6. doi:10.1038/35016103. PMID 10879539.
- Manjunatha U, Boshoff IM Helena, Barry CE (May-Jun 2009). “The mechanism of action of PA-824”. Commun Integr Biol. 2 (3): 215–218. PMC 2717523.
- http://www.pipelinereport.org/browse/tb-treatments/pa-824

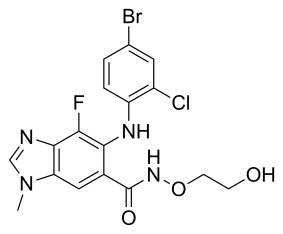
QSAR modeling of the nitroimidazole PA-824. Shown are two hydrogen bond acceptors (green), one hydrogen bond donor (purple), and one hydrophobe (aqua). Credit: NIAID























 LX4211
LX4211






