
2 (R)-3-Cyclopentyl-N-(5-methoxy-thiazolo[5,4-b]pyridin-2-yl)-2-[4-(4-methyl-piperazine-1-sulfonyl)-phenyl]-propionamide
3-Cyclopentyl-N-(5-methoxy-thiazolo[5,4-b]pyridin-2-yl)-2-[4-(4-methyl-piperazine-1-sulfonyl)-phenyl]-propionamide
(3-Cyclopentyl-N-(5-methoxy-thiazolo[5,4-b]pyridin-2-yl)-2-[4-(4-methyl-piperazine-1-sulfonyl)-phenyl]-propionamide)
cas 866772-52-3
NVP-LBX192
LBX-192

54 Discovery and Evaluation of NVP-LBX192, a Liver Targeted Glucokinase Activator
https://acs.confex.com/acs/nerm09/webprogram/Paper75087.html
| Molecular Formula: | C26H33N5O4S2 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight: | 543.70132 g/mol |
Sulfonamide-Thiazolpyridine Derivatives, Glucokinase Activators, Treatment Of Type 2 Diabetes
2009 52 (19) 6142 – 6152
Investigation of functionally liver selective glucokinase activators for the treatment of type 2 diabetes
Journal of Medicinal Chemistry
Bebernitz GR, Beaulieu V, Dale BA, Deacon R, Duttaroy A, Gao JP, Grondine MS, Gupta RC, Kakmak M, Kavana M, Kirman LC, Liang JS, Maniara WM, Munshi S, Nadkarni SS, Schuster HF, Stams T, Denny IS, Taslimi PM, Vash B, Caplan SL
2010 240th (August 22) Medi-198
Glucokinase activators with improved physicochemicalproperties and off target effects
American Chemical Society National Meeting and Exposition
Kirman LC, Schuster HF, Grondine MS et al
2010 240th (August 22) Medi-197
Investigation of functionally liver selective glucokinase activators
American Chemical Society National Meeting and Exposition
Schuster HF, Kirman LC, Bebernitz GC et al
PATENT
http://www.google.com/patents/US7750020
EXAMPLE 1 3-Cyclopentyl-N-(5-methoxy-thiazolo[5,4-b]pyridin-2-yl)-2-[4-(4-methyl-piperazine-1-sulfonyl)-phenyl]-propionamide
A. Phenylacetic Acid Ethyl Ester
A solution of phenylacetic acid (50 g, 0.36 mol) in ethanol (150 mL) is treated with catalytic amount of sulfuric acid (4 mL). The reaction mixture is refluxed for 4 h. The reaction is then concentrated in vacuo. The residue is dissolved in diethyl ether (300 mL) and washed with saturated aqueous sodium bicarbonate solution (2×50 mL) and water (1×100 mL). The organic layer dried over sodium sulfate filtered and concentrated in vacuo to give phenylacetic acid ethyl ester as a colorless oil: 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 1.2 (t, J=7.2, 3H), 3.6 (s, 2H), 4.1 (q, J=7.2, 2H), 7.3 (m, 5H); MS 165 [M+1]+.
B. (4-Chlorosulfonyl-phenyl)-acetic acid ethyl ester
To a cooled chlorosulfonic acid (83.83 g, 48 mL, 0.71 mol) under nitrogen is added the title A compound, phenylacetic acid ethyl ester (59 g, 0.35 mol) over a period of 1 h. Reaction temperature is brought to RT (28° C.), then heated to 70° C., maintaining it at this temperature for 1 h while stirring. Reaction is cooled to RT and poured over saturated aqueous sodium chloride solution (200 mL) followed by extraction with DCM (2×200 mL). The organic layer is washed with water (5×100 mL), followed by saturated aqueous sodium chloride solution (1×150 mL). The organic layer dried over sodium sulfate, filtered and concentrated in vacuo to give crude (4-chlorosulfonyl-phenyl)acetic acid ethyl ester. Further column chromatography over silica gel (60-120 mesh), using 100% hexane afforded pure (4-chlorosulfonyl-phenyl)-acetic acid ethyl ester as a colorless oil.
C. [4-(4-Methyl-piperazine-1-sulfonyl)-phenyl]-acetic acid ethyl ester
A solution of N-methylpiperazine (9.23 g, 10.21 ml, 0.092 mol), DIEA (13 g, 17.4 mL, 0.10 mol) and DCM 80 mL is cooled to 0° C., and to this is added a solution of the title B compound, (4-chlorosulfonyl-phenyl)-acetic acid ethyl ester (22 g, 0.083 mol) in 50 mL of DCM within 30 min. Reaction mixture stirred at 0° C. for 2 h, and the reaction mixture is washed with water (100 mL), followed by 0.1 N aqueous hydrochloric acid solution (1×200 mL). The organic layer dried over sodium sulfate, filtered and concentrated under vacuo to give crude [4-(4-methyl-piperazine-1-sulfonyl)-phenyl]-acetic acid ethyl ester. Column chromatography over silicagel (60-120 mesh), using ethyl acetate afforded pure [4-(4-methyl-piperazine-1-sulfonyl)-phenyl]-acetic acid ethyl ester as white crystalline solid: 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 1.3 (t, J=7.4, 3H), 2.3 (s, 3H), 2.5 (m, 4H), 3.0 (br s, 4H), 3.7 (s, 2H), 4.2 (q, J=7.4, 2H), 7.4 (d, J=8.3, 2H), 7.7 (d, J=7.3, 2H); MS 327 [M+1]+.
D. 3-Cyclopentyl-2-[4-(4-methyl-piperazine-1-sulfonyl)-phenyl]-propionic acid ethyl ester
A solution of the title C compound, [4-(4-methyl-piperazine-1-sulfonyl)-phenyl]-acetic acid ethyl ester (15 g, 0.046 mol) in a mixture of THF (60 mL) and DMTP (10 mL) is cooled to −78° C. under nitrogen. The resulting solution is stirred at −78° C. for 45 min and to this is added LDA (25.6 mL, 6.40 g, 0.059 mol, 25% solution in THF/Hexane). A solution of iodomethylcyclopentane (11.60 g, 0.055 mol) in a mixture of DMTP (12 mL) and THF (20 mL) is added over a period of 15 min at −78° C. and reaction mixture stirred at −78° C. for 3 h further, followed by stirring at 25° C. for 12 h. The reaction mixture is then quenched by the dropwise addition of saturated aqueous ammonium chloride solution (50 mL) and is concentrated in vacuo. The residue is diluted with water (50 mL) and extracted with ethyl acetate (3×100 mL). The organic solution is washed with a saturated aqueous sodium chloride (2×150 mL), dried over sodium sulfate, filtered and concentrated in vacuo. Column chromatography over silica gel (60-120 mesh), using 50% ethyl acetate in hexane as an eluent to afford 3-cyclopentyl-2-[4-(4-methyl-piperazine-1-sulfonyl)-phenyl]-propionic acid ethyl ester as a white solid: 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 0.9-2.1 (m, 11H), 1.2 (t, J=7.1, 3H), 2.3 (s, 3H), 2.5 (br s, 4H), 3.0 (br s, 4H), 3.6 (m, 1H), 4.1 (q, J=7.1, 2H), 7.5 (d, J=8.3, 2H), 7.7 (d, J=8.3, 2H); MS 409 [M+1]+.
E. 3-Cyclopentyl-2-[4-(4-methyl-piperazine-1-sulfonyl)-phenyl]-propionic acid
A solution of the title D compound, 3-cyclopentyl-2-[4-(4-methyl-piperazine-1-sulfonyl)-phenyl]-propionic acid ethyl ester (14 g, 0.034 mol) in methanol:water (30 mL:10 mL) and sodium hydroxide (4.11 g, 0.10 mol) is stirred at 60° C. for 8 h in an oil bath. The methanol is then removed in vacuo at 45-50° C. The residue is diluted with water (25 mL) and extracted with ether (1×40 mL). The aqueous layer is acidified to pH 5 with 3 N aqueous hydrochloric acid solution. The precipitated solid is collected by vacuum filtration, washed with water (20 mL), followed by isopropyl alcohol (20 mL). Finally, solid cake is washed with 100 mL of hexane and dried under vacuum at 40° C. for 6 h to give 3-cyclopentyl-2-[4-(4-methyl-piperazine-1-sulfonyl)-phenyl]-propionic acid as a white solid: 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 1.1-2.0 (m, 11H), 2.4 (s, 3H), 2.7 (br s, 4H), 3.1 (br s, 4H), 3.6 (m, 1H), 7.5 (d, J=8.3, 2H), 7.6 (d, J=8.3, 2H); MS 381 [M+l]+.
F. 5-Methoxy-thiazolo[5,4-b]pyridin-2-ylamine
A solution of 6-methoxy-pyridin-3-ylamine (5.0 g, 0.0403 mol) in 10 mL of acetic acid is added slowly to a solution of potassium thiocyanate (20 g, 0.205 mol) in 100 mL of acetic acid at 0° C. followed by a solution of bromine (2.5 mL, 0.0488 mol) in 5 mL of acetic acid. The reaction is stirred for 2 h at 0° C. and then allowed to warm to RT. The resulting solid is collected by filtration and washed with acetic acid, then partitioned between ethyl acetate and saturated aqueous sodium bicarbonate. The insoluble material is removed by filtration and the organic layer is evaporated and dried to afford 5-methoxy-thiazolo[5,4-b]pyridin-2-ylamine as a tan solid.
G. 3-Cyclopentyl-N-(5-methoxy-thiazolo[5,4-b]pyridin-2-yl)-2-[4-(4-methyl-piperazine-1-sulfonyl)-phenyl]-propionamide
A solution of the title E compound, 3-cyclopentyl-2-[4-(4-methyl-piperazine-1-sulfonyl)-phenyl]-propionic acid (5 g, 0.013 mol) in DCM (250 mL) is cooled to 0° C. and then charged HOBt hydrate (2.66 g, 0.019 mol), followed by EDCI hydrochloride (6 g, 0.031 mol). The reaction mixture is stirred at 0° C. for 5 h. After that the solution of the title F compound, 5-methoxy-thiazolo[5,4-b]pyridin-2-ylamine (2.36 g, 0.013 mol) and D1EA (8 mL, 0.046 mol) in a mixture of DCM (60 mL) and DMF (20 mL) is added dropwise over 30 min. Reaction temperature is maintained at 0° C. for 3 h, then at RT (28° C.) for 3 days. Reaction is diluted with (60 mL) of water and the organic layer is separated and washed with saturated sodium bicarbonate solution (2×50 mL) followed by water washing (2×50 mL) and saturated sodium chloride aqueous solution (1×150 mL). Finally the organic layer is dried over sodium sulfate, filtered, and evaporated under vacuo. The crude product is purified using column chromatography over silica gel (60-120 mesh), using 40% ethyl acetate in hexane as an eluent to afford 3-cyclopentyl-N-(5-methoxy-thiazolo[5,4-b]pyridin-2-yl)-2-[4-(4-methyl-piperazine-1-sulfonyl)-phenyl]-propionamide as a white solid: 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 0.9-2.1 (m, 11H), 2.2 (s, 3H), 2.5 (br s, 4H), 3.1 (br s, 4H), 3.7 (m, 1H), 4.0 (s, 3H), 6.8 (d, J=8.8, 1H), 7.5 (d, J=8.3, 2H), 7.7 (d, J=8.3, 2H), 7.8 (d, J=8.8, 1H), 8.6 (s, 1H); MS 617 [M+1]+.
H. 3-Cyclopentyl-N-(5-methoxy-thiazolo[5,4-b]pyridin-2-yl)-2-[4-(4-methyl-piperazine-1-sulfonyl)-phenyl]-propionamide dihydrochloride
The title G compound, 3-cyclopentyl-2-(4-methyl piperazinyl sulfonyl)phenyl-N-(5-methoxy-thiazolo[5,4-b]pyridin-2-yl)propionamide (2.8 g, 0.0051 mol) is added to a cooled solution of 10% hydrochloric acid in isopropanol (3.75 mL). The reaction mixture is stirred at 0° C. for 1 h and then at RT for 2 h. The solid is separated, triturated with 10 mL of isopropanol and collected by vacuum filtration and washed with 50 mL of hexane. The solid is dried at 70° C. for 48 h to afford 3-cyclopentyl-N-(5-methoxy-thiazolo[5,4-b]pyridin-2-yl)-2-[4-(4-methyl-piperazine-1-sulfonyl)-phenyl]-propionamide dihydrochloride as an off white solid.
EXAMPLE 2 (R)-3-Cyclopentyl-N-(5-methoxy-thiazolo[5,4-b]pyridin-2-yl)-2-[4-(4-methyl-piperazine-1-sulfonyl)-phenyl]-propionamide
The title compound is obtained analogously to Example 1 by employing the following additional resolution step:
The racemic title E compound of Example 1,3-cyclopentyl-2-[4-(4-methyl-piperazine-1-sulfonyl)-phenyl]-propionic acid (10 g, 0.026 mol) in 1,4-dioxane (500 mL) is treated in a three necked 1 liter flask, equipped with heating mantle, water condenser, calcium chloride guard tube and mechanical stirrer with 3.18 g (0.026 mol) of (R)-(+)-1-phenylethylamine. This reaction mixture is then refluxed at 100° C. for 1 h. The clear reaction solution is cooled to RT (27° C.) and stirred for 10 h. The crystallized salt is collected by filtration under vacuum, washed with 5 mL of hexane and dried under vacuum to afford salt A.
The salt A is dissolved in 1,4-dioxane (500 mL) and heated at 100° C. for 1 h. The clear reaction solution is cooled to RT (27° C.) and stirred for 10 h. The crystallized product is collected by filtration under vacuum, washed with 50 mL of hexane, and dried under vacuum to afford salt B.
The salt B is dissolved in 1,4-dioxane (290 mL) and heated at 100° C. for 1 h. The clear reaction solution is cooled to RT (27° C.) and stirred for 10 h. The crystallized product is collected by filtration under vacuum, washed with 30 mL of hexane, and dried under vacuum to afford salt C.
The salt C is dissolved in 1,4-dioxane (100 mL) and heated at 100° C. for 1 h. The clear reaction solution is cooled to RT (27° C.) and stirred for 10 h. The crystallized product is collected by filtration under vacuum, washed with 30 ml of hexane, and dried under vacuum to afford salt D.
The salt D is treated with aqueous hydrochloric acid solution (20 mL, 1 mL of concentrated hydrochloric acid diluted with 100 mL of water) and stirred for 5 min. The white solid precipitates out and is collected by vacuum filtration, washed with 10 mL of cold water, 5 mL of isopropanol and 20 mL of hexane, and dried under vacuum to yield the hydrochloride salt of (R)-(−)-3-cyclopentyl-2-[4-(4-methyl-piperazine-1-sulfonyl)-phenyl]-propionic acid, salt E.
The salt E is neutralized by stirring with aqueous sodium bicarbonate solution (10 mL, 1 g of sodium bicarbonate dissolved in 120 mL of water) for 5 min. The precipitated solid is collected by filtration, washed with 10 mL of cold water, 100 mL of hexane, and dried to afford (R)-(−)-3-cyclopentyl-2-[4-(4-methyl-piperazine-1-sulfonyl)-phenyl]-propionic acid: m.p. 202.2-203.4° C.
Alternatively, the title compound may be obtained by the resolution of the racemic title compound of Example 1 using the following preparative chiral HPLC method:
- Column: Chiralcel OD-R (250×20 mm) Diacel make, Japan;
- Solvent A: water:methanol:acetonitrile (10:80:10 v/v/v);
- Solvent B: water:methanol:acetonitrile (05:90:05 v/v/v);
- Using gradient elution: gradient program (time, min/% B): 0/0, 20/0, 50/100, 55/0, 70/0;
- Flow rate: 6.0 mL/min; and
- Detection: by UV at 305 nm.
EXAMPLE 3 (S)-3-Cyclopentyl-N-(5-methoxy-thiazolo[5,4-b]pyridin-2-yl)-2-[4-(4-methyl-piperazine-1-sulfonyl)-phenyl]-propionamide
The title compound is prepared analogously to Example 2.
J MED CHEM 2009, 52, 6142-52
Investigation of Functionally Liver Selective Glucokinase Activators for the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes
http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/jm900839k

Type 2 diabetes is a polygenic disease which afflicts nearly 200 million people worldwide and is expected to increase to near epidemic levels over the next 10−15 years. Glucokinase (GK) activators are currently under investigation by a number of pharmaceutical companies with only a few reaching early clinical evaluation. A GK activator has the promise of potentially affecting both the β-cells of the pancreas, by improving glucose sensitive insulin secretion, as well as the liver, by reducing uncontrolled glucose output and restoring post-prandial glucose uptake and storage as glycogen. Herein, we report our efforts on a sulfonamide chemotype with the aim to generate liver selective GK activators which culminated in the discovery of 3-cyclopentyl-N-(5-methoxy-thiazolo[5,4-b]pyridin-2-yl)-2-[4-(4-methyl-piperazine-1-sulfonyl)-phenyl]-propionamide (17c). This compound activated the GK enzyme (αKa = 39 nM) in vitro at low nanomolar concentrations and significantly reduced glucose levels during an oral glucose tolerance test in normal mice.
PATENT
EP-1735322-B1
Example 2(R)-3-Cyclopentyl-N-(5-methoxy-thiazolo[5,4-b]pyridin-2-yl)-2-[4-(4-methyl-piperazine-1-sulfonyl)-phenyl]-propionamide
The title compound is obtained analogously to Example 1 by employing the following additional resolution step:
The racemic title E compound of Example 1, 3-cyclopentyl-2-[4-(4-methyl-piperazine-1-sulfonyl)-phenyl]-propionic acid (10 g, 0.026 mol) in 1,4-dioxane (500 mL) is treated in a three necked 1 liter flask, equipped with heating mantle, water condenser, calcium chloride guard tube and mechanical stirrer with 3.18 g (0.026 mol) of (R)-(+)-1-phenylethylamine. This reaction mixture is then refluxed at 100°C for 1 h. The clear reaction solution is cooled to RT (27°C) and stirred for 10 h. The crystallized salt is collected by filtration under vacuum, washed with 5 mL of hexane and dried under vacuum to afford salt A.
The salt A is dissolved in 1,4-dioxane (500 mL) and heated at 100°C for 1 h. The clear reaction solution is cooled to RT (27°C) and stirred for 10 h. The crystallized product is collected by filtration under vacuum, washed with 50 mL of hexane, and dried under vacuum to afford salt B.
The salt B is dissolved in 1,4-dioxane (290 mL) and heated at 100°C for 1 h. The clear reaction solution is cooled to RT (27°C) and stirred for 10 h. The crystallized product is collected by filtration under vacuum, washed with 30 mL of hexane, and dried under vacuum to afford salt C.
The salt C is dissolved in 1,4-dioxane (100 mL) and heated at 100°C for 1 h. The clear reaction solution is cooled to RT (27°C) and stirred for 10 h. The crystallized product is collected by filtration under vacuum, washed with 30ml of hexane, and dried under vacuum to afford salt D.
The salt D is treated with aqueous hydrochloric acid solution (20 mL, 1 mL of concentrated hydrochloric acid diluted with 100 mL of water) and stirred for 5 min. The white solid precipitates out and is collected by vacuum filtration, washed with 10 mL of cold water, 5 mL of isopropanol and 20 mL of hexane, and dried under vacuum to yield the hydrochloride salt of (R)-(-)-3-cyclopentyl-2-[4-(4-methyl-piperazine-1-sulfonyl)-phenyl]-propionic acid, salt E.
The salt E is neutralized by stirring with aqueous sodium bicarbonate solution (10 mL, 1 g of sodium bicarbonate dissolved in 120 mL of water) for 5 min. The precipitated solid is collected by filtration, washed with 10 mL of cold water, 100 mL of hexane, and dried to afford (R)-(-)-3-cyclopentyl-2-[4-(4-methyl-piperazine-1-sulfonyl)-phenyl]-propionic acid: m.p. 202.2-203.4°C.
Alternatively, the title compound may be obtained by the resolution of the racemic title compound of Example 1 using the following preparative chiral HPLC method:
- Column: Chiralcel OD-R (250 x 20 mm) Diacel make, Japan;
- Solvent A: water:methanol:acetonitrile (10:80:10 v/v/v);
- Solvent B: water:methanol:acetonitrile (05:90:05 v/v/v);
- Using gradient elution: gradient program (time, min / %B): 0/0, 20/0, 50/100, 55/0, 70/0;
- Flow rate: 6.0 mL/min; and
- Detection: by UV at 305 nm.
REFERENCES
US 7750020
WO-2005095418-A1
US-20080103167-A1
| Patent ID | Date | Patent Title |
|---|---|---|
| US2015218151 | 2015-08-06 | NOVEL PHENYLACETAMIDE COMPOUND AND PHARMACEUTICAL CONTAINING SAME |
| US7750020 | 2010-07-06 | Sulfonamide-Thiazolpyridine Derivatives As Glucokinase Activators Useful The Treatment Of Type 2 Diabetes |
///NOVARTIS, DIABETES, Sulfonamide-Thiazolpyridine Derivatives, Glucokinase Activators, Treatment Of Type 2 Diabetes, 866772-52-3, Novartis Molecule, functionally liver selective glucokinase activators, treatment of type 2 diabetes , NVP-LBX192, LBX-192
c1(sc2nc(ccc2n1)OC)NC(C(c3ccc(cc3)S(=O)(=O)N4CCN(CC4)C)CC5CCCC5)=O






























 67
67 66
66























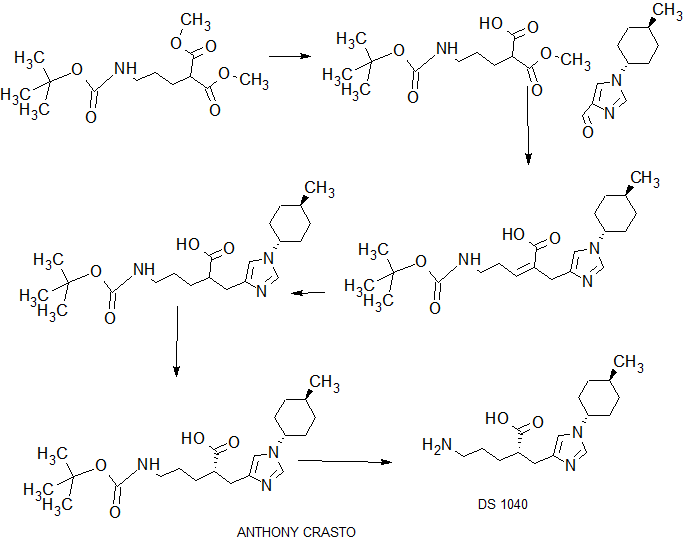
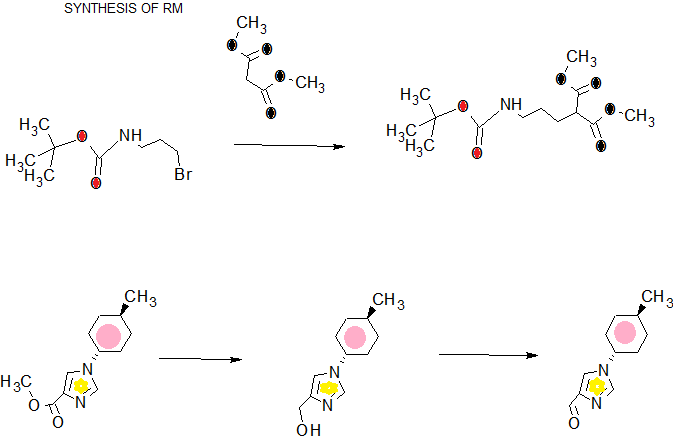
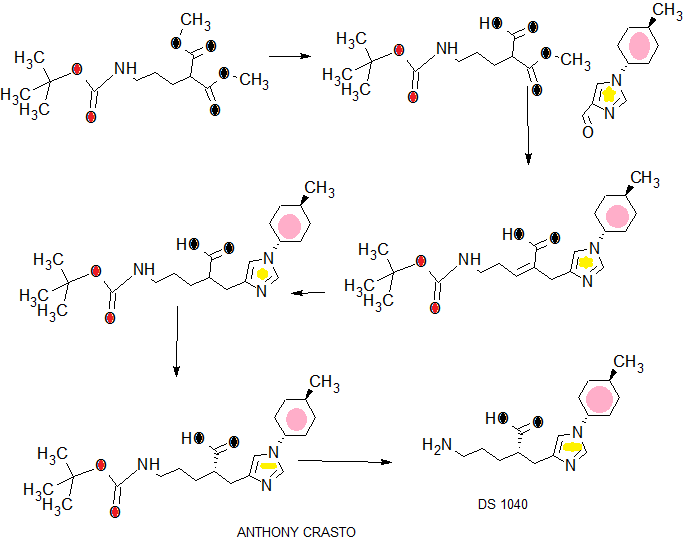


























 DRUG APPROVALS BY DR ANTHONY MELVIN CRASTO …..
DRUG APPROVALS BY DR ANTHONY MELVIN CRASTO …..

 .
.


