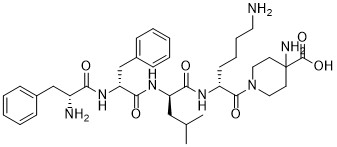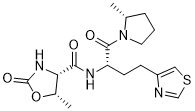
Rovatirelin Hydrate, S-0373,
Rovatirelin, RN: 204386-76-5
UNII: 9DL0X410PY
(4S,5S)-5-methyl-N-((S)-1-((R)-2-methylpyrrolidin-1-yl)-1-oxo-4-(thiazol-4-yl)butan-2-yl)-2-oxooxazolidine-4-carboxamide4-Oxazolidinecarboxamide, 5-methyl-N-[2-(2-methyl-1-pyrrolidinyl)-2-oxo-1-(4-thiazolylmethyl)ethyl]-2-oxo-, [4S-[4α[R*(S*)],5α]]-
Phase III
A thyrotropin-releasing hormone potentially for the treatment of spinocerebellar ataxia.

CAS No.204386-76-5(Rovatirelin)
879122-87-9(Rovatirelin Hydrate)
C17H24N4O4S
Exact Mass: 380.1518

Rovatirelin is a novel synthetic agent that mimics the actions of thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH). Rovatirelin binds to the human TRH receptor with higher affinity (Ki=702nM) than taltirelin (Ki=3877nM). Rovatirelin increased the spontaneous firing of action potentials in the acutely isolated noradrenergic neurons of rat locus coeruleus (LC). Rovatirelin increased locomotor activity. Rovatirelin may have an orally effective therapeutic potential in patients with SCD.
Rovatirelin ([1-[-[(4S,5S)-(5-methyl-2-oxo oxazolidin-4-yl) carbonyl]-3-(thiazol-4-yl)-l-alanyl]-(2R)-2-methylpyrrolidine) is a novel synthetic agent that mimics the actions of thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH). The aim of this study was to investigate the electrophysiological and pharmacological effects of rovatirelin on the central noradrenergic system and to compare the results with those of another TRH mimetic agent, taltirelin, which is approved for the treatment of spinocerebellar degeneration (SCD) in Japan. Rovatirelin binds to the human TRH receptor with higher affinity (Ki=702nM) than taltirelin (Ki=3877nM). Rovatirelin increased the spontaneous firing of action potentials in the acutely isolated noradrenergic neurons of rat locus coeruleus (LC). The facilitatory action of rovatirelin on the firing rate in the LC neurons was inhibited by the TRH receptor antagonist, chlordiazepoxide. Reduction of the extracellular pH increased the spontaneous firing of LC neurons and rovatirelin failed to increase the firing frequency further, indicating an involvement of acid-sensitive K+ channels in the rovatirelin action. In in vivo studies, oral administration of rovatirelin increased both c-Fos expression in the LC and extracellular levels of noradrenaline (NA) in the medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC) of rats. Furthermore, rovatirelin increased locomotor activity. The increase in NA level and locomotor activity by rovatirelin was more potent and longer acting than those by taltirelin. These results indicate that rovatirelin exerts a central nervous system (CNS)-mediated action through the central noradrenergic system, which is more potent than taltirelin. Thus, rovatirelin may have an orally effective therapeutic potential in patients with SCD.
PATENT
WO 9808867

PATENT
WO 9945000

PATENT
WO 2002017954
Example
Preparation of the compound represented by Example 1 set (IX)
The second step

Two

(First step)
Method described in the literature (Synth. Commun., 20, 3507 (1990)) synthesized N- in (tert- butoxide deer Lupo sulfonyl) one 3- (4 one-thiazolyl) one L Aranin (1, 21.79 g, 80 mmol) in Torifuruoro and the mixture was stirred acetic acid (80 ml) were added under ice-cooling for 2 hours and a half. Then stirred for 30 minutes at room temperature was added to the reaction mixture p- toluenesulfonic acid hydrate (15.22 g, 80 mmol). The reaction mixture was concentrated to dryness under reduced pressure. To remove excess Torifuruoro acetic acid by the obtained residue concentrated to dryness under reduced pressure by addition of water and methanol.Obtained obtained residue was collected by filtration crystals ether was added to precipitate the compound (2) 29.8 g (quantitative).
NMR (CD 3 OD): 9.01 (1H, d-, J = 1.8 Hz), 7.70 (2H ; yd), 7.46 (lH, d-, J = 1.8 Hz), 7.23 (2H, yd), 4.38 (1H, dd , J = 4.8 from and 3.8 from Hz), 3.45 (2H ; yd), 2.37 (3H, s).
(Second step)
I 匕合 product (2) 38.85 g E evening Nord (200 ml) of (112.8 mmol) – in THF (600 ml) solution, diphenyl di § zone methane while 攪袢 at room temperature (39 g, 201 mmol) in small portions over 30 minutes were added. The reaction mixture was stirred for 1 hour at room temperature, Ziv E sulfonyl di § zone methane (10 g, 51.5 mmol) was added and stirred for one hour. To the reaction mixture
After decomposing the excess reagent by the addition of acetic acid (0.1 ml), it was concentrated to dryness under reduced pressure and distilled off the solvent. The resulting residue (92 g) with ether (1 L) was crystallized to give compound (3) 49.05 g (96.1%).
mp: 139-140 ° C
[A] D = -34.7 ° (C = 1.006, CHC1 3) 23 ° C)
^ Cm IRCKB ” 1 : 1753, 1602, 1512, 1496, 1260, 1224, 1171, 1124, 1036, 1012. NMR (CD 3 0D): 8.92 (1H, D, J = 2 Hz), 7.70 (2H ; M ), 7.2-7.4 (13H, m) , 6.91 (1H, s), 4.62 (1H, t, J = 5.8 Hz), 3.47 (2H, d, J = 5.8 Hz), 2.36 (3H, s).
Elemental analysis (C 2E H 2S N 2 0 5 S 2 )
Calculated: C, 61.16; H, 5.13; N, 5.49; S, 12.56.
Measured value: C, 61.14; H, 5.32; N, 5.41; S, 12.46.
(Third step)
Cis-one L one 5-methyl-2-one O Kiso O Kisa ethylbenzthiazoline one 4-carboxylic acid 13.95 g (96.14 mmol), compound (3) 49.09 g (96.14 mmol ), N-hydroxybenzotriazole To Riazoru 2.6 g (19.23 mmol) and under ice-cooling in THF (1L) solution of Toryechiruamin 14.1 ml (lOlmmol), was added to the DCC (20.83g, 101 mmol). The cooling bath was removed after stirring for 10 minutes at the same temperature, and stirred for an additional 2 0 hours at room temperature. After removing the precipitated precipitate and the filtrate concentrated to dryness under reduced pressure an oily residue (82.7 g was obtained). The residue was filtered off and dissolved by heating to insoluble matter in acetic acid Echiru (700 ml). The filtrate was successively washed with sodium carbonate aqueous solution and water.After the addition of methanol (20 ml) the organic layer was dried with sulfuric acid mug Neshiumu, was concentrated to a small volume under reduced pressure.Precipitated collected by filtration and acetic acid E Ji Le crystals – ether (2: 3) washing to compound with a mixture (4) 35.69 g (79.8% ) was obtained. After addition was concentrated to dryness under reduced pressure of the mother liquor, and crystallized from acetic acid E Chiru ether mixture compound (4) 2.62 g (5.9% ) was obtained.
mp: 176-177 ° C
[A] D = -39.2 ° (C = 1.007, CHC1 3 , 24 ° C)
^ Cm IRiKB 1 : 1739, 1681, 1508, 1453, 1386, 1237, 1193, 1089.
NMR (CDC1 3 ): 8.71 (1H, d-, J = 1.8 Hz), 8.18 (lH, d-‘J = 3.9 from Hz), 7.2-7.4 (10H ; yd), 6.82 (1H, s), 6.66 (1H, d-, J = 1.8 Hz), 5.79 (1H, s), 5.12 (1H, yd), 4.94 (lH, yd), 4.35 (1H ; dd, J = 1.8 and 4.5 from Hz), 3.40 (1H ; dd, J 5.7 and 15 = Hz), 3.29 (1H ; dd, J = 4.5 of and 15 Hz), 1.27 (3H, d-, J = 6.3 Hz).
Elemental analysis (C 24 H 23 N 3 0 5 S)
Calculated: C, 61.92; H, 4.98; N, 9.03; S, 6.89.
Measured value: C ! 61.95; H, 5.01; N, 8.94; S ) 6.62.
(Fourth step)
Compound (4) 41.24 under ice-cooling to g (88.59 mmol), and the mixture was stirred Anisoru (240ml) and To Rifuruoro acetic acid (120 ml) and the mixture for 15 minutes. And the mixture was stirred for 2 hours 3 0 minutes further room temperature after removal of the cooling bath. The reaction mixture was added to the E one ether (500 ml) to the oily residue obtained by concentrated to dryness under reduced pressure was collected by filtration and pulverized. The resulting powder is water (50 ml) – was removed by filtration methanol (300 ml) warming dissolved insoluble matter in a mixture. The filtrate was concentrated to small volume under reduced pressure, and allowed to stand at room temperature for 3 days adding a seed crystal and methanol. The precipitated crystals were obtained Shi preparative filtration compound (5) 14.89 g (56.1%). The mother liquor was concentrated to dryness under reduced pressure, to give again further compound was crystallized from methanol one ether mixture of the (5) 10.3 g (38%). mp: 214-215 ° C
[]. -4.2 ° = (C = 0.5, H 2 0, 22 ° C)
^ Cm IRCKB 1 : 1753, 1707, 1655, 1548, 1529, 1409, 1343, 1264, 1236, 1102, 1092. NMR (DMS0-D6): 9.02 (1H, D, J = 1.8 Hz), 8.46 (1H, d- ; J = 3.9 from Hz), 7.74 (1H, s),
7.38 (1H, d, J = 1.8 Hz), 4.77 (1H, dq, J = 6.6 and 8.7 Hz), 4.66 (1H, m), 4.21 (1H, d,
J = 8.7 Hz), 3.24 (IH, dd, J = 5.1 and 15 Hz), 3.13 (1H, dd, J = 8.4 and 15 Hz),
1.13 (3H, d, J = 6.6 Hz).
Elemental analysis (C U H 13 N 3 0 5 S)
Calculated: C ; 44.14; H, 4.38; N, 14.04; S ) 10.71.
Measured value: C, 43.94; H, 4.478; N, 14.09; S, 10.58.
(Fifth step)
Compound (5) 12.1 g, (40.48 mmol) and N- hydroxysuccinimide (4.66 g, 40,48 mM) under ice-cooling to THF (242 ml) suspension of,: DCC (8.35 g, 40.48 mmol) was added to 3 and the mixture was stirred for 10 minutes. The cooling bath was removed, and the mixture was further stirred at room temperature for 2 hours. The resulting compound N- hydroxysuccinimide ester solution of (5) was synthesized in a way described in the literature (Tetrahedron, 27, 2599 (1971 )) (R) – (+) – 2- Mechirupiro lysine hydrochloride (5.42 g) and Toryechiruamin (8.46 ml, was added at room temperature to THF (121 ml) suspension of 60.72 mmol). The reaction mixture was stirred for an additional 1 5 hrs. The filtrate after removal of the insoluble matter that has issued analysis was concentrated to dryness under reduced pressure. Residue (24.6 Ga) the insoluble material was removed by filtration was dissolved in water (150 ml). The filtrate was purified by gel filtration column chromatography one (MCI Gel CHP-20P, 600 ml). 4 0% aqueous methanol solution compound of the collected crude eluted cut off fractionated (IX) was obtained 8.87 g. Then after purification by silica gel column chromatography (black port Holm one methanol mixture), to give the compound was freeze-dried (IX) 5.37 g (35.7% ).
mp: 192-194 ° C
[A] D = -1.9 ° (C = 1.005, H 2 0, 25 ° C)
KB Cm- IR 1 : 1755, 1675, 1625, 1541, 1516, 1448, 1232, 1097.
NMR (CD 3 0D): 8.97 (1H, t, J = 2.1 Hz), 7.34 (1H, t, J = 2.1 Hz), 5.19 and 5.04 (total the IH, the each t, J = 7.5 Hz), 4.92 (1H , Dq, J = 6.6 And 8.7 Hz), 4.36 And 4.35 (1H, D, J = 8.7 Hz), 4.07 And 3.92 (Total IH, Eac M), 3.78 (1H ; M), 3.42 (1¾ M), 3.22 (2H, m), 1.5-2.0 ( 4H, m), 1.28 and 1.22 (total 3H, each d, J = 6.6 Hz), 1.21 and 1.02 (total 3H, each d, J = 6.6 Hz).
Elemental analysis (C 16 H 22 N 4 0 4 S H 2 0)
Calculated: C, 49.99; H, 6.29; N, 14.57; S, 8.34.
Measured value: C, 49.99; H, 6.29; N, 14.79; S, 8.36.
PATENT
WO 2006028277
Example
Example 1
B
Step 1 l-N-[N<tert-butoxycarbonyl)-3-(^^^
N.N-dicyclohexylcarbodiimide (10.83 g, 52.5 mmol), N-hydroxybenzotriazole (2.03 g, 15 mmol) and triethylamine (7.7 ml, 55.2 mmol) were added to a solution (130 ml) of N-(tert-butoxycarbonyl)-3-(thiazol-4-yl)-L-alanine (1) (13.62 g, 50 mmol) obtained by the method described in literatures (J. Am. Chem. Soc. 73, 2935 (1951) and Chem. Pharm. Bull. 38, 103 (1950)) and 2(R)-2-methylpyrrolidine p-toluenesulfonic acid (2) (12.79 g, 50 mmol) obtained by the method described in a literature (HeIv. Chim. Acta, 34, 2202 (1951)) in tetrahydrofuran. The mixture was stirred for 20 hours at room temperature. After the precipitates are filtered off, the obtained filtrate was concentrated under reduced pressure. Thus-obtained residue was dissolved in ethyl acetate (200 ml) and the solution were washed with an aqueous solution of sodium hydrogencarbonate and water, successively. The organic layers were dried over magnesium sulfate and concentrated under reduced pressure to give a title compound (3) (16.45 g, 100%) as oil.
NMR (CDCl3): OH 8.76 and 8.75 (1 H, each d, J=2.1Hz, Thia-H-2), 7.08 (1 H, d, J=2.fflz, thia-H-5), 5.45 (1 H, m, NH), 3.45-3.64 (1 H, m, AIa-CoH), 4.14 and 3.81 (1 H, each m, Pyr-CαH), 3.51 (1 H, m, PVr-NCH2), 3.1-3.4 (3 H, m, Pyr-CH2and AIa-CH2), 1.39 (9 H, s, BOC), 1.3-2.0 (4 H, m, PyT-CH2), 1.06 (3 H, d, J=6Hz, Pyr-Me)
Step 2 l-N-[3-(thiazol-4-yl)-L-alanyl]-(2R)-2-methylpyrroHdine di-p-toluenesulfcnate (4)
Compound (3) (33.77 g, 99.48 mmol) and p-toluenesulfonic acid hydrate (37.85 g, 199 mmol) were dissolved in ethyl acetate (101 ml) and the solution was cooled with ice. To the mixture, 4 mol/L solution of hydrogen chloride-ethyl acetate (125 ml) was added, and the mixture was stirred for 2 hours 45 minutes. After the mixture was concentrated under reduced pressure, methanol was added to the residue. The mixture was concentrated. Methanol-toluene (1: 1) was added to the residue and concentrated under reduced pressure to give crystalline residue. The residue was washed with acetone and filtered to give compound (4) as crystals (36 g, 62%). After the mother liquor was concentrated under reduced pressure, methanol and toluene were added to the residue and concentrated. Obtained crystalline residue was washed with acetone to give compound (4) (10.67 g, 18.4%). mp 188-189 0C [α]D 24 +2.2 (c, 1.0, MeOH) IR(KBr)Cm“1: 3431, 3125, 3080, 2963, 1667, 1598, 1537, 1497, 1451, 1364, 1229, 1198, 1170, 1123, 1035, 1011.
NMR (CD3OD): δH 9.04 and 9.03 (1 H, each d, J=2.1Hz, Thia-H-2), 7.70 (2 H, m, aromaticH), 7.46 (1H, d, J=2.1Hz, thia-H-5), 7.23 (2H, m, aromaticH), 4.49and4.46 (1 H, each d, J=6.9Hz, Ala-CαH), 4.14 and 3.75 (1 H, each m, Pyr-CαH), 3.51 (1 H, m, pyr-NCH2), 3.2-3.4 (3 H, m, PyT-CH2 and AIa-CH2), 2.36 (3 H, s, aromatic Me), 1.3-2.0 (4 H, m, pyr-CH2), 1.19 and 1.07 (3 H, each d, J=6.3Hz, Pyr-Me) Anal Calcd For C11H17N3OS 2C7H8O3S Calculated: C, 51.44%; H1 5.70%; N, 7.20%; S, 16.48%. Found: C, 51.36%; H, 5.69%; N, 7.23%; S, 16.31%.
Step 3 l-[N-[(4S,5S)-(5-methyl-2-oxooxazolidin-4-yl)carbonyl]-3-(thiazol-4-yl)-L-alanyl-(2R)-2- methylpyrrolidine trihydrate (I- 1) Step 3 (1) Method A
(4S, 5S)-5-methyl-2-oxooxazolidin-4-yl carboxylic acid (5) (1.368 g, 9.43 mmol) obtained by the method described in literatures (J. Chem. Soc. 1950, 62; Tetrahedron 48; 2507 (1992) and Angew. Chem. 101, 1392 (1989)), Compound (4) (5 g, 8.56 mmol) and N-hydiOxysuccinimide (217 mg, 1.89 mmol) were dissolved in N, N-dimethylformamide (10 ml), and tetrahydrofuran (65 ml) was added. After the mixture was cooled with ice in a cool bath, triethylamine (2.63 ml, 18.86 mmol) and N, N-dicyclohexylcarbodiimide (2.04 g, 9.89 mmol) were added with stirred and the mixture was stirred for additional 30 minutes. The cooling bath was removed and the mixture was stirred for 15 hours at room temperature. The precipitated were filtered off and the filtrate was concentrated under reduced pressure. Water (100 ml) was added to thus-obtained residue (9.95 g) and the mixture was stirred for 1.5 hours at room temperature. After insoluble substance was filtered off, the filtrate was concentrated until it was reduced to about half volume under reduced pressure. The small amount of insoluble substance was filtered off and the filtrate was concentrated until it was reduced to about 2O g under reduced pressure. After the mixture was allowed to stand in a refrigerator for 3 days, the precipitated crystals (2.98 g) were collected by filtration and washed with cold water. The filtrate was extracted twice with chloroform, dried over magnesium sulfate and concentrated under reduced pressure. Ethyl acetate (5 ml) was added to oil residue (1.05 g) and the mixture was stirred to give crystals (136 mg). The obtained crystals were combined and dissolved in purified water (45 ml) with heating. After the solution was allowed to cool to room temperature, the precipitated insoluble substance was filtered off The filtrate was concentrated under reduced pressure and allowed to stand at room temperature overnight. The mixture was cooled with ice, and the crystals were collected by filtration to give Compound (1-1, 2.89 g, 80.3%). mp 194-196 0C
[α]D 22 -2.0 ± 0.4 ° (c, 1.008, H2O), [α]365 +33.1 ± 0.7 ° (c, 1.008, H2O)
IR(Nujor)cm”1: 3517, 3342, 3276, 3130, 3092, 3060, 1754, 1682, 1610, 1551, 1465, 1442,
1379, 1235, 1089. NMR(CD3OD): δH 8.97 and 8.96 (total 1 H, d, J=2.1Hz, Thia-H-2), 7.34 and 7.33 (total 1
H, d, J=2.1Hz, Thia-H-5), 5.18 and 5.04 (total 1 H, each t, J=7.5Hz, Ala-CαH), 4.92 (1
H, dq, J=6.6 and 8.7Hz, Oxa-H-5), 4.36 and 4.35 (total 1 H, d, J=8.7Hz, Oxa-H-4), 4.07 and 3.92 (total 1 H, each m, Pyr-Cα-H), 3.78 (1 H, m, Pyr-NCH2), 3.42 (1 H, m, Pyr- 5 NCH2), 3.22 (2 H, m, AIa-CH2), 1.5-2.0 (4 H, m, Pyr-CH2), 1.28 and 1.22 (total 3 H, each d, J=6.6Hz, Oxa-5-Me), 1.21 and 1.02 (total 3 H, each d, J=6.6Hz, Pyr-2-Me)
Anal. Calcd For C16H22N4O4S 3H2O
Calculated: C, 45.00%; H, 6.71%; N, 13.33%; S, 7.63%.
Found: C, 45.49%; H, 6.60%; N, 13.58%, S, 7.88%. 10
Step 3 (2)
Method B
After Compound (1-2) (410 g, 1.119 mmol) was dissolved in purified water (6.3 L) with heating, the solution was concentrated until the total weight of the mixture was 15 reduced to 1370 g under reduced pressure. The concentrated solution was allowed to stand at room temperature overnight. The solution was cooled with ice for 1 hour and filtered to give the precipitated crystals. The obtained crystals were washed with cold water to give
Compound (T- 1) (448 g, 95.2%) as colorless crystals. Mother liquor was mixed with purified water (300 mL) with heating and the solution was concentrated to 55 g under reduced pressure. 20 After the concentrated solution was allowed to stand at room temperature overnight, the solution was filtered to give the precipitated crystals (T-1, 16.3 g, 3.5%, total amount 464.3 g, 98.7%). mp 194-196 0C
[α]D 22 -0.9 ± 0.4 ° (c, 1.007, H2O), [α]365 + 35.4 ± 0.8 ° (c, 1.007, H2O)
IR(NuJOr)Cm“1: 3511, 3348, 3276, 3130, 3093, 3060, 1755, 1739, 1682, 1611, 1551, 1465, 25. 1442, 1379, 1235, 1089.
AnalCalcdFor: C16H22N4O4S 3H2O
Calculated: C, 45.00%;H, 6.71%;N, 13.33%; S, 7.63%.
Found: C, 45.56%; H, 6.66%; N, 13.43%, S, 7.69%.
30 Step 4 l-[N-[(4S)5S)-(5-methyl-2-oxooxazolidin-4-yl)carbonyl]-3-(thiazol-4-yl)-L-alanyl-(2R)-2- methylpyrrolidine (1-2)
Method A
After l-[N-[(4S,5S)-(5-methyl-2-oxooxazolidin-4-yl)carbonyl]-3-(thiazol-4-yl)-L- 35 alanyl-(2R)-2-methylpyrrolidine monohydrate (4.77 g) obtained by the method described in Patent Literature 8 was crushed in a mortar, it was dried under reduced pressure (66.5 Pa) at 100 0C for 15 hours to give 4.54 g of Compound (1-2). mp 194.5-196.5 0C [α]D 25 -2.1 +. 0.4 ° (c, 1.004, H2O), [α]365 +36.8 ± 0.8 ° (c, 1.004, H2O) Water measurement (Karl Fischer method): 0.27%
IR(NuJOr)Cm”1: 3276, 3180, 3104, 1766, 1654, 1626, 1548, 1517, 1457, 1380, 1235, 1102, 979. NMR(CD3OD):δH 8.97 and 8.96 (total 1 H, d, J 2.1 Hz, Thia-H-2), 7.34 and 7.33 (total 1 H, d, J 2.1 Hz, Thia-H-5), 5.19 and 5.04 (total 1 H, each t, J 7.5 Hz, Ala- CaH), 4.92 (1 H, dq, J 6.6 and 8.7 Hz, Oxa-H-5), 4.36 and 4.35 (total 1 H, d, J 8.7 Hz, Oxa-H-4), 4.07 and 3.92 (total 1 H, each m, Pyr-Cα-H), 3.78 (1 H, m, Pyr-NCH2), 3.42 (1 H, m, Pyr-NCH2), 3.22 (2 H, m, AIa-CH2), 1.5-2.0 (4 H, m, Pyr-CH2), 1.28 and 1.22 (total 3 H, each d, J 6.6 Hz, Oxa-5-Me), 1.21 and 1.02 (total 3 H, each d, J 6.6 Hz, Pyr-2-Me). Anal Calcd For: C16H22N4O4S
Calculated: C, 52.44%; H, 6.05%; N, 15.29%; S, 8.75%. Found: C, 52.24%; H, 5.98%; N, 15.27%, S, 8.57%.
Method B
After Compound (1-1) (17.89 g, 47.3 mmol) was crushed in a mortar, it was dried under reduced pressure (66.5 Pa) at 100 °C for 14 hours to give Compound (1-2, 17.31 g). mp 193-194 0C [α]D 25 -1.9 ± 0.4 ° (c, 1.002, H2O), [α]365 +37.2 ± 0.8 ° (c, 1.002, H2O)
Water measurement (Karl Fischer method): 0.22%
IR(NuJOr)Cm“1: 3273, 3180, 3111, 1765, 1685, 1653, 1626, 1549, 1516, 1456, 1346, 1331,
1277, 1240, 1097, 980.
Anal Calcd For C16H22N4O4S Calculated: C, 52.44%; H, 6.05%; N, 15.29%; S, 8.75%.
Found: C, 52.19%; H, 5.98%; N, 15.42%, S, 8.74%.
REFERENCES
1: Ijiro T, Nakamura K, Ogata M, Inada H, Kiguchi S, Maruyama K, Nabekura J,
Kobayashi M, Ishibashi H. Effect of rovatirelin, a novel thyrotropin-releasing
hormone analog, on the central noradrenergic system. Eur J Pharmacol. 2015 Aug
15;761:413-22. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2015.05.047. Epub 2015 Jul 2. PubMed PMID:
26142830.
////////Rovatirelin Hydrate, S-0373, Rovatirelin, 204386-76-5, clinical, phase 3
C[C@@H]1CCCN1C(=O)[C@H](Cc2cscn2)NC(=O)[C@@H]3[C@@H](OC(=O)N3)C