CD 101
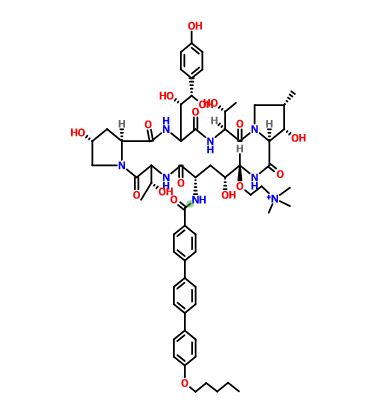
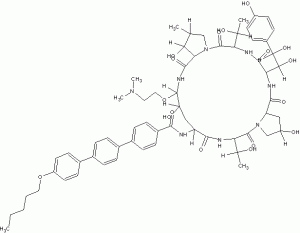
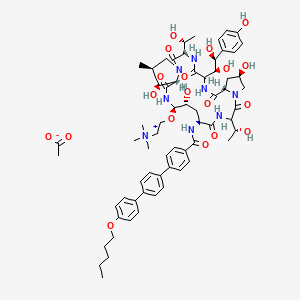
Several structural representations above
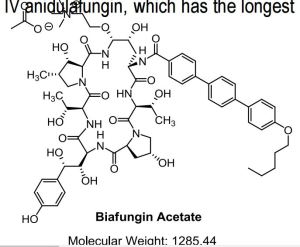
Biafungin™; CD 101 IV; CD 101 Topical; CD101; SP 3025, Biafungin acetate, Echinocandin B
UNII-G013B5478J FRE FORM,
CAS 1396640-59-7 FREE FORM
MF, C63-H85-N8-O17, MW, 1226.4035
Echinocandin B,
1-((4R,5R)-4-hydroxy-N2-((4”-(pentyloxy)(1,1′:4′,1”-terphenyl)-4-yl)carbonyl)-5-(2-(trimethylammonio)ethoxy)-L-ornithine)-4-((4S)-4-hydroxy-4-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-L-allothreonine)-
| Treat and prevent invasive fungal infections; Treat and prevent systemic Candida infections; Treat candidemia |
Biafungin acetate
CAS 1631754-41-0 ACETATE, Molecular Formula, C63-H85-N8-O17.C2-H3-O2, Molecular Weight, 1285.4472,
UNII: W1U1TMN677
CD101 – A novel echinocandin antifungal C. albicans (n=351) MIC90 = 0.06 µg/mL C. glabrata (n=200) MIC90 = 0.06 µg/mL Echinocandins have potent fungicidal activity against Candida species
- Originator Seachaid Pharmaceuticals
- Developer Cidara Therapeutics
- Class Antifungals; Echinocandins; Small molecules
- Mechanism of Action Glucan synthase inhibitors
- Orphan Drug Status Yes – Candidiasis
- On Fast track Candidiasis; Vulvovaginal candidiasis
- Phase II Candidiasis; Vulvovaginal candidiasis
-
Most Recent Events
- 01 Jun 2016 Phase-II clinical trials in Vulvovaginal candidiasis in USA (Topical) (9197627; NCT02733432)
- 31 May 2016 CD 101 receives Qualified Infectious Disease Product status for Vulvovaginal candidiasis in USA
- 31 May 2016 CD 101 receives Fast Track designation for Vulvovaginal candidiasis [Topical] in USA
BIAFUNGIN, CD 101
Watch this space as I add more info…………….
U.S. – Fast Track (Treat candidemia);
U.S. – Fast Track (Treat and prevent invasive fungal infections);
U.S. – Orphan Drug (Treat and prevent invasive fungal infections);
U.S. – Orphan Drug (Treat candidemia);
U.S. – Qualified Infectious Disease Program (Treat candidemia);
U.S. – Qualified Infectious Disease Program (Treat and prevent invasive fungal infections)
Fungal infections have emerged as major causes of human disease, especially among the immunocompromised patients and those hospitalized with serious underlying disease. As a consequence, the frequency of use of systemic antifungal agents has increased significantly and there is a growing concern about a shortage of effective antifungal agents. Although resistance rates to the clinically available antifungal agents remains low, reports of breakthrough infections and the increasing prevalence of uncommon fungal species that display elevated MIC values for existing agents is worrisome. Biafungin (CD101, previously SP 3025) is a novel echinocandin that displays chemical stability and long-acting pharmacokinetics that is being developed for once-weekly or other intermittent administration (see posters #A-693 and A- 694 for further information). In this study, we test biafungin and comparator agents against a collection of common Candida and Aspergillus species, including isolates resistant to azoles and echinocandins.
The echinocandins are an important class of antifungal agents, but are administered once daily by intravenous (IV) infusion. An echinocandin that could be administered once weekly could facilitate earlier hospital discharges and could expand usage to indications where daily infusions are impractical. Biafungin is a highly stable echinocandin for once-weekly IV administration. The compound was found to have a spectrum of activity and potency comparable to other echinocandins. In chimpanzees single dose pharmacokinetics of IV and orally administered biafungin were compared to IV anidulafungin, which has the longest half-life (T1/2 ) of the approved echinocandins.
Background Vulvovaginal candidiasis (VVC) is a highly prevalent mucosal infection VVC is caused by Candida albicans (~85%) and non-albicans (~15%) 5-8% of women have recurrent VVC (RVVC) which is associated with a negative impact on work/social life Oral fluconazole prescribed despite relapse, potential DDIs and increased risk to pregnant women No FDA-approved therapy for RVVC and no novel agent in >20 years

Cidara Therapeutics 6310 Nancy Ridge Drive, Suite 101 San Diego, CA 92121
The incidence of invasive fungal infections, especially those due to Aspergillus spp. and Candida spp., continues to increase. Despite advances in medical practice, the associated mortality from these infections continues to be substantial. The echinocandin antifungals provide clinicians with another treatment option for serious fungal infections. These agents possess a completely novel mechanism of action, are relatively well-tolerated, and have a low potential for serious drug–drug interactions. At the present time, the echinocandins are an option for the treatment of infections due Candida spp (such as esophageal candidiasis, invasive candidiasis, and candidemia). In addition, caspofungin is a viable option for the treatment of refractory aspergillosis. Although micafungin is not Food and Drug Administration-approved for this indication, recent data suggests that it may also be effective. Finally, caspofungin- or micafungin-containing combination therapy should be a consideration for the treatment of severe infections due to Aspergillus spp. Although the echinocandins share many common properties, data regarding their differences are emerging at a rapid pace. Anidulafungin exhibits a unique pharmacokinetic profile, and limited cases have shown a potential far activity in isolates with increased minimum inhibitory concentrations to caspofungin and micafungin. Caspofungin appears to have a slightly higher incidence of side effects and potential for drug–drug interactions. This, combined with some evidence of decreasing susceptibility among some strains ofCandida, may lessen its future utility. However, one must take these findings in the context of substantially more data and use with caspofungin compared with the other agents. Micafungin appears to be very similar to caspofungin, with very few obvious differences between the two agents.
Echinocandins are a new class of antifungal drugs[1] that inhibit the synthesis of glucan in the cell wall, via noncompetitive inhibition of the enzyme 1,3-β glucan synthase[2][3] and are thus called “penicillin of antifungals”[4] (a property shared with papulacandins) as penicillin has a similar mechanism against bacteria but not fungi. Beta glucans are carbohydrate polymers that are cross-linked with other fungal cell wall components (The bacterial equivalent is peptidoglycan). Caspofungin, micafungin, and anidulafungin are semisynthetic echinocandin derivatives with clinical use due to their solubility, antifungal spectrum, and pharmacokinetic properties.[5]
List of echinocandins:[17]
- Pneumocandins (cyclic hexapeptides linked to a long-chain fatty acid)
- Echinocandin B not clinically used, risk of hemolysis
- Cilofungin withdrawn from trials due to solvent toxicity
- Caspofungin (trade name Cancidas, by Merck)
- Micafungin (FK463) (trade name Mycamine, by Astellas Pharma.)
- Anidulafungin (VER-002, V-echinocandin, LY303366) (trade name Eraxis, by Pfizer)
History
Discovery of echinocandins stemmed from studies on papulacandins isolated from a strain of Papularia sphaerosperma (Pers.), which were liposaccharide – i.e., fatty acid derivatives of a disaccharide that also blocked the same target, 1,3-β glucan synthase – and had action only on Candida spp. (narrow spectrum). Screening of natural products of fungal fermentation in the 1970s led to the discovery of echinocandins, a new group of antifungals with broad-range activity against Candida spp. One of the first echinocandins of the pneumocandin type, discovered in 1974, echinocandin B, could not be used clinically due to risk of high degree of hemolysis. Screening semisynthetic analogs of the echinocandins gave rise to cilofungin, the first echinofungin analog to enter clinical trials, in 1980, which, it is presumed, was later withdrawn for a toxicity due to the solvent system needed for systemic administration. The semisynthetic pneumocandin analogs of echinocandins were later found to have the same kind of antifungal activity, but low toxicity. The first approved of these newer echinocandins was caspofungin, and later micafungin and anidulafungin were also approved. All these preparations so far have low oral bioavailability, so must be given intravenously only. Echinocandins have now become one of the first-line treatments for Candida before the species are identified, and even as antifungal prophylaxis in hematopoietic stem cell transplant patients.
CIDARA THERAPEUTICS DOSES FIRST PATIENT IN PHASE 2 TRIAL OF CD101 TOPICAL TO TREAT VULVOVAGINAL CANDIDIASIS
SAN DIEGO–(BUSINESS WIRE)–Jun. 9, 2016– Cidara Therapeutics, Inc. (Nasdaq:CDTX), a biotechnology company developing novel anti-infectives and immunotherapies to treat fungal and other infections, today announced that the first patient has been dosed in RADIANT, a Phase 2 clinical trial comparing the safety and tolerability of the novel echinocandin, CD101, to standard-of-care fluconazole for the treatment of acute vulvovaginal candidiasis (VVC). RADIANT will evaluate two topical formulations of CD101, which is Cidara’s lead antifungal drug candidate.
“There have been no novel VVC therapies introduced for more than two decades, so advancing CD101 topical into Phase 2 is a critical step for women with VVC and for Cidara,” said Jeffrey Stein, Ph.D., president and chief executive officer of Cidara. “Because of their excellent safety record and potency against Candida, echinocandin antifungals are recommended as first line therapy to fight systemic Candida infections. CD101 topical will be the first echinocandin tested clinically in VVC and we expect to demonstrate safe and improved eradication of Candida with rapid symptom relief for women seeking a better option over the existing azole class of antifungals.”
RADIANT is a Phase 2, multicenter, randomized, open-label, active-controlled, dose-ranging trial designed to evaluate the safety and tolerability of CD101 in women with moderate to severe episodes of VVC. The study will enroll up to 125 patients who will be randomized into three treatment cohorts. The first cohort will involve the treatment of 50 patients with CD101 Ointment while a second cohort of 50 patients will receive CD101 Gel. The third cohort will include 25 patients who will be treated with oral fluconazole.
The primary endpoints of RADIANT will be the safety and tolerability of a single dose of CD101 Ointment and multiple doses of CD101 Gel in patients with acute VVC. Secondary endpoints include therapeutic efficacy in acute VVC patients treated with CD101. Treatment evaluations and assessments will occur on trial days 7, 14 and 28.
The RADIANT trial will be conducted at clinical trial centers across the United States. More information about the trial is available at www.clinicaltrials.gov, identifier NCT02733432.
About VVC and RVVC
Seventy-five percent of women worldwide suffer from VVC in their lifetime, and four to five million women in the United Statesalone have the recurrent form of the infection, which is caused by Candida. Many women will experience recurrence after the completion of treatment with existing therapies. Most VVC occurs in women of childbearing potential (the infection is common in pregnant women), but it affects women of all ages. In a recent safety communication, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration(FDA) advised caution in the prescribing of oral fluconazole for yeast infections during pregnancy based on a published study concluding there is an increased risk of miscarriage. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) guidelines recommend using only topical antifungal products to treat pregnant women with vulvovaginal yeast infections. Vaginal infections are associated with a substantial negative impact on day-to-day functioning and adverse pregnancy outcomes including preterm delivery, low birth weight, and increased infant mortality in addition to predisposition to HIV/AIDS. According to the CDC, certain species of Candida are becoming increasingly resistant to existing antifungal medications. This emerging resistance intensifies the need for new antifungal agents.
About CD101 Topical
CD101 topical is the first topical agent in the echinocandin class of antifungals and exhibits a broad spectrum of fungicidal activity against Candida species. In May 2016, the FDA granted Qualified Infectious Disease Product (QIDP) and Fast Track Designation to CD101 topical for the treatment of VVC and the prevention of RVVC.
About Cidara Therapeutics
Cidara is a clinical-stage biotechnology company focused on the discovery, development and commercialization of novel anti-infectives for the treatment of diseases that are inadequately addressed by current standard-of-care therapies. Cidara’s initial product portfolio comprises two formulations of the company’s novel echinocandin, CD101. CD101 IV is being developed as a once-weekly, high-exposure therapy for the treatment and prevention of serious, invasive fungal infections. CD101 topical is being developed for the treatment of vulvovaginal candidiasis (VVC) and the prevention of recurrent VVC (RVVC), a prevalent mucosal infection. In addition, Cidara has developed a proprietary immunotherapy platform, Cloudbreak™, designed to create compounds that direct a patient’s immune cells to attack and eliminate pathogens that cause infectious disease. Cidara is headquartered inSan Diego, California. For more information, please visit www.cidara.com.
REF http://ir.cidara.com/phoenix.zhtml?c=253962&p=irol-newsArticle&ID=2176474
CLIP
Cidara Therapeutics raises $42 million to develop once-weekly anti-fungal therapy
Cidara Therapeutics (formerly K2 Therapeutics) grabbed $42 million in a private Series B funding round Wednesday to continue developing its once-weekly anti-fungal therapy. Just in June 2014, the company completed a $32 million Series A financing led by 5AM Ventures, Aisling Capital, Frazier Healthcare and InterWest Partners, which was the fourth largest A round in 2014 for innovative startups[1]. FierceBiotech named the company as one of 2014 Fierce 15 biotech startups.
Cidara has an impressive executive team. The company was co-founded by Kevin Forrest, former CEO of Achaogen (NASDAQ: AKAO), and Shaw Warren. Jeffrey Stein, former CEO of Trius Therapeutics (NASDAQ: TSRX) and Dirk Thye, former president of Cerexa, have joined Cidara as CEO and CMO, respectively. Trius successfully developed antibiotic tedizolid and was acquired in 2013 by Cubist Pharmaceuticals (NASDAQ: CBST) for $818 million.
Cidara’s lead candidate, biafungin (SP3025), was acquired from Seachaid Pharmaceuticals for $6 million. Biafungin’s half-life is much longer than that of similar drugs known as echinocandins (e.g., caspofungin, micafungin, anidulafungin), which may allow it to be developed as a once-weekly therapy, instead of once daily. The company is also developing a topical formulation of biafungin, namely topifungin. Cidara intends to file an IND and initiate a Phase I clinical trial in the second half of 2015.
Merck’s Cancidas (caspofungin), launched in 2001, was the first of approved enchinocandins. The drug generated annual sales of $596 million in 2008. The approved echinocandins must be administered daily by intravenous infusion. Biafungin with improved pharmacokinetic characteristics has the potential to bring in hundreds of millions of dollars per year.
[1] Nat Biotechnol. 2015, 33(1), 18.
CLIP
Biafungin is a potent and broad-spectrum antifungal agent with excellent activity against wild-type and troublesome azole- and echinocandin-resistant strains of Candida spp. The activity of biafungin is comparable to anidulafungin. • Biafungin was active against both wild-type and itraconazole-resistant strains of Aspergillus spp. from four different species. • In vitro susceptibility testing of biafungin against isolates of Candida and Aspergillus may be accomplished by either CLSI or EUCAST broth microdilution methods each providing comparable results. • The use of long-acting intravenous antifungal agents that could safely be given once a week to select patients is desirable and might decrease costs with long-term hospitalizations. Background: A novel echinocandin, biafungin, displaying long-acting pharmacokinetics and chemical stability is being developed for once-weekly administration. The activities of biafungin and comparator agents were tested against 173 fungal isolates of the most clinically common species. Methods: 106 CAN and 67 ASP were tested using CLSI and EUCAST reference broth microdilution methods against biafungin (50% inhibition) and comparators. Isolates included 27 echinocandin-resistant CAN (4 species) with identified fks hotspot (HS) mutations and 20 azole nonsusceptible ASP (4 species). Results: Against C. albicans, C. glabrata and C. tropicalis, the activity of biafungin (MIC50, 0.06, 0.12 and 0.03 μg/ml, respectively by CLSI method) was comparable to anidulafungin (AND; MIC50, 0.03, 0.12 and 0.03 μg/ml, respectively) and caspofungin (CSP; MIC50, 0.12, 0.25 and 0.12 μg/ml, respectively; Table). C. krusei strains were very susceptible to biafungin, showing MIC90 values of 0.06 μg/ml by both methods. Biafungin (MIC50/90, 1/2 μg/ml) was comparable to AND and less potent than CSP against C. parapsilosis using CLSI methodology. CLSI and EUCAST methods displayed similar results for most species, but biafungin (MIC50, 0.06 μg/ml) was eight-fold more active than CSP (MIC50, 0.5 μg/ml) against C. glabrata using the EUCAST method. Overall, biafungin was two- to four-fold more active against fks HS mutants than CSP and results were comparable to AND. Biafungin was active against A. fumigatus (MEC50/90, ≤0.008/0.015 μg/ml), A. terreus (MEC50/90, 0.015/0.015 μg/ml), A. niger (MEC50/90, ≤0.008/0.03 μg/ml) and A. flavus (MEC50/90, ≤0.008/≤0.008 μg/ml) using CLSI method. EUCAST results for ASP were also low for all echinocandins and comparable to CLSI results. Conclusions: Biafungin displayed comparable in vitro activity with other echinocandins against common wild-type CAN and ASP and resistant subsets that in combination with the long-acting profile warrants further development of this compound. 1. Arendrup MC, Cuenca-Estrella M, Lass-Florl C, Hope WW (2013). Breakpoints for antifungal agents: An update from EUCAST focussing on echinocandins against Candida spp. and triazoles against Aspergillus spp. Drug Resist Updat 16: 81-95. 2. Castanheira M, Woosley LN, Messer SA, Diekema DJ, Jones RN, Pfaller MA (2014). Frequency of fks mutations among Candida glabrata isolates from a 10-year global collection of bloodstream infection isolates. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 58: 577-580. 3. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (2008). M27-A3. Reference Method for Broth Dilution Antifungal Susceptibility Testing of Yeasts: third edition. Wayne, PA: CLSI. 4. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (2008). M38-A2. Reference Method for Broth Dilution Antifungal Susceptibility Testing of Filamentous Fungi: Second Edition. Wayne, PA: CLSI. 5. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (2012). M27-S4. Reference Method for Broth Dilution Antifungal Susceptibility Testing of Yeasts: 4th Informational Supplement. Wayne, PA: CLSI. 6. European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (2014). Breakpoint tables for interpretation of MICs and zone diameters. Version 4.0, January 2014. Available at: http://www.eucast.org/clinical_breakpoints/. Accessed January 1, 2014. 7. Pfaller MA, Diekema DJ (2010). Epidemiology of invasive mycoses in North America. Crit Rev Microbiol 36: 1-53. 8. Pfaller MA, Diekema DJ, Andes D, Arendrup MC, Brown SD, Lockhart SR, Motyl M, Perlin DS (2011). Clinical breakpoints for the echinocandins and Candida revisited: Integration of molecular, clinical, and microbiological data to arrive at species-specific interpretive criteria. Drug Resist Updat 14: 164-176. ABSTRACT Activity of a Novel Echinocandin Biafungin (CD101) Tested against Most Common Candida and Aspergillus Species, Including Echinocandin- and Azole-resistant Strains M CASTANHEIRA, SA MESSER, PR RHOMBERG, RN JONES, MA PFALLER JMI Laboratories, North Liberty, Iowa, USA C
PATENT
https://www.google.com/patents/WO2015035102A2?cl=en
BIAFUNGIN ACETATE IS USED AS STARTING MATERIAL
Example 30b: Synthesis of Compound 31


Step a. Nitration of Biafungin Acetate

To a stirring solution of biafungin (1 00 mg, 0.078 mmol) in glacial acetic acid(1 .5 ml_) was added sodium nitrite (1 1 mg, 0.159 mmol) and the reaction was stirred at ambient temperature for 20 hours. The mixture was applied directly to reversed phase H PLC (Isco CombiFlash Rf; 50g RediSep C1 8 column, 5 to 95% acetonitrile in Dl water containing 0.1 % formic acid: 15 minute gradient). The pure fractions were pooled and lyophilized to yield 85 mg of the desired product as a light yellow solid, formate salt. 1 H-NMR (300 M Hz, Methanol-d4) δ 8.58 (d, 1 H, J = 1 1 .7 Hz), 8.47 (t, 2H, J = 8.7Hz), 8.05 (d, 1 H, J = 2.1 Hz), 7.99 (d, 2H, J = 9.3 Hz), 7.82 (d, 2H, J = 8.7 Hz), 7.79-7.60 (m, 12H), 7.1 7 (d, 1 H, J = 8.7 Hz), 7.03 (d, 2H, J = 9 Hz), 5.48 (d, 1 H, J = 6 Hz), 5.08 (dd, 1 H, J = 1 .2, 5.7 Hz), 4.95-4.73 (m, 5H), 4.68-4.56 (m, 2H), 4.53 (d, 1 H, J = 5.7 Hz), 4.48-4.39 (m, 2H), 4.31 -3.79 (m, 6H), 4.04 (t, 2H, J = 5.7 Hz), 3.72-3.44 (m,3H), 3.1 8 (s, 9H), 2.60-1 .99 (m, 5H), 1 .83 (m, 2H, J = 8.7 Hz), 1 .56-1 .35 (m, 5H), 1 .28 (d, 6H, J = 4.2 Hz), 1 .09 (d, 3H, J = 1 0.2 Hz), 0.99 (t, 3H, J = 8.7 Hz) ; LC/MS, [M/2+H]+: 635.79, 635.80 calculated.
Step b. Reduction of Nitro-Biafungin To Amino-Biafungin

To a stirring solution of Nitro-Biafungin (1 00 mg, 0.075 mmol) in glacial acetic acid(1 .5 ml_) was added zinc powder (50 mg, 0.77 mmol) and the reaction was stirred at ambient temperature for 1 hour. The mixture was filtered and applied directly to reversed phase HPLC (Isco CombiFlash Rf, 50g Redisep C18 column; 5 to 95% acetonitrile in Dl water containing 0.1 % formic acid: 15 minute gradient). The pure fractions were pooled and lyophilized to yield 55 mg of the desired product as a white solid, formate salt. 1 H-NMR (300 MHz, Methanol-d4) 5 8.47 (bs, 1 H), 7.99 (d, 2H, J = 1 0.8Hz), 7.82 (d, 2H, J = 7.5 Hz), 7.80-7.67 (m, 6H), 7.62 (d, 2H, J = 8.7 Hz), 7.03 (d, 2H, J = 7.5 Hz), 6.77 (d, 1 H, J = 1 .9 Hz), 6.68 (d, 1 H, J = 8.2 Hz), 6.55 (dd, 2H, J = 8.2, 1 .9 Hz), 5.43 (d, 1 H, J = 2.5 Hz), 5.05 (d, 1 H, J = 3 Hz), 4.83-4.73 (m, 2H), 4.64- 4.56 (m, 2H), 4.43-4.34 (m, 2H), 4.31 -4.15 (m, 4H), 4.03-4.08 (m, 1 H), 4.1 1 -3.89 (m, 8H), 3.83 (d, 1 H, J = 1 0.8 Hz), 3.68-3.47 (m, 3H), 3.1 7 (s, 9H), 2.57-2.42 (m, 2H), 2.35-2.27 (m, 1 H), 2.14-1 .98 (m, 2H), 1 .83 (m, 2H, J = 6 Hz), 1 .56-1 .38 (m, 4H), 1 .28 (dd, 6H, J = 6.5, 2 Hz), 1 .09 (d, 3H, J = 7 Hz), 0.986 (t, 3H, J = 7 Hz); High Res LC/MS: [M+H]+ 1241 .61 63; 1241 .6136 calculated.
Step c. Reaction of Amino-Biafungin with lnt-2 to Produce Compound 31

To a stirring solution of Amino-Biafungin (50 mg, 0.04 mmol) in DM F (1 ml_) was added formyl-Met-Leu-Phe- -Ala-OSu (lnt-2) (36 mg, 0.06 mmol) and DI PEA (7 uL, 0.04 mmol). The reaction was stirred at ambient temperature for 1 8 hours. The mixture was applied directly to reversed phase HPLC (Isco CombiFlash Rf; 50g Redisep C1 8 column; 5 to 95% acetonitrile in Dl water containing 0.1 % formic acid: 15 minute gradient). The pure fractions were pooled and lyophilized to yield 26 mg of a white solid as a formate salt. 1 H-NMR (300 M Hz, Methanol-d4) 5 8.55 (bs, 1 H), 8.44 (t, 1 H, J = 10 Hz), 8.1 8 (d, 1 H, J = 6 Hz), 8.1 1 (s, 1 H), 7.99 (d, 2H, J = 1 0 Hz), 7.84-7.70 (m, 6H), 7.63 (d, 2H, J = 7.8 Hz), 7.32-7.1 9 (m, 6H), 7.03 (d, 4H, J = 9 Hz), 6.87 (d, 1 H, J = 8.1 Hz), 5.44 (d, 1 H, J = 1 0.5 Hz), 5.05 (d, 1 H, J = 4.5 Hz), 4.83-4.74 (m, 2H), 4.66-4.50 (m, 6H), 4.45-4.29 (m, 10H), 4.1 9-3.82 (m, 1 0H), 3.67-3.57 (m, 6H), 3.1 7 (s, 9H), 2.64-2.46 (m, 6 H), 2.14-1 .92 (m, 6H), 1 .84 (m, 4H, J = 6 Hz), 1 .62-1 .40 (m, 8H), 1 .32-1 .22 (m, 6H), 1 .09 (d, 3H, J = 9 Hz), 0.99 (t, 3H, J = 7.5 Hz), 0.88 (m, 6H, J = 6.8 Hz) ; High Res LC/MS, [M/2+H]+ 865.4143, 865.4147 calculated.
REFERENCES
- Denning, DW (June 2002). “Echinocandins: a new class of antifungal.”. The Journal of antimicrobial chemotherapy 49 (6): 889–91. doi:10.1093/jac/dkf045. PMID 12039879.
- Morris MI, Villmann M (September 2006). “Echinocandins in the management of invasive fungal infections, part 1”. Am J Health Syst Pharm 63 (18): 1693–703.doi:10.2146/ajhp050464.p1. PMID 16960253.
- Morris MI, Villmann M (October 2006). “Echinocandins in the management of invasive fungal infections, Part 2”. Am J Health Syst Pharm 63 (19): 1813–20.doi:10.2146/ajhp050464.p2. PMID 16990627.
- ^ Jump up to:a b “Pharmacotherapy Update – New Antifungal Agents: Additions to the Existing Armamentarium (Part 1)”.
- Debono, M; Gordee, RS (1994). “Antibiotics that inhibit fungal cell wall development”.Annu Rev Microbiol 48: 471–497. doi:10.1146/annurev.mi.48.100194.002351.
17 Eschenauer, G; Depestel, DD; Carver, PL (March 2007). “Comparison of echinocandin antifungals.”. Therapeutics and clinical risk management 3 (1): 71–97. PMC 1936290.PMID 18360617.
///////////Biafungin™, CD 101 IV, CD 101 Topical, CD101, SP 3025, PHASE 2, CIDARA, Orphan Drug, Fast Track Designation, Seachaid Pharmaceuticals, Qualified Infectious Disease Product, QIDP, UNII-G013B5478J, 1396640-59-7, 1631754-41-0, Vulvovaginal candidiasis, Echinocandin B, FUNGIN
FREE FORM
CCCCCOc1ccc(cc1)c2ccc(cc2)c3ccc(cc3)C(=O)N[C@H]4C[C@@H](O)[C@H](NC(=O)[C@@H]5[C@@H](O)[C@@H](C)CN5C(=O)[C@@H](NC(=O)C(NC(=O)[C@@H]6C[C@@H](O)CN6C(=O)C(NC4=O)[C@@H](C)O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)c7ccc(O)cc7)[C@@H](C)O)OCC[N+](C)(C)C
AND OF ACETATE
CCCCCOc1ccc(cc1)c2ccc(cc2)c3ccc(cc3)C(=O)N[C@H]4C[C@@H](O)[C@H](NC(=O)[C@@H]5[C@@H](O)[C@@H](C)CN5C(=O)[C@@H](NC(=O)C(NC(=O)[C@@H]6C[C@@H](O)CN6C(=O)[C@@H](NC4=O)[C@@H](C)O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)c7ccc(O)cc7)[C@@H](C)O)OCC[N+](C)(C)C.CC(=O)[O-]
Three antifungal drugs approved by the United States Food and Drug Administration, caspofungin, anidulafungin, and micafungin, are known to inhibit β-1 ,3-glucan synthase which have the structures shown below.

caspofungin

Anidulafungin

Other exemplary p-1 ,3-glucan synthase inhibitors include,

echinocandin B

cilofungin

pneumocandin A0

pneumocandin B0

L-705589

L-733560

A-174591 

 or a salt thereof,
or a salt thereof,
Biafungin

or a salt thereof,
Amino-biafungin

or a salt thereof,

Amino-AF-053 


ASP9726
Yet other exemplary p-1 ,3-glucan synthase inhibitors include, without limitation:

Papulacandin B


Ergokonin
//////////////