DOI: 10.1039/C5GC02920A, Communication
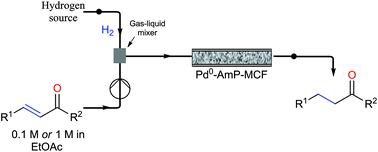
A continuous-flow approach towards the selective nanopalladium-catalyzed hydrogenation of the olefinic bond in various Michael acceptors, which could lead to a greener and more sustainable process, has been developed.
Nanopalladium-catalyzed conjugate reduction of Michael acceptors – application in flow
Nanopalladium-catalyzed conjugate reduction of Michael acceptors – application in flow
E-mail: jeb@organ.su.se
DOI: 10.1039/C5GC02920A
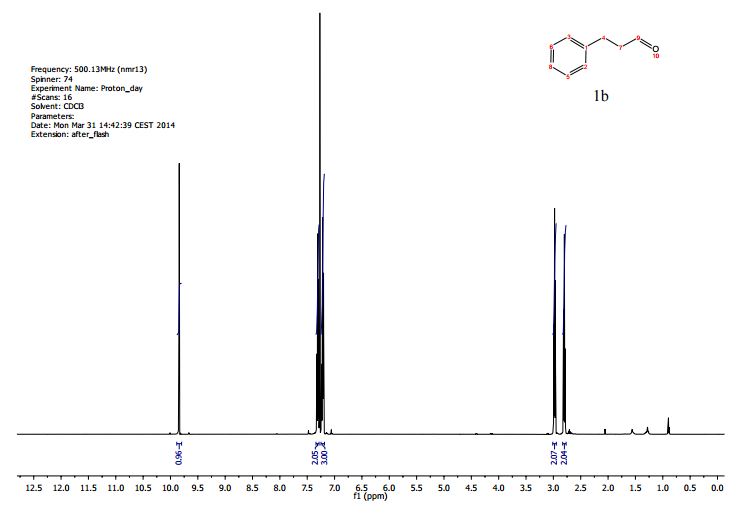
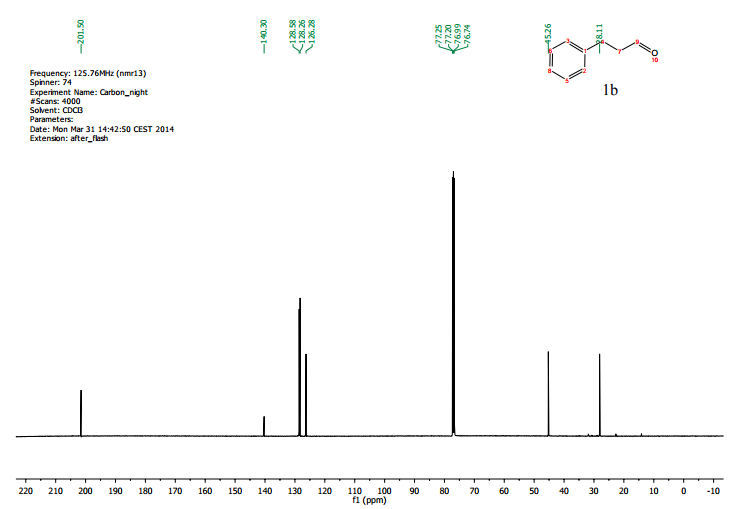
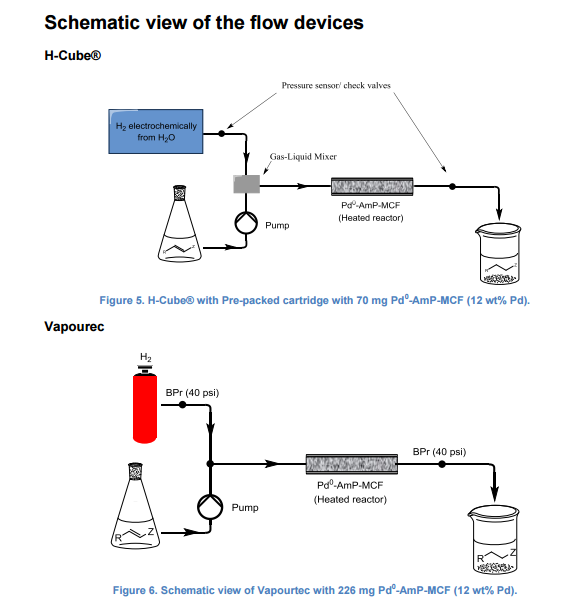
A continuous-flow approach towards the selective nanopalladium-catalyzed hydrogenation of the olefinic bond in various Michael acceptors, which could lead to a greener and more sustainable process, has been developed. The nanopalladium is supported on aminofunctionalized mesocellular foam. Both aromatic and aliphatic substrates, covering a variation of functional groups such as acids, aldehydes, esters, ketones, and nitriles were selectively hydrogenated in high to excellent yields using two different flow-devices (H-Cube® and Vapourtec). The catalyst was able to hydrogenate cinnamaldehyde continuously for 24 h (in total hydrogenating 19 g cinnanmaldehyde using 70 mg of catalyst in the H-cube®) without showing any significant decrease in activity or selectivity. Furthermore, the metal leaching of the catalyst was found to be very low (ppb amounts) in the two flow devices.
////////Nanopalladium-catalyzed, conjugate reduction, Michael acceptors, application, flow chemistry