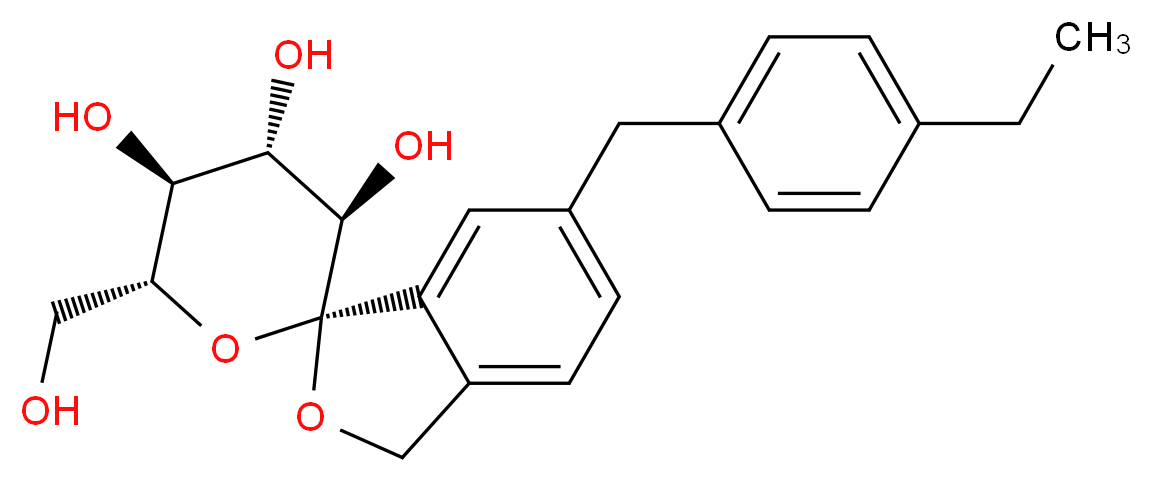
TOFOGLIFLOZIN
托格列净
CSG-452, R-7201, RG-7201
CAS..1201913-82-7 monohydrate
903565-83-3 (anhydrous)
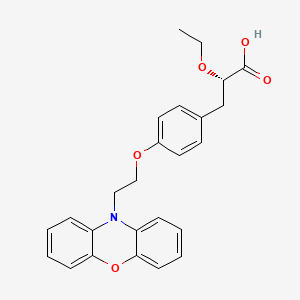
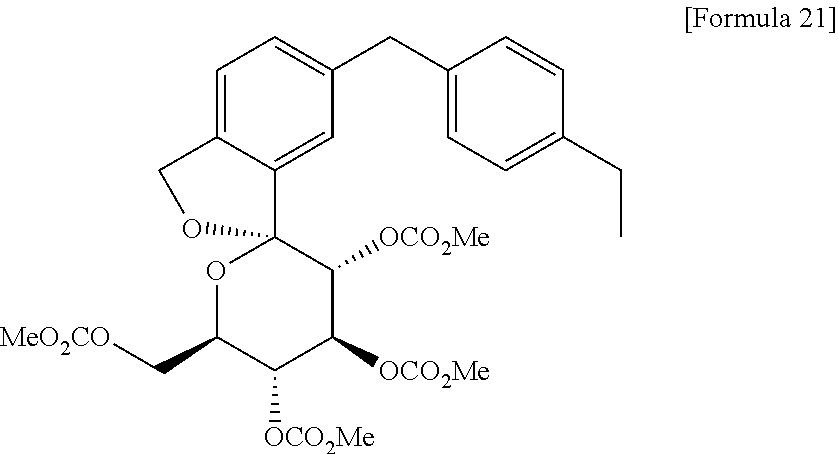
(1S,3′R,4′S,5′S,6′R)-6-(4-Ethylbenzyl)-6′-(hydroxymethyl)-3′,4′,5′,6′-tetrahydro-3H-spiro[2-benzofuran-1,2′-pyran]-3′,4′,5′-triol hydrate (1:1)
THERAPEUTIC CLAIM Treatment of diabetes mellitus
CHEMICAL NAMES
1. Spiro[isobenzofuran-1(3H),2′-[2H]pyran]-3′,4′,5′-triol, 6-[(4-ethylphenyl)methyl]-3′,4′,5′,6′-tetrahydro-6′-(hydroxymethyl)-, hydrate (1:1), (1S,3’R,4’S,5’S,6’R)-
2. (1S,3’R,4’S,5’S,6’R)-6-[(4-ethylphenyl)methyl]-6′-(hydroxymethyl)-3′,4′,5′,6′-tetrahydro-3H-spiro[2-benzofuran-1,2′-pyran]-3′,4′,5′-triol monohydrate
3. (1S,3’R,4’S,5’S,6’R)-6-[(4-ethylphenyl)methyl]-3′,4′,5′,6′-tetrahydro-6′-(hydroxymethyl)-
spiro[isobenzofuran-1(3H),2′-[2H]pyran]-3′,4′,5′-triol monohydrate
(3S,3’R,4’S,5’S,6’R)-5-[(4-ethylphenyl)methyl]-6′-(hydroxymethyl)spiro[1H-2-benzofuran-3,2′-oxane]-3′,4′,5′-triol;hydrate
MW404.5, MF C22H26O6
INNOVATOR Chugai Pharmaceuticals
Sanofi, kowa
Deberza®………..KOWA/Apleway®……………SANOFI
CODE DESIGNATION CSG 452
Tofogliflozin (USAN, codenamed CSG452) is an experimental drug for the treatment of diabetes mellitus and is being developed byChugai Pharma in collaboration with Kowa and Sanofi.[1] It is an inhibitor of subtype 2 sodium-glucose transport protein (SGLT2), which is responsible for at least 90% of the glucose reabsorption in the kidney. As of September 2012, the drug is in Phase III clinical trials.[2][3]
Tofogliflozin is an SGLT-2 inhibitor first launched in 2014 in Japan by Sanofi and Kowa for the oral treatment of type II diabetes.
The product was discovered by Chugai and was licensed to Roche in 2007. In 2011, this license agreement was terminated. In 2012, the product was licensed to Kowa and Sanofi by Chugai Pharmaceutical in Japan for the treatment of diabetes type 2. In 2015, the license between Kowa and Chugai was expanded for developments and marketing of the agent in the U.S. and the E.U.
Chemistry
The active moiety or anhydrous form (ChemSpider ID: 28530778, CHEMBL2110731) has the chemical formula C22H26O6 and amolecular mass of 386.44 g/mol.
The United States Adopted Name tofogliflozin applies to the monohydrate, which is the form used as a drug.[4] The International Nonproprietary Name tofogliflozin applies to the anhydrous compound[5] and the drug form is referred to as tofogliflozin hydrate.
Several drugs are available for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), but few patients achieve and maintain glycaemic control without weight gain and hypoglycaemias. Sodium glucose co-transporter 2 (SGLT-2) inhibitors are an emerging class of drugs with an original mechanism of action involving inhibition of renal glucose reabsorption. Two agents of this class, dapagliflozin and canagliflozin, have already been approved, although we need more data on cardiovascular outcomes along with bladder and breast cancer. Tofogliflozin is a further SGLT-2 inhibitor, which exhibits the highest selectivity for SGLT-2, the most potent antidiabetic action and a reduced risk of hypoglycaemia. Recently, a 52-week, multicentre, open-label, randomised controlled trial in Japanese T2DM patients has shown that tofogliflozin exhibits adequate safety and efficacy as monotherapy or as add-on treatment in patients suboptimally controlled with oral agents. Despite the very promising characteristics of this new drug, important questions remain to be answered, mainly additional data on safety outcomes and potential beneficial effects of tofogliflozin, for instance in prediabetes and diabetic nephropathy. Moreover, it would be welcome to examine the utility of its therapeutic use in combination with insulin and metformin.
Tofogliflozin has recently demonstrated safety and efficacy as monotherapy or add-on treatment . This is very important, granted our expectations of SGLT-2 inhibitors as useful alternative oral hypoglycaemic agents. Although important questions remain to be answered, the results of the new trial add to the importance of SGLT-2 inhibitors as a useful new class of oral hypoglycaemic agents.
CLIP
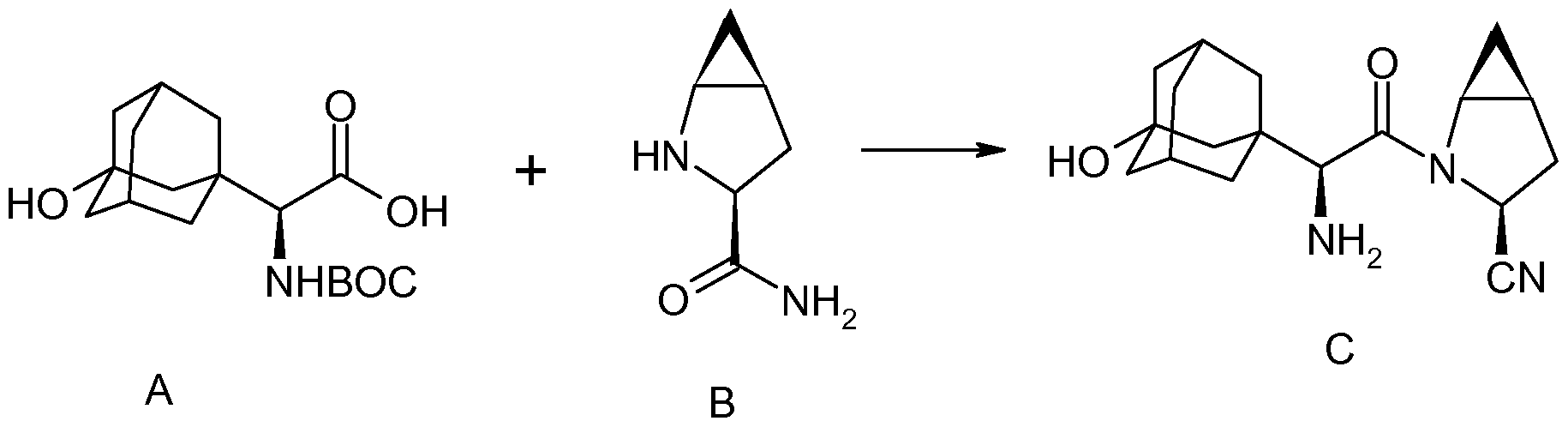
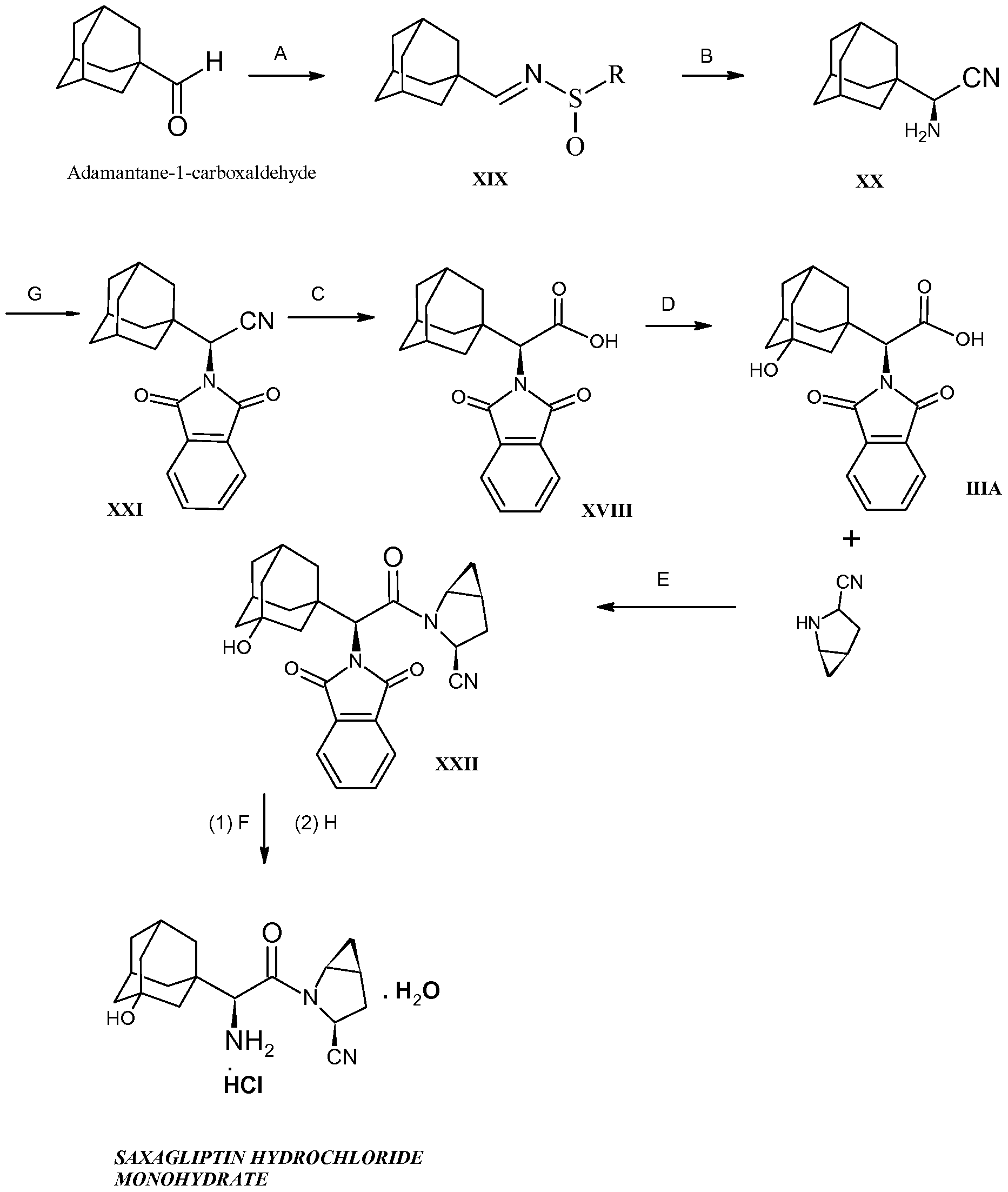
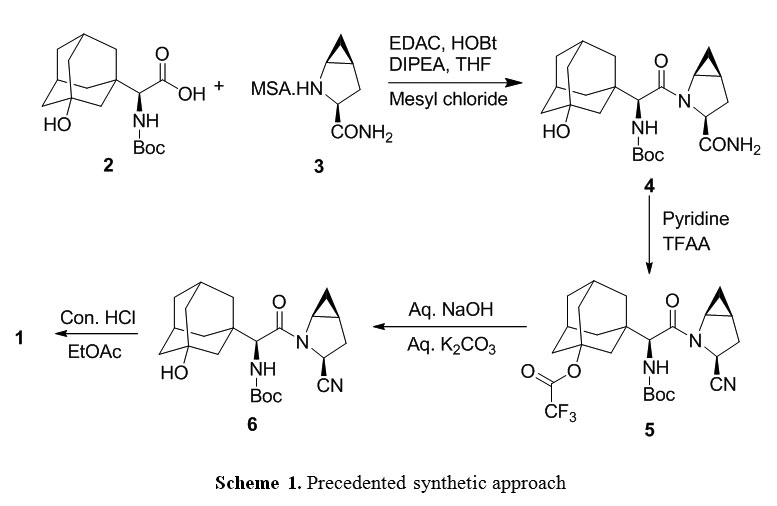
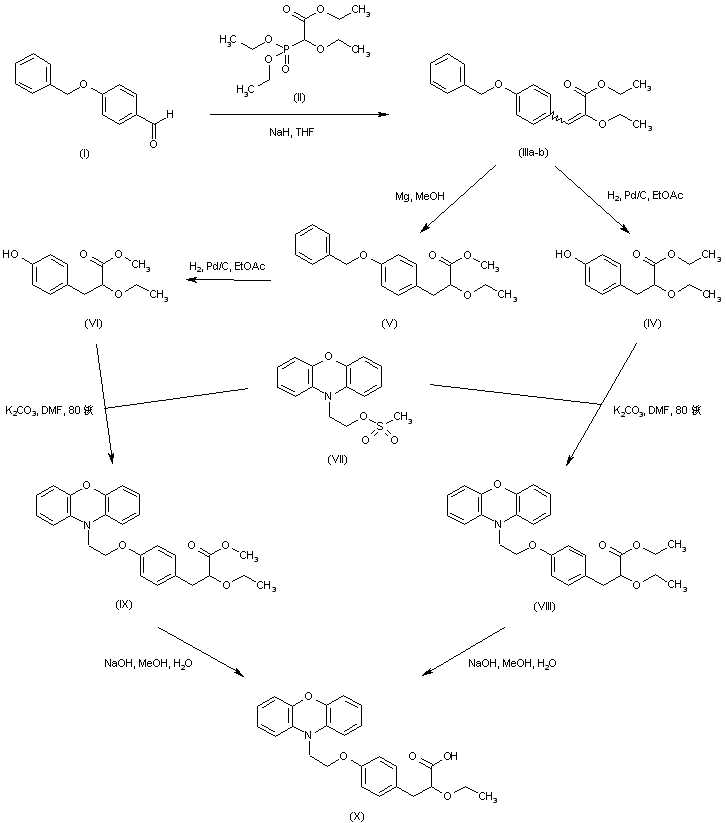
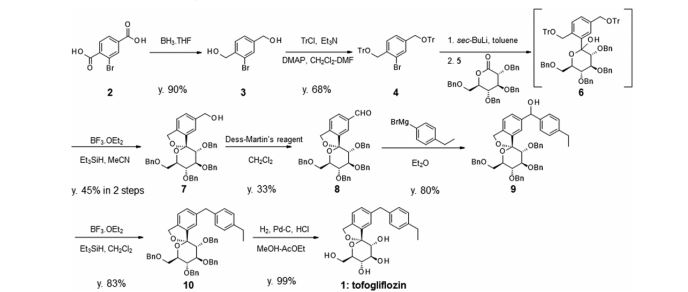
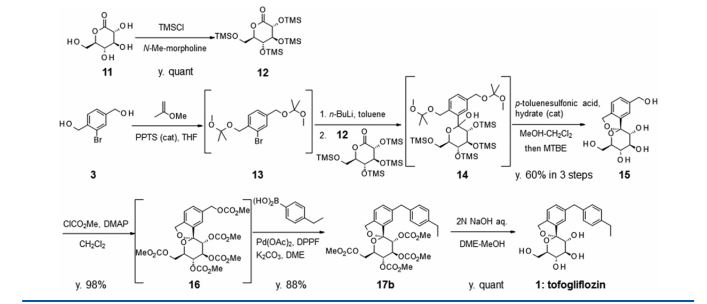
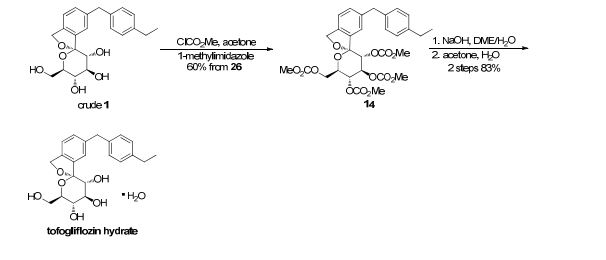
There are two scalable synthetic routes reported to prepare tofogliflozin.2 An efficient production synthesis of tofogliflozin hydrate from alcohol 2 was first described by Murakata et al. (Scheme 1, route 1).2a In 2016, Ohtake et al. reported an improved synthetic route, which achieved in just 7 linear steps (Scheme 1, route 2).2b They selected the optimal protecting groups for the purpose of chemoselective activation and crystalline purification, and obtained the pure tofogliflozin in a good overall yield. However, these methods suffer from several drawbacks. Firstly, some reagents, such as BH3 (Scheme 1, route 2) and 2-Methoxyproene (3, Scheme 1), are toxic or highly volatile. Meanwhile, the use of Palladium reagents may lead to an excess of residual heavy metal in the final product. Secondly, manufacturing costs in these methods are high due to the application of expensive raw materials and reagents. Last but not least, the key tactical stages that involve Br/Li exchange of aryl bromide followed by addition to gluconolactone 5 need the cryogenic conditions (< -60 oC), and this method is not suitable for industrial production. Herein, we report a newly developed synthetic method for tofogliflozin hydrate starting from readily available raw materials and affording good overall yield.

SCHEME 2 FOR
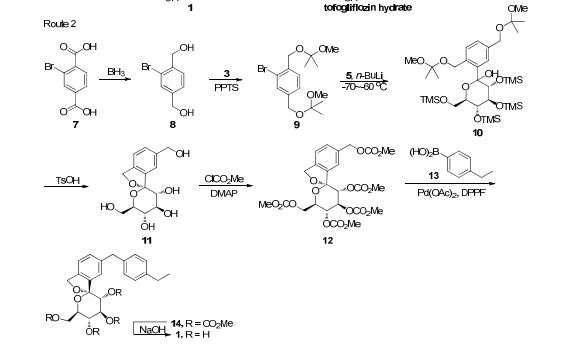
2. (a) Murakata, M.; Ikeda, T.; Kimura, N.; Kawase, A.; Nagase, M.; Yamamoto, K.; Takata, N.; Yoshizaki, S.; Takano, K. Crystal of spiroketal derivative, and process for production thereof. European Appl. EP 2308886 A1, April 13, 2011. (b) Ohtake, Y.; Emura, T.; Nishimoto, M.; Takano, K.; Yamamoto, K.; Tsuchiya, S.; Yeu, S.; Kito, Y.; Kimura, N.; Takeda, S.; Tsukazaki, M.; Murakata, M.; Sato, T. J. Org. Chem. 2016, 81, 2148.
CLIP
Ohtake, Y.; Sato, T.; Kobayashi, T.; Nishimoto, M.; Taka, N.; Takano, K.; Yamamoto, K.; Ohmori, M.; Yamaguchi, M.; Takami, K.; Yeu, S.-H.; Ahn, K.-H.; Matsuoka, H.; Morikawa, K.; Suzuki, M.; Hagita, H.; Ozawa, K.; Yamaguchi, K.; Kato, M.; Ikeda, S. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 7828−7840
DOI: 10.1021/acs.joc.5b02734 J. Org. Chem. 2016, 81, 2148−2153
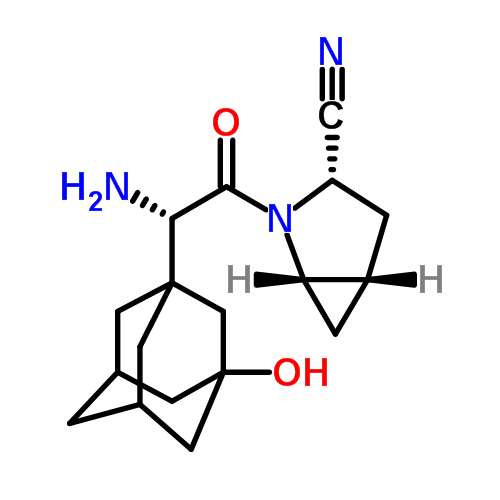
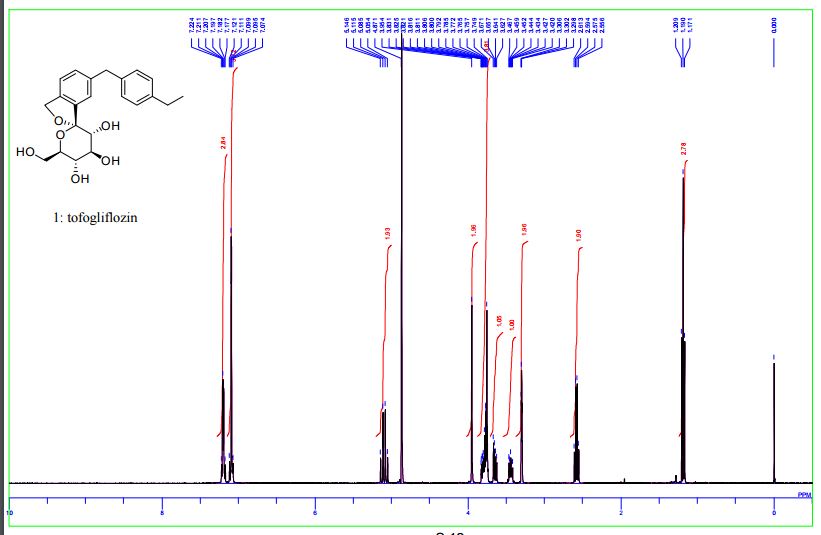
(1S,3′R,4′S,5′S,6′R)-6-[(4-Ethylphenyl)methyl]-6′-(hydroxymethyl)-3′,4′,5′,6′-tetrahydro-3H-spiro[2-benzofuran-1,2′- pyran]-3′,4′,5′-triol (1, tofogliflozin).
To a solution of 17b (89.9 g, 145 mmol) in DME (653 mL) and MeOH (73.0 mL), 2 N NaOH aq. solution (726 mL, 1.45 mol) was added dropwise for 1 h at waterbath temperature. After stirring at rt for 1 h, 2 N H2SO4 aq. solution (436 mL) was added slowly to the mixture. Water (700 mL) was added to the mixture, and the resultant mixture was extracted with AcOEt (500 mL × 2). The resultant organic layer was washed with brine (1.00 L) and then dried over anhydrous Na2SO4 (250 g). The mixture was concentrated in vacuo to obtain 1 (57.3 g, quant) as a colorless amorphous solid;
[α]D 26 +24.2° (c 1.02, MeOH);
1 H NMR (400 MHz, CD3OD) δ: 1.19 (3H, t, J = 7.6 Hz), 2.58 (2H, q, J = 7.6 Hz), 3.42−3.47 (1H, m), 3.63−3.67 (1H, m), 3.75−3.88 (4H, m), 3.95 (2H, s), 5.06 (1H, d, J = 12.5 Hz), 5.12 (1H, d, J = 12.5 Hz), 7.07−7.14 (4H, m), 7.17−7.23 (3H, m);
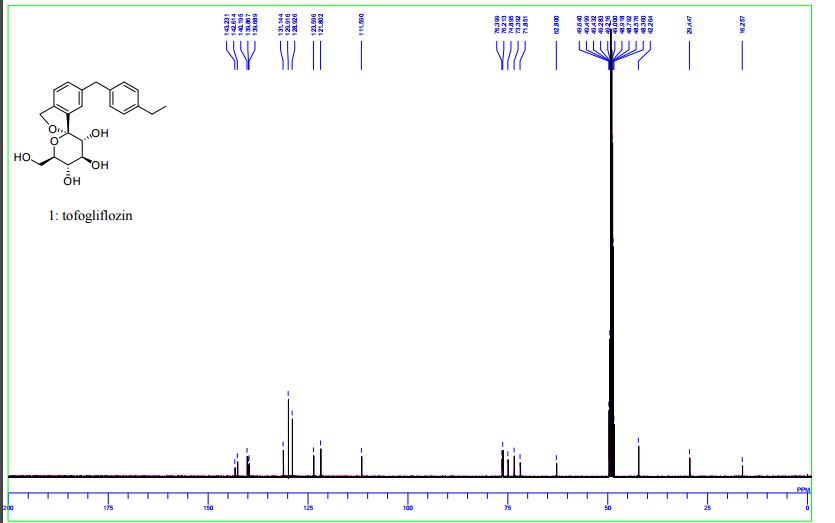
13C NMR (100 MHz, CD3OD) δ: 16.3, 29.4, 42.3, 62.8, 71.9, 73.4, 74.9, 76.2, 76.4, 111.6, 121.8, 123.6, 128.9, 129.9, 131.1, 139.7, 139.9, 140.2, 142.6, 143.2;
MS (ESI) m/z: 387 [M + H]+ ; HRMS (ESI) calcd for C22H27O6 [M + H]+ 387.1802, found 387.1801
DOI: 10.1021/acs.joc.5b02734 J. Org. Chem. 2016, 81, 2148−2153
Ohtake, Y.; Sato, T.; Kobayashi, T.; Nishimoto, M.; Taka, N.; Takano, K.; Yamamoto, K.; Ohmori, M.; Yamaguchi, M.; Takami, K.; Yeu, S.-H.; Ahn, K.-H.; Matsuoka, H.; Morikawa, K.; Suzuki, M.; Hagita, H.; Ozawa, K.; Yamaguchi, K.; Kato, M.; Ikeda, S. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 7828−7840
SGLT2 inhibitors inhibitors represent a novel class of agents that are being developed for the treatment or improvement in glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes. Glucopyranosyl-substituted benzene derivative are described in the prior art as SGLT2 inhibitors, for example in
WO 01/27128, WO 03/099836, WO 2005/092877, WO 2006/034489,
WO 2006/064033, WO 2006/117359, WO 2006/117360,
WO 2007/025943, WO 2007/028814, WO 2007/031548,
WO 2007/093610, WO 2007/128749, WO 2008/049923, WO 2008/055870, WO 2008/055940.
PATENTS
WO 2006080421
WO2009154276A1
WO 2011074675
WO 2012115249
Papers
Chinese Chemical Letters, 2013 , vol. 24, 2 pg. 131 – 133
Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 2012 , vol. 55, 17 pg. 7828 – 7840
NMR
WO 2011074675

1 H-NMR (CD 3 OD) δ: 1.19 (3H, t, J = 7.5Hz), 2.59 (2H, q, J = 7.5Hz) ,3.42-3 .46 (1H , m), 3.65 (1H, dd, J = 5.5,12.0 Hz) ,3.74-3 .82 (4H, m), 3.96 (2H, s), 5.07 (1H , d, J = 12.8Hz), 5.13 (1H, d, J = 12.8Hz) ,7.08-7 .12 (4H, m) ,7.18-7 .23 (3H, m) .
MS (ESI +): 387 [M +1] +.
Second set
http://pubs.acs.org/doi/full/10.1021/jm300884k
J. Med. Chem., 2012, 55 (17), pp 7828–7840
DOI: 10.1021/jm300884k
1H NMR (400 MHz, CD3OD) δ: 1.20 (3H, t, J = 7.6 Hz), 2.58 (2H, q, J = 7.6 Hz), 3.42–3.47 (1H, m), 3.63–3.67 (1H, m), 3.75–3.88 (4H, m), 3.95 (2H, s), 5.06 (1H, d, J = 12.3 Hz), 5.12 (1H, d, J = 12.5 Hz), 7.07–7.14 (4H, m), 7.17–7.23 (3H, m).
13C NMR (100 MHz, CD3OD) δ: 16.3, 29.4, 42.3, 62.8, 71.9, 73.4, 74.9, 76.2, 76.4, 111.6, 121.8, 123.6, 128.9, 129.9, 131.1, 139.7, 139.9, 140.2, 142.6, 143.2.
MS (ESI): 387 [M + H]+. HRMS (ESI), m/z calcd for C22H27O6 [M + H]+ 387.1802, found 387.1801.
THIRD SET
(1S,3′R,4′S,5′S,6′R)-6-[(4-Ethylphenyl)methyl]-6′-(hydroxymethyl)-3′,4′,5′,6′-tetrahydro-3H-spiro[2-benzofuran-1,2′- pyran]-3′,4′,5′-triol (1, tofogliflozin).
To a solution of 17b (89.9 g, 145 mmol) in DME (653 mL) and MeOH (73.0 mL), 2 N NaOH aq. solution (726 mL, 1.45 mol) was added dropwise for 1 h at waterbath temperature. After stirring at rt for 1 h, 2 N H2SO4 aq. solution (436 mL) was added slowly to the mixture. Water (700 mL) was added to the mixture, and the resultant mixture was extracted with AcOEt (500 mL × 2). The resultant organic layer was washed with brine (1.00 L) and then dried over anhydrous Na2SO4 (250 g). The mixture was concentrated in vacuo to obtain 1 (57.3 g, quant) as a colorless amorphous solid;
[α]D 26 +24.2° (c 1.02, MeOH);
1 H NMR (400 MHz, CD3OD) δ: 1.19 (3H, t, J = 7.6 Hz), 2.58 (2H, q, J = 7.6 Hz), 3.42−3.47 (1H, m), 3.63−3.67 (1H, m), 3.75−3.88 (4H, m), 3.95 (2H, s), 5.06 (1H, d, J = 12.5 Hz), 5.12 (1H, d, J = 12.5 Hz), 7.07−7.14 (4H, m), 7.17−7.23 (3H, m);
13C NMR (100 MHz, CD3OD) δ: 16.3, 29.4, 42.3, 62.8, 71.9, 73.4, 74.9, 76.2, 76.4, 111.6, 121.8, 123.6, 128.9, 129.9, 131.1, 139.7, 139.9, 140.2, 142.6, 143.2;
MS (ESI) m/z: 387 [M + H]+ ; HRMS (ESI) calcd for C22H27O6 [M + H]+ 387.1802, found 387.1801
DOI: 10.1021/acs.joc.5b02734 J. Org. Chem. 2016, 81, 2148−2153
Ohtake, Y.; Sato, T.; Kobayashi, T.; Nishimoto, M.; Taka, N.; Takano, K.; Yamamoto, K.; Ohmori, M.; Yamaguchi, M.; Takami, K.; Yeu, S.-H.; Ahn, K.-H.; Matsuoka, H.; Morikawa, K.; Suzuki, M.; Hagita, H.; Ozawa, K.; Yamaguchi, K.; Kato, M.; Ikeda, S. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 7828−7840
PATENT
Prepn
WO 2011074675
[Example 1] (1S, 3’R, 4’S, 5’S, 6’R) -6 – [(4 – ethyl-phenyl) methyl] -3 ‘, 4’, 5 ‘, 6′-tetrahydro- -6′-(hydroxymethyl) – spiro [isobenzofuran -1 (3H), 2’-[2H] pyran] -3 ‘, 4′, one of the preparation step [compound of formula (IX)] 5’-triol Preparation of methanol (2 – hydroxymethyl-phenyl – bromo-4)
To the mixing solution (1mol / L, 78.9kg, 88.4mol) of borane-tetrahydrofuran complex in tetrahydrofuran (6.34kg, 61.0mol) and, trimethoxyborane, two tetrahydrofuran (33.1kg) in – bromoterephthalic was added at below 30 ℃ solution (7.5kg, 30.6mol) of the acid, and the mixture was stirred for 1 hour at 25 ℃. Then cooled to 19 ℃ The reaction mixture was stirred for 30 minutes and added a mixed solution of tetrahydrofuran and methanol (3.0kg) of (5.6kg). In addition to methanol (15.0kg) in the mixture was kept for a while.
Again, to the mixing solution (1mol / L, 78.9kg, 88.4mol) of borane-tetrahydrofuran complex in tetrahydrofuran (6.34kg, 61.0mol) and, trimethoxyborane, two tetrahydrofuran (33.0kg) in – was added at below 30 ℃ solution (7.5kg, 30.6mol) of bromo terephthalic acid, and the reaction was carried out for 1 hour at 25 ℃. Then cooled to 18 ℃ The reaction mixture was stirred for 30 minutes and added a mixed solution of tetrahydrofuran and methanol (3.0kg) of (5.6kg). After addition of methanol (15.0kg) in the mixture is combined with the reaction mixture obtained in the previous reaction, and then the solvent was distilled off under reduced pressure. After addition of methanol (36kg) residue was obtained, and the solvent was evaporated under reduced pressure. Furthermore, (54 ℃ dissolved upon confirmation) which was dissolved by warming was added to methanol (36kg) to the residue. After cooling to room temperature the solution was stirred for 30 minutes added water (60kg). After addition of water (165kg) In addition to this mixture was cooled to 0 ℃, and the mixture was stirred for one hour. Centrifuge the obtained crystals were washed twice with water (45kg), and dried for 2 hours under reduced pressure to give (11.8kg, 54.4mol, 89% yield) of the title compound.
1 H-NMR (DMSO-d 6) δ: 4.49 (4H, t, J = 5.8Hz), 5.27 (1H, t, J = 5.8Hz), 5.38 (1H, t, J = 5.8Hz), 7.31 (1H, d, J = 7.5Hz), 7.47 (1H, d, J = 7.5Hz), 7.50 (1H, s).
Preparation of benzene (ethoxy methyl – methyl – – methoxy-1 1) – bromo-1 ,4 – 2:2 process bis
(- Bromo-4 – 2-hydroxyethyl methyl phenyl) in tetrahydrofuran (57kg) in the solution (8.0kg, 36.9mol) of methanol, I added (185.12g, 0.74mol) of pyridinium p-toluenesulfonate. After cooling to -15 ℃ below the mixture, 2 – was added at -15 ℃ or less (7.70kg, 106.8mol) methoxy propene, and the mixture was stirred 1 h at -15 ~ 0 ℃. Was added aqueous potassium carbonate (25 wt%, 40kg) and the reaction mixture was warmed to room temperature and separate the organic layer was added toluene (35kg). After washing with water (40kg) The organic layer was evaporated under reduced pressure. Was dissolved in toluene (28kg) and the residue obtained was obtained as a toluene solution of the title compound.
1 H-NMR (CDCl 3) δ: 1.42 (6H, s), 1.45 (6H, s), 3.24 (3H, s), 3.25 (3H, s), 4.45 ( 2H, s), 4.53 (2H, s), 7.28 (1H, dd, J = 1.5,8.0 Hz), 7.50 (1H, d, J = 8.0Hz), 7. 54 (1H, d, J = 1.5Hz).
MS (ESI +): 362 [M +2] +.
Preparation of on – (3R, 4S, 5R, 6R) -3,4,5 – tris (trimethylsilyloxy)-6 – trimethylsilyloxy methyl – tetrahydropyran-2: Step 3
Glucono -1,5 – – D-(+) in tetrahydrofuran (70kg) in the solution (35.8kg, 353.9mol) of N-methylmorpholine (7.88kg, 44.23mol) and lactone, chlorotrimethylsilane ( was added at 40 ℃ less 29.1kg, and 267.9mol), and the mixture was stirred for 2 hours at 30 ~ 40 ℃ resulting mixture. Was cooled to 0 ℃ the reaction mixture was added toluene (34kg) water (39kg), and the organic layer was separated. Twice sodium dihydrogen phosphate aqueous solution (5 wt%, 39.56kg) in, washed once with water (39kg) the organic layer the solvent was evaporated under reduced pressure. Was dissolved in toluene (34.6kg) and the residue obtained was obtained as a toluene solution of the title compound.
1 H-NMR (CDCl 3) δ: 0.13 (9H, s), 0.17 (9H, s), 0.18 (9H, s), 0.20 (9H, s), 3.74- 3.83 (3H, m), 3.90 (1H, t, J = 8.0Hz), 3.99 (1H, d, J = 8.0Hz), 4.17 (1H, dt, J = 2 .5,8.0 Hz).
Step 4: (1S, 3’R, 4’S, 5’S, 6’R) -3 ‘, 4’, 5 ‘, 6′-tetrahydro -6,6′ – bis (hydroxymethyl) – spiro [ (3H), 2’-[2H] pyran] -3 ‘, 4′, 5’-Preparation of triol isobenzofuran-1

(Methyl – – – methoxy 1-ethoxy-methyl) – bromo-1 ,4 – 2 prepared in step 2 bis cooled to below -10 ℃ toluene solution of benzene, hexane solution to (15 wt% n-butyl lithium , was added at below 0 ℃ 18.2kg, and 42.61mol), and the mixture was stirred 1.5 h at 5 ℃ resulting mixture. (10.5kg, 40.7mol), was added tetrahydrofuran (33.4kg) then magnesium bromide diethyl ether complex in the mixture, and the mixture was stirred for 1 hour at 25 ℃. Was added at below -10 ℃ toluene solution of the on – tris (trimethylsilyloxy) -6 – – 3,4,5 cooled to -15 ℃ below the mixture prepared in step 3 trimethylsilyloxy methyl – tetrahydropyran-2 was. After stirring 0.5 h at -15 ℃ or less, poured into 20% aqueous ammonium chloride solution to (80kg) of this solution, and the organic layer was separated. After washing with water (80kg) and the organic layer obtained, and the solvent was evaporated under reduced pressure. I was dissolved in methanol (43kg) residue was obtained. Was stirred for 1 hour at 20 ℃ was added (1.4kg, 7.4mol) and p-toluenesulfonic acid monohydrate in the mixture. Thereafter, it was stirred for another hour and cooled to 0 ℃, centrifuged crystals obtained was washed with methanol (25kg), and dried for 8 hours at reduced pressure under 40 ℃, (5.47kg, yield the title compound I got 50%) rate.
1 H-NMR (DMSO-d 6) δ :3.20-3 .25 (1H, m) ,3.41-3 .45 (1H, m) ,3.51-3 .62 (4H, m) , 4.39 (1H, t, J = 6.0Hz) ,4.52-4 .54 (3H, m), 4.86 (1H, d, J = 4.5Hz), 4.93 (1H, d, J = 5.5Hz), 4.99 (1H, d, J = 12.5Hz), 5.03 (1H, d, J = 12.5Hz), 5.23 (1H, t, J = 5 .8 Hz) ,7.24-7 .25 (2H, m), 7.29 (1H, dd, J = 1.5,8.0 Hz).
Step 5: (1S, 3’R, 4’S, 5’S, 6’R) -6 – [(methoxycarbonyl) methyl] -3 ‘, 4’, 5 ‘, 6′-tetrahydro-3’ , 4 ‘, 5′-tris (methoxycarbonyl) oxy-6′-[(methoxycarbonyl) methyl] – Preparation of [(3H), 2’-[2H] pyran isobenzofuran] spiro

(1S, 3’R, 4’S, 5’S, 6’R) – tetrahydro -6,6 ‘- bis (hydroxymethyl) – spiro [isobenzofuran -1 (3H), 2’-[2H] pyran ] -3 ‘, 4′, 5’-triol 4 (5.3kg, 17.8mol) and – dissolved in acetonitrile (35kg) (13.7kg, 112.1mol) a chloroformate, in the solution of dimethylaminopyridine I was added at 12 ℃ or less (10.01kg, 105.9mol) methyl. Heated to 20 ℃, After stirring for 1 h, was added ethyl acetate (40kg) and water (45kg), and the organic layer was separated and the mixture. Once (45.4kg) aqueous solution consisting of (9.01kg) sodium chloride and potassium hydrogen sulfate (1.35kg), sodium chloride aqueous solution (weight 10%, 44.5kg), sodium chloride aqueous solution (the organic layer was washed successively 20% by weight, in 45.0kg), and the solvent was evaporated under reduced pressure. Was dissolved in ethylene glycol dimethyl ether (18kg) and the residue obtained was then evaporated under reduced pressure. Was dissolved in ethylene glycol dimethyl ether (13.2kg) again and the residue obtained was obtained as ethylene glycol dimethyl ether solution of the title compound. I was used as it was in the six step.
1 H-NMR (CDCl 3) δ: 3.54 (3H, s), 3.77 (6H, s), 3.811 (3H, s), 3.812 (3H, s), 4.23 ( 1H, dd, J = 2.8,11.9 Hz), 4.32 (1H, dd, J = 4.0,11.9 Hz) ,4.36-4 .40 (1H, m), 5.11 -5.24 (5H, m), 5.41 (1H, d, J = 9.8Hz), 5.51 (1H, t, J = 9.8Hz), 7.25 (1H, d, J = 7.5Hz), 7.42 (1H, d, J = 7.5Hz), 7.44 (1H, s).
MS (ESI +): 589 [M +1] +, 606 [M +18] +.
Step 6: (1S, 3’R, 4’S, 5’S, 6’R) -6 – [(4 – ethyl-phenyl) methyl] -3 ‘, 4’, 5 ‘, 6’-tetrahydro-3 ‘4’, 5′-tris (methoxycarbonyl) oxy-6′-[(methoxycarbonyl) methyl] – Preparation of [(3H), 2′-[2H] pyran isobenzofuran] spiro

[(Methoxycarbonyl) methyl] -3 ‘, 4’, 5 ‘, 6’-tetrahydro – (1S, 3’R, 4’S, 5’S, 6’R) -6 which had been prepared in Step 5 – 3 ‘, 4′, 5′-tris (methoxycarbonyl) oxy-6′-[(methoxycarbonyl) methyl] – spiro [isobenzofuran -1 (3H), 2’-[2H] pyran] Ethylene glycol dimethyl ether in solution, 2 – (2.46kg, 17.8mol), 4 butanol (25kg), anhydrous potassium carbonate – – methyl-2 were sequentially added (3.73kg, 24.9mol) ethyl phenyl boronic acid, in the reaction vessel was replaced with argon atmosphere, was bubbled with argon mixture. To the mixture – after the addition (0.72kg, 0.88mol) and palladium (II) chloride dichloromethane adduct [1,1 ‘-bis (diphenylphosphino) ferrocene], it was replaced with argon again inside of the vessel, one at 80 ℃ I was stirring time. After cooling, I added sequentially (0.859kg, 5.3mol) of ethylene glycol dimethyl ether (9.85kg), ethyl acetate (19kg), N-acetyl-L-cysteine in the mixture. After stirring for 2.5 h the mixture was filtered and added Celite (5.22kg), and washed with ethyl acetate (78kg) and the filter residue. The combined washings and filtrate, and the solvent is evaporated off under reduced pressure, and in addition (0.58kg, 3.6mol) and ethanol (74kg), N-acetyl-L-cysteine residue was obtained, which is heated to 70 ℃ or I was dissolved residue is then. After addition of water (9.4kg) in the solution, cooled to 60 ℃, and the mixture was stirred for 1 h. After confirming solid precipitated, cooled to 0 ℃ from 60 ℃ over 2.5 hours or more The mixture was stirred for 1 hour or more at 5 ℃ less. Centrifuge the resulting solid was washed twice with a mixture of water (35kg) and ethanol (55kg). Was dissolved at 70 ℃ ethanol (77kg) again, wet powder was obtained (10.21kg), cooled to 60 ℃ added water (9.7kg), and the mixture was stirred for 1 h. After confirming solid precipitated, cooled to 0 ℃ from 60 ℃ over 2.5 hours or more, and the mixture was stirred for 1 hour or more at 5 ℃ less. (9.45kg, dry powder rate 8.47kg, 13.7mol which was centrifuged obtained crystals were washed with a mixture of water (32kg) and ethanol (51kg), was obtained as a moist powder the title compound, 77% overall yield from the previous step).
1 H-NMR (CDCl 3) δ: 1.20 (3H, t, J = 7.5Hz), 2.60 (2H, q, J = 7.5Hz), 3.50 (3H, s), 3 .76 (3H, s), 3.77 (3H, s), 3.81 (3H, s), 3.96 (2H, s), 4.23 (1H, dd, J = 2.8,11 .9 Hz), 4.33 (1H, dd, J = 4.5,11.9 Hz) ,4.36-4 .40 (1H, m) ,5.11-5 .20 (3H, m), 5 .41 (1H, d, J = 10.0Hz), 5.51 (1H, t, J = 10.0Hz) ,7.07-7 .11 (4H, m), 7.14 (1H, d, J = 7.8Hz), 7.19 (1H, dd, J = 1.5,7.8 Hz), 7.31 (1H, d, J = 1.5Hz).
MS (ESI +): 619 [M +1] +, 636 [M +18] +.
Step 7: (1S, 3’R, 4’S, 5’S, 6’R) -6 – [(4 – ethyl-phenyl) methyl] -3 ‘, 4’, 5 ‘, 6’-tetrahydro-6 , 4 ‘, 5′-Preparation of triol’ – -3 [(3H), 2′-[2H] pyran isobenzofuran] spiro – (hydroxymethyl) ‘

(1S, 3’R, 4’S, 5’S, 6’R) -6 – [(4 – ethyl-phenyl) methyl] -3 ‘, 4’, 5 ‘, 6′-tetrahydro-3’, 4 ‘, 5′-tris (methoxycarbonyl) oxy-6′-[(methoxycarbonyl) methyl] – wet powder spiro [(3H), 2’-[2H] pyran isobenzofuran -1] (8.92kg, In addition at 20 ℃ (4mol / L, 30.02kg, the 104.2mol) aqueous solution of sodium hydroxide, 1 hour the reaction mixture to a solution of (28kg) ethylene glycol dimethyl ether dry end conversion 8.00kg, of 12.9mol) the mixture was stirred. And the organic layer was separated by addition of water (8.0kg) in the mixture. The ethyl acetate aqueous sodium chloride solution (25 wt%, 40kg) and a (36kg) in the organic layer and the aqueous layer was removed after washing. The washed again aqueous sodium chloride solution (25 wt%, 40kg) in the organic layer was evaporated under reduced pressure. Were added and acetone (32.0kg) water (0.8kg) residue was obtained. After the solvent was evaporated under reduced pressure, dissolved in acetone (11.7kg) in water (15.8kg) and the residue obtained was cooled to below 5 ℃. Was added below 10 ℃ water (64kg) to the mixture, and the mixture was stirred for 1 hour at below 10 ℃. Centrifuge the resulting crystals were washed with a mixture of water (8.0kg) and (1.3kg) acetone. For 8 hours through-flow drying 13 ~ 16 ℃ temperature ventilation, under the conditions of 24-33% relative humidity the wet powder, the monohydrate crystal (3.94kg, 9.7mol, 75% yield) of the title compound I was obtained as: (4.502 wt% water content).
Method of measuring the amount of water:
Analysis: coulometric KF titration analyzer: trace moisture measurement device manufactured by Mitsubishi Chemical Corporation Model KF-100
Anolyte: Aqua micron AX (manufactured by Mitsubishi Chemical Corporation)
Catholyte: Aqua micron CXU (manufactured by Mitsubishi Chemical Corporation)
1 H-NMR (CD 3 OD) δ: 1.19 (3H, t, J = 7.5Hz), 2.59 (2H, q, J = 7.5Hz) ,3.42-3 .46 (1H , m), 3.65 (1H, dd, J = 5.5,12.0 Hz) ,3.74-3 .82 (4H, m), 3.96 (2H, s), 5.07 (1H , d, J = 12.8Hz), 5.13 (1H, d, J = 12.8Hz) ,7.08-7 .12 (4H, m) ,7.18-7 .23 (3H, m) .
MS (ESI +): 387 [M +1] +.
PATENT
US20110306778
Example 1 Synthesis of 1,1-anhydro-1-C-[5-(4-ethylphenyl)methyl-2-(hydroxymethyl)phenyl]-β-D-glucopyranose Step 1: Synthesis of 3,4,5-tris(trimethylsilyloxy)-6-trimethylsilyloxymethyl-tetrahydropyran-2-one
To a solution of D-(+)-glucono-1,5-lactone (7.88 kg) and N-methylmorpholine (35.8 kg) in tetrahydrofuran (70 kg) was added trimethylsilyl chloride (29.1 kg) at 40° C. or below, and then the mixture was stirred at a temperature from 30° C. to 40° C. for 2 hours. After the mixture was cooled to 0° C., toluene (34 kg) and water (39 kg) were added thereto. The organic layer was separated and washed with an aqueous solution of 5% sodium dihydrogen phosphate (39.56 kg×2) and water (39 kg×1). The solvent was evaporated under reduced pressure to give the titled compound as an oil. The product was used in the next step without further purification.
1H-NMR (CDCl3) δ: 0.13 (9H, s), 0.17 (9H, s), 0.18 (9H, s), 0.20 (9H, s), 3.74-3.83 (3H, m), 3.90 (1H, t, J=8.0 Hz), 3.99 (1H, d, J=8.0 Hz), 4.17 (1H, dt, J=2.5, 8.0 Hz).
Step 2: Synthesis of 2,4-dibromo-1-(1-methoxy-1-methylethoxymethyl)benzene
Under a nitrogen atmosphere, to a solution of 2,4-dibromobenzyl alcohol (40 g, 0.15 mol) in tetrahydrofuran (300 ml) was added 2-methoxypropene (144 ml, 1.5 mol) at room temperature, and then the mixture was cooled to 0° C. At the same temperature, pyridinium p-toluenesulfonic acid (75 mg, 0.30 mmol) was added and the mixture was stirred for 1 hour. The reaction mixture was poured into a saturated aqueous solution of sodium hydrogen carbonate cooled to 0° C., and extracted with toluene. The organic layer was washed with a saturated aqueous solution of sodium chloride, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate, and the solvent was evaporated under reduced pressure to give the titled compound as an oil in quantitative yield. The product was used in the next step without further purification.
1H-NMR (CDCl3) δ: 1.44 (6H, s), 3.22 (3H, 4.48 (2H, s), 7.42 (1H, d, J=8.0 Hz), 7.44 (1H, dd, J=1.5, 8.0 Hz), 7.68 (1H, d, J=1.5 Hz).
Step 3: Synthesis of 2,3,4,5-tetrakis(trimethylsilyloxy)-6-trimethylsilyloxymethyl-2-(5-(4-ethylphenyl)hydroxymethyl-2-(1-methoxy-1-methylethoxymethyl)phenyl)tetrahydropyran

Under a nitrogen atmosphere, 2,4-dibromo-1-(1-methoxy-1-methylethoxymethyl)benzene (70 g, 207 mmol), which was obtained in the previous step, was dissolved in toluene (700 mL) and t-butylmethyl ether (70 ml), and n-butyllithium in hexane (1.65 M, 138 ml, 227 mmol) was added dropwise at 0° C. over 30 minutes. After the mixture was stirred for 1.5 hours at 0° C., the mixture was added dropwise to a solution of 3,4,5-tris(trimethylsilyloxy)-6-trimethylsilyloxymethyl-tetrahydropyran-2-one (Example 1, 108 g, 217 mol) in tetrahydrofuran (507 ml) at −78° C., and the reaction mixture was stirred for 2 hours at the same temperature. Triethylamine (5.8 ml, 41 mmol) and trimethylsilyl chloride (29.6 ml, 232 mmol) were added thereto, and the mixture was warmed to 0° C. and stirred for 1 hour to give a solution containing 2,3,4,5-tetrakis(trimethylsilyloxy)-6-trimethylsilyloxymethyl-2-(5-bromo-2-(1-methoxy-1-methylethoxymethyl)phenyl)tetrahydropyran.
The resulting solution was cooled to −78° C., and n-butyllithium in hexane (1.65 M, 263 ml, 434 mmol) was added dropwise thereto at the same temperature. After the mixture was stirred at −78° C. for 30 minutes, 4-ethylbenzaldehyde (62 ml, 455 mmol) was added dropwise at −78° C., and the mixture was stirred at the same temperature for 2 hours. A saturated aqueous solution of ammonium chloride was added to the reaction mixture, and the organic layer was separated, and washed with water. The solvent was evaporated under reduced pressure to give a product containing the titled compound as an oil (238 g). The product was used in the next step without further purification.
A portion of the oil was purified by HPLC (column: Inertsil ODS-3, 20 mm I.D.×250 mm; acetonitrile, 30 mL/min) to give four diastereomers of the titled compound (two mixtures each containing two diastereomers).
Mixture of Diastereomers 1 and 2:
1H-NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) δ: −0.47 (4.8H, s), −0.40 (4.2H, s), −0.003-0.004 (5H, m), 0.07-0.08 (1314, m), 0.15-0.17 (18H, m), 1.200 and 1.202 (3H, each t, J=8.0 Hz), 1.393 and 1.399 (3H, each s), 1.44 (3H, s), 2.61 (2H, q, J=8.0 Hz), 3.221 and 3.223 (3H, each s), 3.43 (1H, t, J=8.5 Hz), 3.54 (1H, dd, J=8.5, 3.0 Hz), 3.61-3.66 (1H, m), 3.80-3.85 (3H, m), 4.56 and 4.58 (1H, each d, J=12.4 Hz), 4.92 and 4.93 (1H, each d, J=12.4 Hz), 5.80 and 5.82 (1H, each d, J=3.0 Hz), 7.14 (2H, d, J=8.0 Hz), 7.28-7.35 (3H, m), 7.50-7.57 (2H, m).
MS (ESI+): 875 [M+Na]+.
Mixture of Diastereomers 3 and 4:
1H-NMR (500 MHz, toluene-d8, 80° C.) δ: −0.25 (4H, s), −0.22 (5H, s), 0.13 (5H, s), 0.16 (4H, s), 0.211 and 0.214 (9H, each s), 0.25 (9H, s), 0.29 (9H, s), 1.21 (3H, t, J=7.5 Hz), 1.43 (3H, s), 1.45 (3H, s), 2.49 (2H, q, J=7.5 Hz), 3.192 and 3.194 (3H, each s), 3.91-4.04 (4H, m), 4.33-4.39 (2H, m), 4.93 (1H, d, J=14.5 Hz), 5.10-5.17 (1H, m), 5.64 and 5.66 (1H, each s), 7.03 (2H, d, J=8.0 Hz), 7.28-7.35 (3H, m), 7.59-7.64 (1H, m), 7.87-7.89 (1H, m).
MS (ESI+): 875 [M+Na]+.
Step 4: Synthesis of 1,1-anhydro-1-C-[5-(4-ethylphenyl)hydroxymethyl-2-(hydroxymethyl)phenyl]-β-D-glucopyranose
Under a nitrogen atmosphere, the oil containing 2,3,4,5-tetrakis(trimethylsilyloxy)-6-trimethylsilyloxymethyl-2-(5-(4-ethylphenyl)hydroxymethyl-2-(1-methoxy-1-methylethoxymethyl)phenyl)tetrahydropyran (238 g), which was obtained in the previous step, was dissolved in acetonitrile (693 ml). Water (37 ml) and 1N HCl aq (2.0 ml) were added and the mixture was stirred at room temperature for 5.5 hours. Water (693 ml) and n-heptane (693 ml) were added to the reaction mixture and the aqueous layer was separated. The aqueous layer was washed with n-heptane (693 ml×2), and water was evaporated under reduced pressure to give a product containing water and the titled compound (a diastereomer mixture) as an oil (187 g). The product was used in the next step without further purification.
1H-NMR (500 MHz, CD3OD) δ: 1.200 (3H, t, J=7.7 Hz), 1.201 (3H, t, J=7.7 Hz), 2.61 (2H, q, J=7.7 Hz), 3.44-3.48 (1H, m), 3.63-3.68 (111, m), 3.76-3.84 (4H, m), 5.09 (1H, d, J=12.8 Hz), 5.15 (1H, d, J=12.8 Hz), 5.79 (1H, s), 7.15 (2H, d, J=7.7 Hz), 7.24 and 7.25 (1H, each d, J=8.4 Hz), 7.28 (2H, d, J=7.7 Hz), 7.36 (1H, dd, J=8.4, 1.5 Hz), 7.40-7.42 (114, m).
MS (ESI+): 425 [M+Na]+.
Step 5: Synthesis of 1,1-anhydro-1-C-[5-(4-ethylphenyl)methyl-2-(hydroxymethyl)phenyl]-β-D-glucopyranose (crude product)
To a solution of the oil containing 1,1-anhydro-1-C-[5-(4-ethylphenyl)hydroxymethyl-2-(hydroxymethyl)phenyl]-β-D-glucopyranose (187 g), which was obtained in the previous step, in 1,2-dimethoxyethane (693 ml) was added 5% Pd/C (26 g, 6.2 mmol, water content ratio: 53%), and the mixture was stirred in the atmosphere of hydrogen gas at room temperature for 4 hours. After filtration, the filtrate was evaporated under reduced pressure to give an oil containing the titled compound (59 g). The purity of the resulting product was 85.7%, which was calculated based on the area ratio measured by HPLC. The product was used in the next step without further purification.
1H-NMR (CD3OD) δ: 1.19 (3H, t, J=7.5 Hz), 2.59 (2H, q, J=7.5 Hz), 3.42-3.46 (1H, m), 3.65 (1H, dd, J=5.5, 12.0 Hz), 3.74-3.82 (4H, m), 3.96 (2H, s), 5.07 (1H, d, J=12.8 Hz), 5.13 (1H, d, J=12.8 Hz), 7.08-7.12 (4H, m), 7.18-7.23 (3H, m).
MS (ESI+): 387 [M+1]+.
Measurement Condition of HPLC:
Column: Cadenza CD-C18 50 mm P/NCD032
Mobile phase: Eluent A: H2O, Eluent B: MeCN
Gradient operation: Eluent B: 5% to 100% (6 min), 100% (2 min)
Flow rate: 1.0 mL/min
Temperature: 35.0° C.
Detection wavelength: 210 nm
Step 6: Synthesis of 1,1-anhydro-1-C-[5-(4-ethylphenyl)methyl-2-(hydroxymethyl)phenyl]-2,3,4,6-tetra-O-methoxycarbonyl-β-D-glucopyranose
Under a nitrogen atmosphere, to a solution of the oil containing 1,1-anhydro-1-C-[5-(4-ethylphenyl)methyl-2-(hydroxymethyl)phenyl]-β-D-glucopyranose (59 g) and 4-(dimethylamino)pyridine (175 g, 1436 mmol) in acetonitrile (1040 ml) was added dropwose methyl chloroformate (95 ml, 1231 mmol) at 0° C. The mixture was allowed to warm to room temperature while stirred for 3 hours. After addition of water, the mixture was extracted with isopropyl acetate. The organic layer was washed with an aqueous solution of 3% potassium hydrogensulfate and 20% sodium chloride (three times) and an aqueous solution of 20% sodium chloride, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate, and the solvent was evaporated under reduced pressure. To the resulting residue was added ethanol (943 mL) and the mixture was heated to 75° C. to dissolve the residue. The mixture was cooled to 60° C. and a seed crystal of the titled compound was added thereto. The mixture was cooled to room temperature and stirred for 1 hour. After precipitation of solid was observed, water (472 ml) was added thereto, and the mixture was stirred at room temperature for 2 hours. The resulting crystal was collected by filtration, washed with a mixture of water and ethanol (1:1), and dried under reduced pressure to give the titled compound (94 g). To the product (91 g) was added ethanol (1092 ml), and the product was dissolved by heating to 75° C. The solution was cooled to 60° C. and a seed crystal of the titled compound was added thereto. The mixture was cooled to room temperature and stirred for 1 hour. After precipitation of solid was observed, water (360 ml) was added thereto, and the mixture was stirred at room temperature for 2 hours. The resulting crystal was collected by filtration, washed with a mixture of water and ethanol (1:1), and dried under reduced pressure to give the titled compound [83 g, total yield from 2,4-dibromo-1-(1-methoxy-1-methylethoxymethyl)benzene used in Step 3: 68%].
1H-NMR (CDCl3) δ: 1.20 (3H, t, J=7.5 Hz), 2.60 (2H, q, J=7.5 Hz), 3.50 (3H, s), 3.76 (3H, s), 3.77 (3H, s), 3.81 (3H, s), 3.96 (2H, s), 4.23 (1H, dd, J=2.5, 11.8 Hz), 4.33 (1H, dd, J=4.5, 12.0 Hz), 4.36-4.40 (1H, m), 5.11-5.20 (3H, m), 5.41 (1H, d, J=10.0 Hz), 5.51 (1H, t, J=10.0 Hz), 7.07-7.11 (4H, m), 7.14 (1H, d, J=7.5 Hz), 7.19 (1H, dd, J=1.5, 7.8 Hz), 7.31 (1H, d, J=1.5 Hz).
MS (ESI+): 619 [M+1]+, 636 [M+18]+.
Another preparation was carried out in the same manner as Step 6, except that a seed crystal was not used, to give the titled compound as a crystal.
Step 7: Synthesis of 1,1-anhydro-1-C-[5-(4-ethylphenyl)methyl-2-(hydroxymethyl)phenyl]-β-D-glucopyranose

To a solution of 1,1-anhydro-1-C-[5-(4-ethylphenyl)methyl-2-(hydroxymethyl)phenyl]-2,3,4,6-tetra-O-methoxycarbonyl-β-D-glucopyranose (8.92 kg as wet powder, corresponding to 8.00 kg of dry powder) in 1,2-dimethoxyethane (28 kg) was added a solution of sodium hydroxide (4 mol/L, 30.02 kg) at 20° C., and the mixture was stirred for 1 hour. Water (8.0 kg) was added to the mixture and the layers were separated. To the organic layer were added an aqueous solution of 25% sodium chloride (40 kg) and ethyl acetate (36 kg). The organic layer was separated, washed with an aqueous solution of 25% sodium chloride (40 kg), and the solvent was evaporated under reduced pressure. The purity of the resulting residue was 98.7%, which was calculated based on the area ratio measured by HPLC. To the resulting residue were added acetone (32.0 kg) and water (0.8 kg), and the solvent was evaporated under reduced pressure. To the resulting residue were added acetone (11.7 kg) and water (15.8 kg), and the solution was cooled to 5° C. or below. Water (64 kg) was added to the solution at 10° C. or below, and the mixture was stirred at the same temperature for 1 hour. The resulting crystal was collected by centrifugation, and washed with a mixture of acetone (1.3 kg) and water (8.0 kg). The resulting wet powder was dried by ventilation drying under a condition at air temperature of 13 to 16° C. and relative humidity of 24% to 33% for 8 hours, to give a monohydrate crystal (water content: 4.502%) of the titled compound (3.94 kg). The purity of the resulting compound was 99.1%, which was calculated based on the area ratio measured by HPLC.
1H-NMR (CD3OD) δ: 1.19 (3H, t, J=7.5 Hz), 2.59 (2H, q, J=7.5 Hz), 3.42-3.46 (1H, m), 3.65 (1H, dd, J=5.5, 12.0 Hz), 3.74-3.82 (4H, m), 3.96 (2H, s), 5.07 (1H, d, J=12.8 Hz), 5.13 (1H, d, J=12.8 Hz), 7.08-7.12 (4H, m), 7.18-7.23 (311, m).
MS (ESI+): 387 [M+1]+.
Measurement Condition of HPLC:
Column: Capcell pack ODS UG-120 (4.6 mm I.D.×150 mm, 3 μm, manufactured by Shiseido Co., Ltd.)
Mobile phase: Eluent A: H2O, Eluent B: MeCN
Mobile phase sending: Concentration gradient was controlled by mixing Eluent A and Eluent B as indicated in the following table.
|
TABLE 1 |
|
|
|
Time from |
|
|
|
injection (min) |
Eluent A (%) |
Eluent B (%) |
|
|
|
0 to 15 |
90→10 |
10→90 |
|
15 to 17.5 |
10 |
90 |
|
17.5 to 25 |
90 |
10 |
|
|
Flow rate: 1.0 mL/min
Temperature: 25.0° C.
Detection wavelength: 220 nm
Method for Measurement of Water Content:
Analysis method: coulometric titration method
KF analysis apparatus: Type KF-100 (trace moisture measuring apparatus manufactured by Mitsubishi Chemical Corporation)
Anode solution: Aquamicron AX (manufactured by Mitsubishi Chemical Corporation)
Cathode solution: Aquamicron CXU (manufactured by Mitsubishi Chemical Corporation)
PATENT
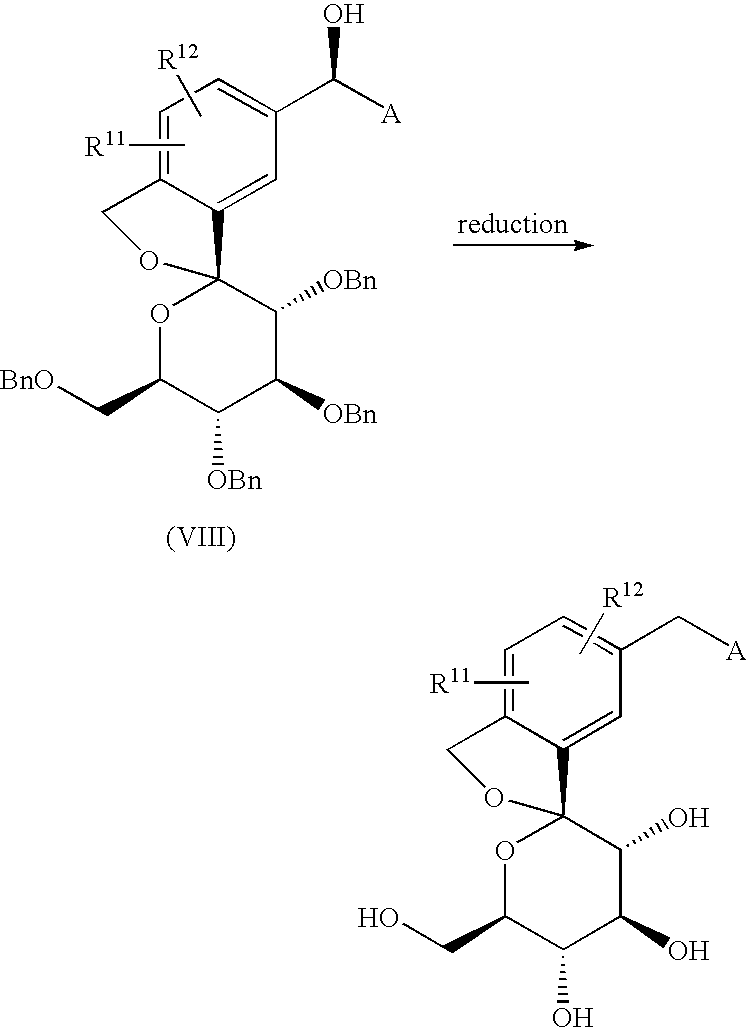
US20090030006
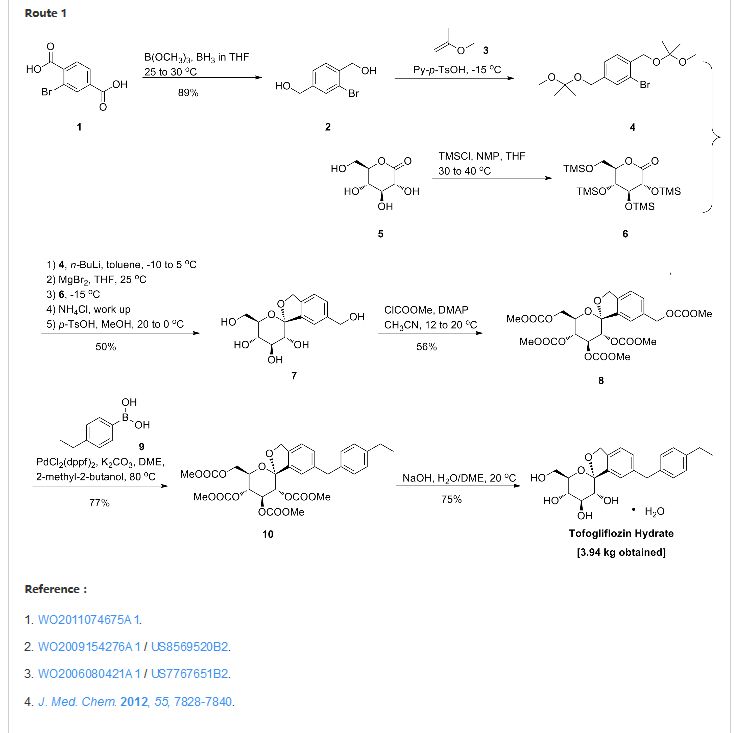
The compound of the present invention can be synthesized as shown in Scheme 1:
wherein R11 and R12 have the same meaning as defined above for substituents on Ar1, A is as defined above, and P represents a protecting group for a hydroxyl group.
CLIP
Tofogliflozin hydrate (Deberza�)
Tofogliflozin hydrate, which is a sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitor, was approved in Japan for the treatment of type 2 diabetes
at the same time as luseogliflozin hydrate (XIX). The drug was discovered by Chugai Pharmaceutical and jointly developed
with Sanofi-Aventis and Kowa.263
Tofogliflozin hydrate reduces glucose levels by inhibiting the reuptake of glucose by selectively
inhibiting SGLT2, and plays a key role in the reuptake of glucose in the proximal tubule of the kidneys.264–266 The synthetic
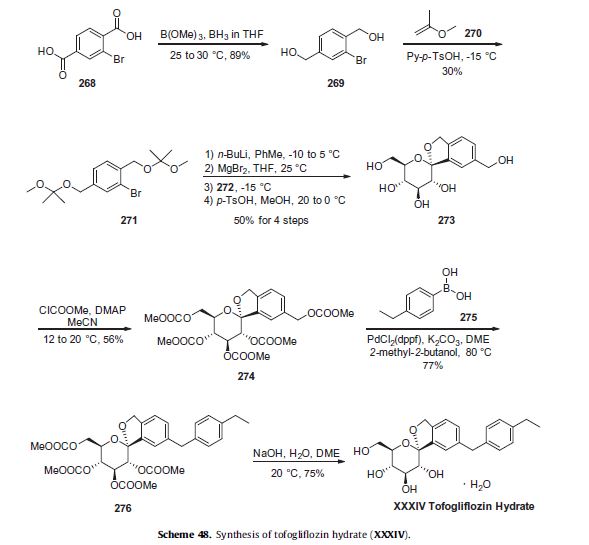
approach described in Scheme 48 represents the largest scale reported to date in a patent application.263,266–268
Reduction of commercially available 2-bromoterephtalic acid (268, Scheme 48) through the use of trimethoxyborane and borane-THF proceeded in 89% yield to afford diol 269.
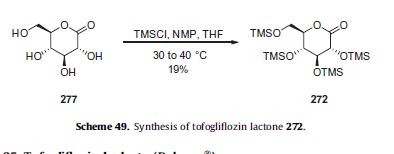
Subjection of this compound to 2-methoxypropene (270) under acidic conditions generated bis-acetonide 271. This bromide then underwent lithium–halogen exchange followed by exposure to magnesium bromide and treatment with lactone 272 (which was prepared by persilylation of commercially available (3R,4S,5S,6R)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-hydroxymethyl)tetrahydro-2Hpyran-2-one (277, Scheme 49).
This mixture was worked up with aqueous ammonium chloride and upon treatment with p-TsOH in methanol resulted in spiroacetal 273. Next, global protection of all alcohol functionalities within 273 was affected by reaction with methylchloroformate and DMAP in acetonitrile.
The benzyl carbonate within 274 was selectively exchanged via Suzuki coupling with 4-ethylphenylboronic acid (275) to afford methylene dibenzyl system 276. Subsequent treatment with aqueous sodium hydroxide in methanol followed by crystallization from 1:6 acetone and water furnished the desired product tofogliflozin hydrate (XXXIV) in 75% yield.
263 Takamitsu, K.; Tsutomu, S.; Masahiro, N. WO Patent 2006080421A1, 2006.
264. http://www.info.pmda.go.jp/shinyaku/P201400036/index.html.
265. Pafili, K.; Papanas, N. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2014, 15, 1197.
266. Ohtake, Y.; Sato, T.; Kobayashi, T.; Nishimoto, M.; Taka, N.; Takano, K.;Yamamoto, K.; Ohmori, M.; Yamaguchi, M.; Takami, K.; Yeu, S. Y.; Ahn, K. H.;Matsuoka, H.; Morikawa, K.; Suzuki, M.; Hagita, H.; Ozawa, K.; Yamaguchi, K.;Kato, M.; Ikeda, S. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 7828.
267. Murakata, M.; Ikeda, T.; Kawase, A.; Nagase, M.; Kimura, N.; Takeda, S.;Yamamoto, K.; Takano, K.; Nishimoto, M.; Ohtake, Y.; Emura, T.; Kito, Y. WOPatent 2011074675A1, 2011.
268. Murakata, M.; Takuma, I.; Nobuaki, K.; Masahiro, N.; Kawase, A.; Nagase, M.;Yamamoto, K.; Takata, N.; Yoshizaki, S. WO Patent 2009154276A1, 2009.
Paper
A Scalable Synthesis of Tofogliflozin Hydrate
Pharmaceutical Research Center, Disha Pharmaceutical Group Co., Ltd., Weihai 264205, China
Org. Process Res. Dev., Article ASAP
A newly process for the synthesis of tofogliflozin hydrate, a sodium-glucose cotransporter type 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor, was described. Three improvements were achieved, including the development of a regioselective Friedel–Crafts reaction, a high-yield reduction, and a mild metal–halogen exchange. These improvements ultimately resulted in the isolation of tofogliflozin hydrate as a white solid in >99% purity (HPLC area) and 23% overall yield after 12 steps without column chromatography.

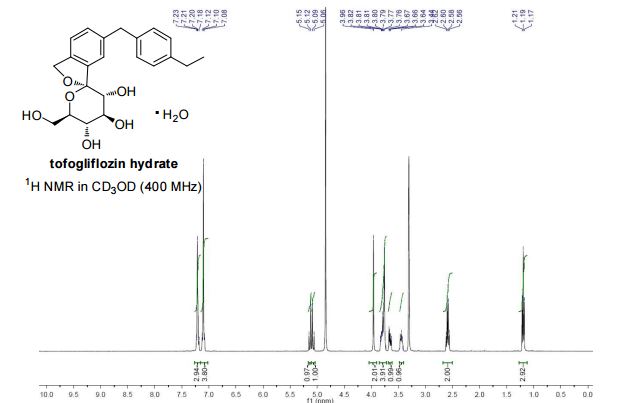
Tofogliflozin hydrate white solid with 99.56% purity by HPLC. Water content: 4.47%.
Mp: 71−80 oC. [α]20 D = +23.9 (c = 1.0, CH3OH).
1H NMR (400 MHz, CD3OD) δ 7.23-7.18 (m, 3H), 7.12-7.08(m, 4H), 5.13 (d, J = 12.4 Hz, 1H), 5.07 (d, J = 12.4 Hz, 1H), 3.96 (s, 2H), 3.83-3.73 (m, 4H), 3.65 (dd, J = 11.9, 5.5 Hz, 1H), 3.41-3.47 (m, 1H), 2.59 (q, J = 7.6 Hz, 2H), 1.19 (t, J = 7.6 Hz, 3H).
13C NMR (100 MHz, CD3OD) δ 143.2, 142.6, 140.2, 139.9, 139.7, 131.2, 129.9, 128.9, 123.6, 121.8, 111.6, 76.4, 76.2, 74.9, 73.4, 71.9, 62.8, 42.3, 29.5, 16.3.
HRMS (ESI) m/z: [M+H]+ Calcd for C22H27O6 387.1802; Found 387.1805.
IR (KBr, cm-1) ν: 3362, 2962, 2927, 1637, 1513, 1429, 1095, 1034, 808, 770. Spectroscopic data were identical with those reported.1b, 2
1. (a) Suzuki, M.; Honda, K.; Fukazawa, M.; Ozawa, K.; Hagita, H.; Kawai, T.; Takeda, M.; Yata, T.; Kawai, M.; Fukuzawa, T.; Kobayashi, T.; Sato, T.; Kawabe, Y.; Ikeda, S. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2012, 341, 692.
(b) Ohtake, Y.; Sato, T.; Kobayashi, T.; Nishimoto, M.; Taka, N.; Takano, K.; Yamamoto, K.; Ohmori, M.; Yamaguchi, M.; Takami, K.; Yeu, S.-H.; Ahn. K.-H.; Matsuoka, H.; Morikawa, K.; Suzuki, M.; Hagita, H.; Ozawa, K.; Yamaguchi, K.; Kato, M.; Ikeda, S. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 7828.
(c) Ikeda, S.; Takano, Y.; Cynshi, O.; Tanaka, R.; Christ, A. D.; Boerlin, V.; Beyer, U.; Beck, A.; Ciorciaro, C.; Meyer, M.; Kadowaki, T. Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism 2015, 17, 984.
2. (a) Murakata, M.; Ikeda, T.; Kimura, N.; Kawase, A.; Nagase, M.; Yamamoto, K.; Takata, N.; Yoshizaki, S.; Takano, K. Crystal of spiroketal derivative, and process for production thereof. European Appl. EP 2308886 A1, April 13, 2011.
(b) Ohtake, Y.; Emura, T.; Nishimoto, M.; Takano, K.; Yamamoto, K.; Tsuchiya, S.; Yeu, S.; Kito, Y.; Kimura, N.; Takeda, S.; Tsukazaki, M.; Murakata, M.; Sato, T. J. Org. Chem. 2016, 81, 2148.
References
- Chugai Pharmaceutical: Development Pipeline
- Nagata, T.; Fukazawa, M.; Honda, K.; Yata, T.; Kawai, M.; Yamane, M.; Murao, N.; Yamaguchi, K.; Kato, M.; Mitsui, T.; Suzuki, Y.; Ikeda, S.; Kawabe, Y. (2012). “Selective SGLT2 inhibition by tofogliflozin reduces renal glucose reabsorption under hyperglycemic but not under hypo- or euglycemic conditions in rats”. AJP: Endocrinology and Metabolism 304 (4): E414–E423. doi:10.1152/ajpendo.00545.2012.PMID 23249697.
- Ohtake, Y.; Sato, T.; Kobayashi, T.; Nishimoto, M.; Taka, N.; Takano, K.; Yamamoto, K.; Ohmori, M.; Yamaguchi, M.; Takami, K.; Yeu, S. Y.; Ahn, K. H.; Matsuoka, H.; Morikawa, K.; Suzuki, M.; Hagita, H.; Ozawa, K.; Yamaguchi, K.; Kato, M.; Ikeda, S. (2012). “Discovery of Tofogliflozin, a NovelC-Arylglucoside with anO-Spiroketal Ring System, as a Highly Selective Sodium Glucose Cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) Inhibitor for the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes”. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 55 (17): 7828–7840. doi:10.1021/jm300884k.PMID 22889351.
- Statement on a nonproprietary name adopted by the USAN council: Tofogliflozin.
- http://www.who.int/entity/medicines/publications/druginformation/innlists/RL65.pdf
Tofogliflozin monohydrate
 |
| Systematic (IUPAC) name |
|
(1S,3′R,4′S,5′S,6′R)-6-(4-Ethylbenzyl)-6′-(hydroxymethyl)-3′,4′,5′,6′-tetrahydro-3H-spiro[2-benzofuran-1,2′-pyran]-3′,4′,5′-triol hydrate (1:1)
|
| Legal status |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers |
| CAS Number |
1201913-82-7
903565-83-3 (anhydrous) |
| ATC code |
None |
| PubChem |
CID 46908928 |
| ChemSpider |
28527871 |
| KEGG |
D09978 |
| ChEMBL |
CHEMBL2105711 |
| Synonyms |
CSG452 |
| Chemical data |
| Formula |
C22H28O7 |
| Molar mass |
404.45 g/mol |
//////////TOFOGLIFLOZIN, 托格列净 , CSG-452, R-7201, RG-7201, 1201913-82-7 , 903565-83-3, oral hypoglycaemic agents, SGLT-2 inhibitors, type 2 diabetes mellitus, Deberza
CCc1ccc(cc1)Cc2ccc3c(c2)[C@]4([C@@H]([C@H]([C@@H]([C@H](O4)CO)O)O)O)OC3.O
The glucopyranosyl-substituted benzene derivatives are proposed as inducers of urinary sugar excretion and as medicaments in the treatment of diabetes.
The term “canagliflozin” as employed herein refers to canagliflozin, including hydrates and solvates thereof, and crystalline forms thereof and has the following structure:
The compound and methods of its synthesis are described in WO 2005/012326 and WO 2009/035969 for example. Preferred hydrates, solvates and crystalline forms are described in the patent applications WO 2008/069327 for example.
atigliflozin, including hydrates and solvates thereof, and crystalline forms thereof and has the following structure:
The compound and methods of its synthesis are described in WO 2004/007517 for example.
ipragliflozin, including hydrates and solvates thereof, and crystalline forms thereof and has the following structure:
The compound and methods of its synthesis are described in WO 2004/080990, WO 2005/012326 and WO 2007/114475 for example.
tofogliflozin, including hydrates and solvates thereof, and crystalline forms thereof and has the following structure:
The compound and methods of its synthesis are described in WO 2007/140191 and WO 2008/013280 for example.
remogliflozin and prodrugs of remogliflozin, in particular remogliflozin etabonate, including hydrates and solvates thereof, and crystalline forms thereof. Methods of its synthesis are described in the patent applications EP 1213296 and EP 1354888 for example.
sergliflozin and prodrugs of sergliflozin, in particular sergliflozin etabonate, including hydrates and solvates thereof, and crystalline forms thereof. Methods for its manufacture are described in the patent applications EP 1344780 and EP 1489089 for example.
luseoghflozin, including hydrates and solvates thereof, and crystalline forms thereof and has the following structure:
ertugliflozin, including hydrates and solvates thereof, and crystalline forms thereof and has the following structure:
and is described for example in WO 2010/023594.
The compound of the formula
is described for example in WO 2008/042688 or WO 2009/014970.
Dapagliflozin
The compound is described for example in WO 03/099836. Crystalline forms are described for example in WO 2008/002824.
Remogliflozin and Remogliflozin Etabonate
The compound is described for example in EP 1354888 A1.
Sergliflozin and Sergliflozin Etabonate
The compounds are described in EP 1 329 456 A1 and a crystalline form ofSergliflozin etabonate is described in EP 1 489 089 A1.
1-Chloro-4-(β-D-glucopyranos-1-yl)-2-(4-ethyl-benzyl)-benzene
The compound is described in WO 2006/034489.
(1S)-1,5-anhydro-1-[5-(azulen-2-ylmethyl)-2-hydroxyphenyl]-D-glucitol
The compound (4-(Azulen-2-ylmethyl)-2-(β-D-glucopyranos-1-yl)-1-hydroxy-benzene) is described in WO 2004/013118 and WO 2006/006496. The crystalline choline salt thereof is described in WO 2007/007628.
(1S)-1,5-anhydro-1-[3-(1-benzothien-2-ylmethyl)-4-fluorophenyl]-D-glucitol
The compound is described in WO 2004/080990 and WO 2005/012326. A cocrystal with L-proline is described in WO 2007/114475.
Thiophen Derivatives of the Formula (7-1)
wherein R denotes methoxy or trifluoromethoxy. Such compounds and their method of production are described in WO 2004/007517, DE 102004063099 and WO 2006/072334.
1-(β-D-glucopyranosyl)-4-methyl-3-[5-(4-fluorophenyl)-2-thienylmethyl]benzene
The compound is described in WO 2005/012326. A crystalline hemihydrate is described in WO 2008/069327.
Spiroketal Derivatives of the Formula (9-1)
wherein R denotes methoxy, trifluoromethoxy, ethoxy, ethyl, isopropyl or tert. butyl. Such compounds are described in WO 2007/140191 and WO 2008/013280.






 COCK WILL TEACH YOU NMR
COCK WILL TEACH YOU NMR COCK SAYS MOM CAN TEACH YOU NMR
COCK SAYS MOM CAN TEACH YOU NMR
 DRUG APPROVALS BY DR ANTHONY MELVIN CRASTO …..FOR BLOG HOME CLICK HERE
DRUG APPROVALS BY DR ANTHONY MELVIN CRASTO …..FOR BLOG HOME CLICK HERE