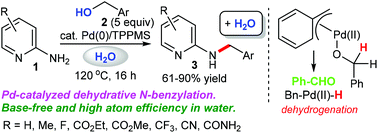
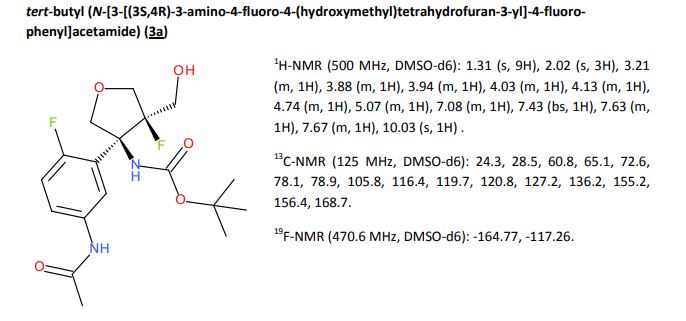
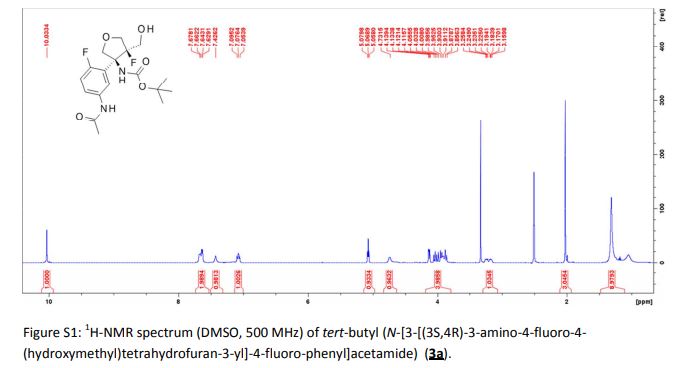
A detailed study of literature-known and novel S-containing pincer-type ligands for ruthenium-catalyzed homogeneous hydrogenation and dehydrogenation reactions was carried out. The scope and limitations of these catalysts were carefully investigated, and it was shown that simple bench-stable SNS–Ru complexes can be used to facilitate the hydrogenation of a variety of different substrates at a maximum H2 pressure of 20 bar under operationally simple, easy to scale up, glovebox-free conditions by using starting materials and reagents that do not require any special purification prior to use. It was also shown that such complexes can be used to catalyze the dehydrogenative coupling of alcohols and amines to get amides as well as for the dehydrogenative dimerization of alcohols to esters.
SNS-Ligands for Ru-Catalyzed Homogeneous Hydrogenation and Dehydrogenation Reactions
†Institute of Organic Chemistry, Johannes Kepler University Linz, Altenbergerstr. 69, 4040 Linz, Austria
‡Patheon Austria, part of Thermo Fisher Scientific, St. Peterstr. 25, 4020 Linz, Austria
Org. Process Res. Dev., Article ASAP
DOI: 10.1021/acs.oprd.8b00142
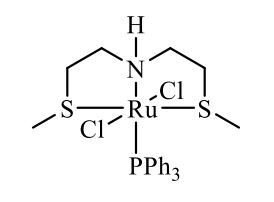
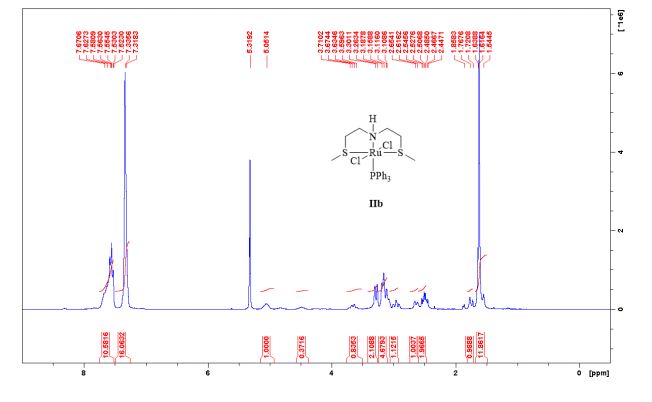
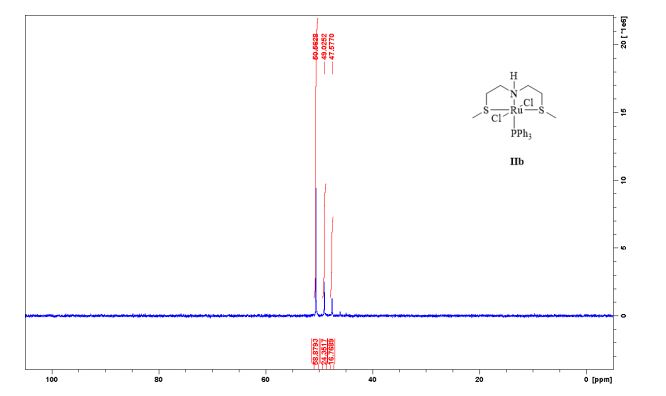
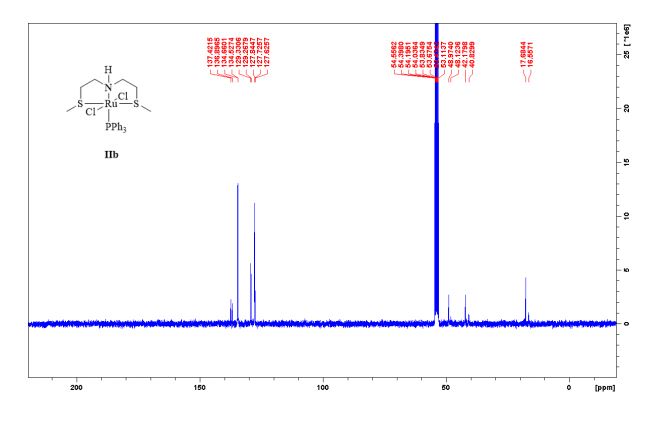
Complex IIb:
Method A was applied, using 180 mg of ligand 11b (1.09 mmol) and 993 mg of 27 (1.04 mmol) to give the complex IIb as yellow powder in 83% yield. The complex was isolated as mixture of three isomers.
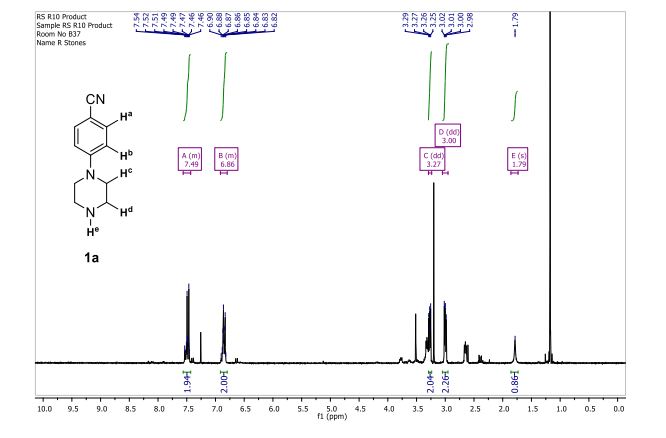
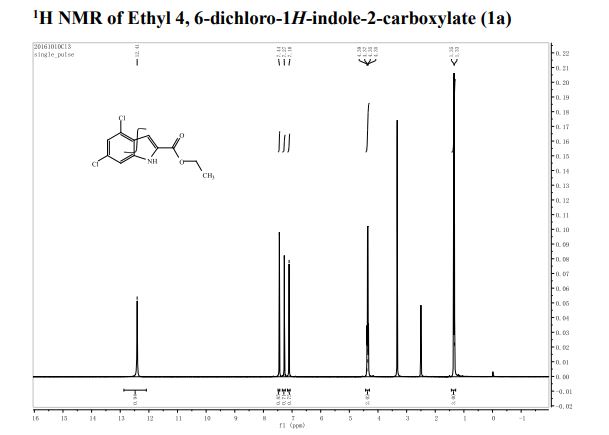
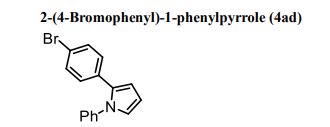
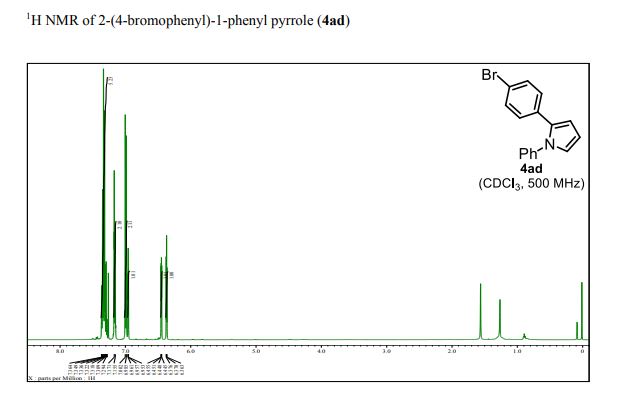
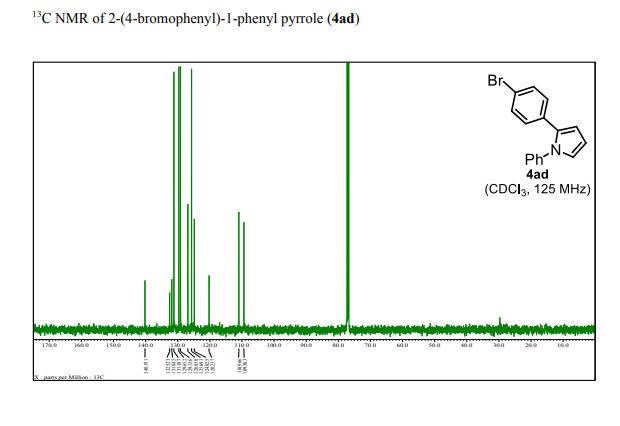
1 H-NMR (CDCl3, 300 MHz, 298 K), δ / ppm: 7.75-7.50 (m, 10H), 7.41-7.25 (m, 16H), 5.05 (bs, 1H), 3.73-2.9 (m, 9H), 2.71-2.41 (m, 3H), 1.89-1.71 (m, 1H), 1.64-1.54 (m, 12H);
31P-NMR (CDCl3, 121 MHz, 298 K), δ / ppm: 50.6 (59%), 49.0 (24%), 47.6 (17%);
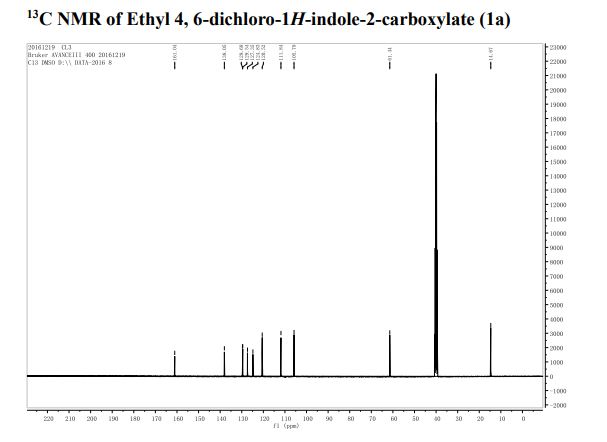
13C NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3, 298 K): δ / ppm = 137.1 (d, J = 39.5 Hz), 134.6 (d, J = 10.0 Hz), 129.3, 127.8 (d, J = 8.9 Hz), 49.0, 42.2, 17.7;
HRMS (ESI+): m/z calcd for C24H30ClNPRuS2 [M – Cl]+: 564.0284; found: 564.0272.
1 H-NMR (CDCl3, 300 MHz, 298 K), δ / ppm: 7.75-7.50 (m, 10H), 7.41-7.25 (m, 16H), 5.05 (bs, 1H), 3.73-2.9 (m, 9H), 2.71-2.41 (m, 3H), 1.89-1.71 (m, 1H), 1.64-1.54 (m, 12H);
31P-NMR (CDCl3, 121 MHz, 298 K), δ / ppm: 50.6 (59%), 49.0 (24%), 47.6 (17%);
13C NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3, 298 K): δ / ppm = 137.1 (d, J = 39.5 Hz), 134.6 (d, J = 10.0 Hz), 129.3, 127.8 (d, J = 8.9 Hz), 49.0, 42.2, 17.7;
///////////////SNS-Ligands, Ru-Catalyzed, Homogeneous Hydrogenation, Dehydrogenation Reactions