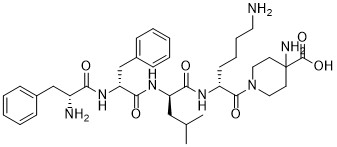
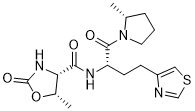
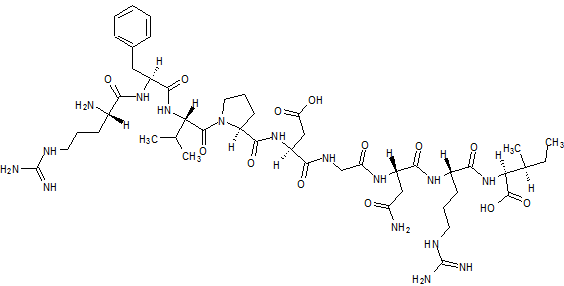
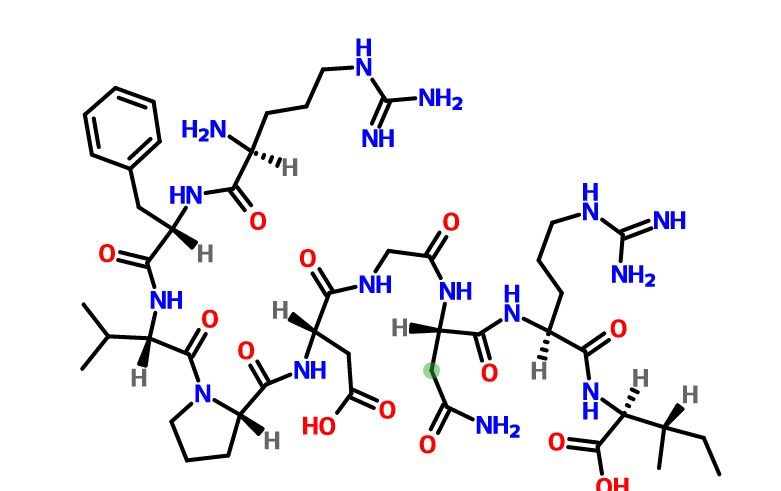
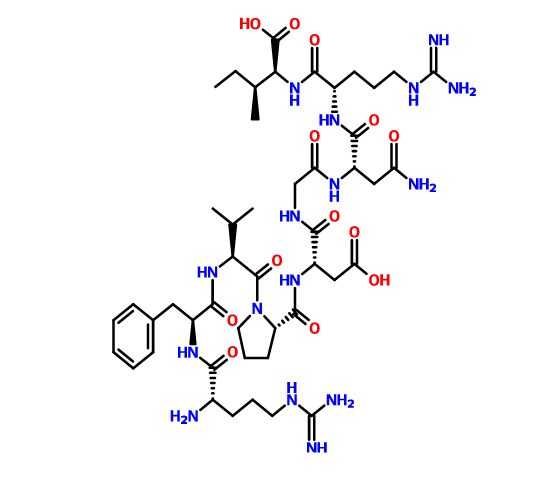
Difelikefalin, CR-845; MR-13A-9; MR-13A9
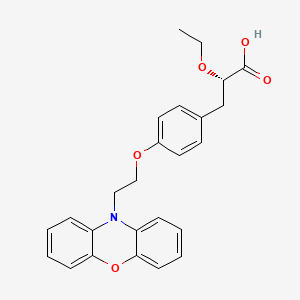
4-amino-1- (D-phenylalanyl-D-phenylalanyl-D-leucyl-D-lysyl) piperidine-4-carboxylic acid
Phase III
C36H53N7O6, 679.40573
| Originator | Ferring Pharmaceuticals |
|---|---|
| Developer | Cara Therapeutics |
| Class | Analgesic drugs (peptides) |
| Mechanism Of Action | Opioid kappa receptor agonists |
| Who Atc Codes | D04A-X (Other antipruritics), N02A (Opioids) |
| Ephmra Codes | D4A (Anti-Pruritics, Including Topical Antihistamines, Anaesthetics, etc), N2A (Narcotics) |
| Indication | Pain, Osteoarthritis, Pruritus |
A kappa opioid receptor agonist potentially for treatment of post-operative pain and uremic pruritus.
Difelikefalin, also known CR845, is a novel and potent kappa opioid receptor agonist. CR845 exhibit low P450 CYP inhibition and low penetration into the brain. CR845 may be useful in the prophylaxis and treatment of pain and inflammation associated with a variety of diseases and conditions .

No. CAS 1024828-77-0
Difelikefalin ( INN ) (Developmental Code Names CR845 , FE-202845 ), Also Known As D -Phe- D -Phe- D -Leu- D -Lys- [Ganma- (4-N-Piperidinyl) Amino Carboxylic Acid] (As The Acetate Salt ), Is An Analgesic Opioid Peptide [2] Acting As A Peripherally-Specific , Highly Selective Agonist Of The kappa-Opioid Receptor (KOR). [1] [3] [4] [5] It Is Under Development By Cara Therapeutics As An Intravenous Agent For The Treatment Of Postoperative Pain . [1] [3] [5] An Oral Formulation Has Also Been Developed. [5] Due To Its Peripheral Selectivity, Difelikefalin Lacks The Central Side Effects Like Sedation , Dysphoria , And Hallucinations Of Previous KOR-Acting Analgesics Such As Pentazocine And Phenazocine . [1] [3] In Addition To Use As An Analgesic, Difelikefalin Is Also Being Investigated For The Treatment Of Pruritus (Itching). [1] [3] [4 ] Difelikefalin Has Completed Phase II Clinical Trials For Postoperative Pain And Has Demonstrated Significant And “Robust” Clinical Efficacy, Along With Being Safe And Well-Tolerated. [3] [5] It Is Also In Phase II Clinical Trials For Uremic Pruritus In Hemodialysis Patients. [4]
Difelikefalin Acts As An Analgesic By Activating KORs On Peripheral Nerve Terminals And KORs Expressed By Certain Immune System Cells . [1] Activation Of KORs On Peripheral Nerve Terminals Results In The Inhibition Of Ion Channels Responsible For Afferent Nerve Activity , Causing Reduced Transmission Of Pain Signals , While Activation Of KORs Expressed By Immune System Cells Results In Reduced Release Of Proinflammatory , Nerve-Sensitizing Mediators (Eg, Prostaglandins ). [1]
PATENT
Patent Document 2: Japanese Unexamined Patent Publication No. 2013-241447
1 (1) Synthesis of Cbz-D-Lys (Boc) -α-Boc-Pic-OMe (3)
to the four-necked flask of 2L, α-Boc-Pic- OMe · HCl [α-Boc-4 – aminopiperidine-4-carboxylic acid methyl hydrochloride] were charged (2) 43.7g (148mmol), was suspended in EtOAc 656mL (15v / w). To the suspension of 1-hydroxybenzotriazole (HOBt) 27.2g (178mmol), while cooling with Cbz-D-Lys (Boc) -OH 59.2g (156mmol) was added an ice-bath 1-ethyl -3 – (3-dimethylcarbamoyl amino propyl) was added to the carbodiimide · HCl (EDC · HCl) 34.1g (178mmol). After 20 minutes, stirring was heated 12 hours at room temperature. After completion of the reaction, it was added and the organic layer was 1 N HCl 218 mL of (5.0v / w). NaHCO to the resulting organic layer 3 Aq. 218ML (5.0V / W), Et 3 N 33.0 g of (326Mmol) was stirred for 30 minutes, and the mixture was separated. The organic layer HCl 218ML 1N (5.0V / W), NaHCO 3 Aq. 218mL (5.0v / w), NaClaq . Was washed successively with 218ML (5.0V / W), Na 2 SO 4 dried addition of 8.74g (0.2w / w). Subjected to vacuum filtration, was concentrated under reduced pressure resulting filtrate by an evaporator, and pump up in the vacuum pump, the Cbz-D-Lys (Boc) -α-Boc-Pic-OMe (3) 88.9g as a white solid obtained (96.5% yield, HPLC purity 96.5%).
In An Eggplant-Shaped Flask Of 2L, Cbz-D-Lys (Boc) -Arufa-Boc-Pic-OMe (3) 88.3g (142mmol) were charged, it was added and dissolved 441mL (5.0v / w) the EtOAc. The 5% Pd / C to the reaction solution 17.7g (0.2w / w) was added, After three nitrogen substitution reduced pressure Atmosphere, Was Performed Three Times A Hydrogen Substituent. The Reaction Solution Was 18 Hours With Vigorous Stirring At Room Temperature To Remove The Pd / C And After The Completion Of The Reaction Vacuum Filtration. NaHCO The Resulting Filtrate 3 Aq. 441ML And (5.0V / W) Were Added For Liquid Separation, And The Organic Layer Was Extracted By The Addition Of EtOAc 200ML (2.3V / W) In The Aqueous Layer. NaHCO The Combined Organic Layer 3 Aq. 441ML And (5.0V / W) Were Added for liquid separation, and the organic layer was extracted addition of EtOAc 200mL (2.3v / w) in the aqueous layer. NaClaq the combined organic layers. 441mL and (5.0v / w) is added to liquid separation, was extracted by the addition EtOAc 200ML Of (2.3V / W) In The Aqueous Layer. The Combined Organic Layer On The Na 2 SO 4 Dried Addition Of 17.7 g of (0.2W / W), Then The Filtrate Was Concentrated Under Reduced Pressure Obtained Subjected To Vacuum Filtration By an evaporator, and pump up in the vacuum pump, D-Lys (Boc) -α-Boc-Pic- OMe (4) to give 62.7g (90.5% yield, HPLC purity 93.6%).
in the four-necked flask of 2L, D-Lys (Boc) -α-Boc-Pic-OMe (4) was charged 57.7 g (120 mmol), was suspended in EtOAc 576mL (10v / w). HOBt 19.3g (126mmol) to this suspension, was added EDC · HCl 24.2g (126mmol) while cooling in an ice bath added Cbz-D-Leu-OH 33.4g (126mmol). After 20 minutes, after stirring the temperature was raised 5 hours at room temperature, further the EDC · HCl and stirred 1.15 g (6.00 mmol) was added 16 h. After completion of the reaction, it was added liquid separation 1N HCl 576mL (10v / w) . NaHCO to the resulting organic layer 3 Aq. 576ML (10V / W), Et 3 N 24.3 g of (240Mmol) was stirred for 30 minutes, and the mixture was separated. The organic layer HCl 576ML 1N (10V / W), NaHCO 3 Aq. 576mL (10v / w), NaClaq . Was washed successively with 576ML (10V / W), Na 2 SO 4 dried addition of 11.5g (0.2w / w). After the filtrate was concentrated under reduced pressure obtained subjected to vacuum filtration by an evaporator, and pump up in the vacuum pump, the Cbz-D-Leu-D- Lys (Boc) -α-Boc-Pic-OMe (5) 85.8g It was obtained as a white solid (98.7% yield, HPLC purity 96.9%).
in an eggplant-shaped flask of 1L, Cbz-D-Leu- D-Lys (Boc) -α-Boc-Pic -OMe the (5) 91.9g (125mmol) were charged, was added and dissolved 459mL (5.0v / w) the EtOAc. The 5% Pd / C to the reaction solution 18.4g (0.2w / w) was added, After three nitrogen substitution reduced pressure atmosphere, was performed three times a hydrogen substituent. The reaction solution was subjected to 8 hours with vigorous stirring at room temperature to remove the Pd / C and after the completion of the reaction vacuum filtration. NaHCO the resulting filtrate 3 Aq. 200mL (2.2v / w) were added to separate liquid, NaHCO to the organic layer 3 Aq. 200mL (2.2v / w), NaClaq . It was sequentially added washed 200mL (2.2v / w). To the resulting organic layer Na 2 SO 4 dried added 18.4g (0.2w / w), to the filtrate concentrated under reduced pressure obtained subjected to vacuum filtration by an evaporator, and a pump-up with a vacuum pump. The resulting amorphous solid was dissolved adding EtOAc 200mL (2.2v / w), was crystallized by the addition of heptane 50mL (1.8v / w). Was filtered off precipitated crystals by vacuum filtration, the crystals were washed with a mixed solvent of EtOAc 120mL (1.3v / w), heptane 50mL (0.3v / w). The resulting crystal 46.1g to added to and dissolved EtOAc 480mL (5.2v / w), was crystallized added to the cyclohexane 660mL (7.2v / w). Was filtered off under reduced pressure filtered to precipitate crystals, cyclohexane 120mL (1.3v / w), and washed with a mixed solvent of EtOAc 20mL (0.2v / w), and 30 ° C. vacuum dried, D-Leu- as a white solid D-Lys (Boc) -α- Boc-Pic-OMe (6) to give 36.6 g (48.7% yield, HPLC purity 99.9%).
to the four-necked flask of 1L, D-Leu-D- Lys (Boc) -α-Boc-Pic-OMe with (6) 35.8g (59.6mmol) was charged, it was suspended in EtOAc 358mL (10v / w). To this suspension HOBt 9.59g (62.6mmol), Cbz- D-Phe-OH 18.7g was cooled in an ice bath is added (62.6mmol) while EDC · HCl 12.0g (62.6mmol) It was added. After 20 minutes, a further EDC · HCl After stirring the temperature was raised 16 hours was added 3.09 g (16.1 mmol) to room temperature. After completion of the reaction, it was added and the organic layer was 1N HCl 358mL of (10v / w). NaHCO to the resulting organic layer 3 Aq. 358ML (10V / W), Et 3 N 12.1 g of (119Mmol) was stirred for 30 minutes, and the mixture was separated. The organic layer HCl 358ML 1N (10V / W), NaHCO 3 Aq. 358mL (10v / w), NaClaq . Was washed successively with 358ML (10V / W), Na 2 SO 4 dried addition of 7.16g (0.2w / w). After the filtrate was concentrated under reduced pressure obtained subjected to vacuum filtration by an evaporator, and pump up in the vacuum pump, Cbz-D-Phe-D -Leu-D-Lys (Boc) -α-Boc-Pic-OMe (7) was obtained 52.5g as a white solid (yield quant, HPLC purity 97.6%).
in an eggplant-shaped flask of 2L, Cbz-D-Phe- D-Leu-D-Lys ( Boc) -α-Boc-Pic- OMe (7) the 46.9g (53.3mmol) were charged, the 840ML EtOAc (18V / W), H 2 added to and dissolved O 93.8mL (2.0v / w) It was. The 5% Pd / C to the reaction mixture 9.38g (0.2w / w) was added, After three nitrogen substitution reduced pressure atmosphere, was performed three times a hydrogen substituent. The reaction solution was subjected to 10 hours with vigorous stirring at room temperature to remove the Pd / C and after the completion of the reaction vacuum filtration. NaHCO the resulting filtrate 3 Aq. 235mL (5.0v / w) were added to separate liquid, NaHCO to the organic layer 3 Aq. 235mL (5.0v / w), NaClaq . It was added sequentially cleaning 235mL (5.0v / w). To the resulting organic layer Na 2 SO 4 dried addition of 9.38g (0.2w / w), then the filtrate was concentrated under reduced pressure obtained subjected to vacuum filtration by an evaporator, pump up with a vacuum pump to D-Phe -D-Leu-D-Lys ( Boc) -α-Boc-Pic-OMe (7) was obtained 39.7g (yield quant, HPLC purity 97.3%).
In An Eggplant-Shaped Flask Of 20ML Boc-D-Phe-D -Phe-D- Leu-D- lys (Boc) -α -Boc- Pic-OMe (9) and 2.00gg, IPA 3.3mL (1.65v / w), was suspended by addition of PhMe 10mL (5v / w). It was stirred at room temperature for 19 hours by addition of 6N HCl / IPA 6.7mL (3.35v / w). The precipitated solid was filtered off by vacuum filtration and dried under reduced pressure to a white solid of D-Phe-D-Phe- D- Leu-D-Lys-Pic- OMe 1.59ghydrochloride (1) (yield: 99 .0%, HPLC purity 98.2%) was obtained.
In An Eggplant-Shaped Flask Of 20ML-D-Phe-D- Phe D-Leu -D-Lys- pic-OMe hydrochloride crude crystals (1) were charged 200mg, EtOH: MeCN = 1: after stirring for 1 hour then heated in a mixed solvent 4.0 mL (20v / w) was added 40 ° C. of 5 , further at room temperature for 2 was time stirring slurry. Was filtered off by vacuum filtration, the resulting solid was dried under reduced pressure a white solid ((1) Purification crystals) was obtained 161 mg (80% yield, HPLC purity 99.2% ).
(1)) Of (A) To A Round-Bottomed Flask Of 10ML D-Phe-D-Phe-D- -D-Lys Leu-Pic-OMe Hydrochloride Salt (1) Was Charged With Purified Crystal 38.5Mg (0.0488Mmol), H 2 Was Added And Dissolved O 0.2ML (5.2V / W). 1.5H Was Stirred Dropwise 1N NaOH 197MyuL (0.197mmol) at room temperature. After completion of the reaction, concentrated under reduced pressure by an evaporator added 1N HCl 48.8μL (0.0488mmol), to obtain a D-Phe-D-Phe- D-Leu-D-Lys- Pic (A) (yield: quant , HPLC purity 99.7%).
(Trifluoroacetic Acid (TFA)
Use) (1) D-Phe-D-Phe-D-Leu-D-Lys-Pic-OMe TFA Synthesis Of Salt (1)
TFA 18ML Eggplant Flask Of 50ML (18V / W) , 1- Dodecanethiol 1.6ML (1.6V / W), Triisopropylsilane 0.2ML (0.2V / W), H 2 Sequentially Added Stirring The O 0.2ML (0.2V / W) Did. The Solution To The Boc-D-Phe- D- Phe-D-Leu-D -Lys (Boc) -α-Boc-Pic-OMe the (9) 1.00g (1.01mmol) was added in small portions with a spatula. After completion of the reaction, concentrated under reduced pressure by an evaporator, it was added dropwise the resulting residue in IPE 20mL (20v / w). The precipitated solid was filtered off, the resulting solid was obtained and dried under reduced pressure to D-Phe-D-Phe- D-Leu -D-Lys-Pic-OMe · TFA salt as a white solid (1) (Osamu rate 93.0%, HPLC purity 95.2%).
to a round-bottomed flask of 10mL D-Phe-D-Phe -D-Leu-D-Lys-Pic-OMe TFA were charged salt (1) 83mg (0.0843mmol), was added and dissolved H2O 431μL (5.2v / w). Was 12h stirring dropwise 1N NaOH 345μL (0.345mmol) at room temperature. After completion of the reaction, concentrated under reduced pressure by an evaporator added 1N HCl 84.3μL (0.0843mmol), to obtain a D-Phe-D-Phe- D-Leu-D-Lys-Pic (A) ( yield: quant, HPLC purity 95.4%).
3 (HCl / EtOAc
Use) (1) In An Eggplant-Shaped Flask Of 30ML Boc-D-Phe-D -Phe-D-Leu-D-Lys (Boc) -Arufa-Boc-Pic-OMe (9) 1. It was charged with 00g (1.01mmol ), was added and dissolved EtOAc7.0mL (7.0v / w). 4N HCl / EtOAc 5.0mL (5.0v / w) was added after 24h stirring at room temperature, the precipitated solid was filtered off by vacuum filtration, washed with EtOAc 2mL (2.0v / w). The resulting solid D-Phe-D-Phe- D-Leu-D-Lys-Pic-OMe hydrochloride (1) was obtained 781mg of a white solid was dried under reduced pressure (the 96.7% yield, HPLC purity 95.4%).
eggplant flask of 10mL D-Phe-D-Phe -D-Leu-D-Lys-Pic-OMe hydrochloride were charged salt (1) 90 mg (0.112 mmol), H 2 was added and dissolved O 0.47mL (5.2v / w). Was 12h stirring dropwise 1N NaOH 459μL (0.459mmol) at room temperature. After completion of the reaction, concentrated under reduced pressure by an evaporator added 1N HCl 0.112μL (0.112mmol), was obtained D-Phe-D-Phe- D-Leu-D-Lys-Pic (A) ( yield: quant, HPLC purity 93.1%).
Compound (1) Of The Compound By Hydrolysis Synthesis Of (The A) (Compound (1) Without
Purification) Eggplant Flask 10ML D-Phe-D-Phe -D-Leu-D-Lys-Pic-OMe (1) Charged Hydrochloride Were (Without Pre-Step Purification) 114.5Mg (0.142Mmol), H 2 Was Added And Dissolved O 595MyuL (5.2V / W). Was 14H Stirring Dropwise 1N NaOH 586MyuL (0.586Mmol) At Room Temperature. After Completion Of the reaction, concentrated under reduced pressure by an evaporator added 1N HCl 0.15μL (0.150mmol), was obtained D-Phe-D-Phe- D-Leu-D-Lys-Pic (A) (yield: quant, HPLC purity 95.2 %).
Path Not Via The Compound (1) (Using Whole Guard Boc-D-Phe-D-Phe-D-Leu-D-Lys (Boc) -Alpha-Boc-Pic-OMe
(A)) (1) D–Boc Phe- D-Phe-D-Leu-D-Lys (Boc) -Arufa-Boc-Pic-OH Synthesis Of
Eggplant Flask Of 30ML Boc-D-Phe-D -Phe-D-Leu-D- Lys (Boc) -α- Boc-Pic -OMe (9) were charged 1.00g (1.00mmol), was added and dissolved MeOH 5.0mL (5.0v / w). After stirring for four days by the addition of 1N NaOH 1.1 mL (1.10mmol) at room temperature, further MeOH 5.0mL (5.0v / w), 1N NaOH 2.0mL the (2.0mmol) at 35 ℃ in addition 3h and the mixture was stirred. After completion of the reaction, 1 N HCl 6.1 mL was added, After distilling off the solvent was concentrated under reduced pressure was separated and the organic layer was added EtOAc 5.0mL (5.0mL) .NaClaq. 5.0mL (5.0v / w) Wash the organic layer was added, the organic layer as a white solid was concentrated under reduced pressure to Boc-D-Phe-D- Phe-D-Leu-D-Lys (Boc) – α-Boc-Pic-OH 975.1mg (99.3% yield, HPLC purity 80.8% )
to a round-bottomed flask of 20mL Boc-D-Phe-D -Phe-D-Leu-D-Lys (Boc) It was charged -α-Boc-Pic-OH ( 10) 959mg (0.978mmol), was added and dissolved EtOAc 4.9mL (5.0v / w). And 4h stirring at room temperature was added dropwise 4N HCl / EtOAc 4.9mL (5.0mL) at room temperature. After completion of the reaction, it was filtered under reduced pressure, a white solid as to give D-Phe-D-Phe- D-Leu-D-Lys-Pic the (A) (96.4% yield, HPLC purity 79.2%) .
References
- S. Sinatra Raymond; Jonathan S. Jahr;. J. Michael Watkins-Pitchford (14 October 2010) The Essence Of Analgesia And Analgesics …. Cambridge University Press Pp 490-491 ISBN 978-1-139-49198-3 .
- A Janecka, Perlikowska R, Gach K, Wyrebska A, Fichna J (2010) “Development Of Opioid Peptide Analogs For Pain Relief”.. Curr Pharm Des… 16 (9):. 1126-35 Doi : 10.2174 / 138161210790963869 . PMID 20030621 .
- Apfelbaum Jeffrey (8 September 2014). Ambulatory Anesthesia, An Issue Of Anesthesiology Clinics, . Elsevier Health Sciences. Pp. 190-. ISBN 978-0-323-29934-3 .
- Cowan Alan;. Gil Yosipovitch (10 April 2015) Pharmacology Of Itch …. Springer Pp 307- ISBN 978-3-662-44605-8 .
- Allerton Charlotte (2013). Pain Therapeutics: Current And Future Treatment Paradigms …. Royal Society Of Chemistry Pp 56- ISBN 978-1-84973-645-9 .
REFERENCES
1: Cowan A, Kehner GB, Inan S. Targeting Itch With Ligands Selective For kappa Opioid
. Receptors Handb Exp Pharmacol 2015; 226:.. 291-314 Doi:
.. 10.1007 / 978-3-662-44605-8_16 Review PubMed PMID: 25861786.
 |
|
| Systematic (IUPAC) Name | |
|---|---|
|
Amino–4 1- ( D -Phenylalanyl- D -Phenylalanyl- D -Leucyl- D -Lysyl) Piperidine-4-Carboxylic Acid
|
|
| Clinical data | |
| Of Routes Administration |
Intravenous |
| Pharmacokinetic Data | |
| Bioavailability | Pasento 100 ( IV ) [1] |
| Metabolism | Metabolized Not [1] |
| Biological half-life | Hours 2 [1] |
| Excretion | As Unchanged Excreted Drug Via Bile And Urine [1] |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | 1024828-77-0 |
| ATC code | None |
| ChemSpider | 44208824 |
| Chemical data | |
| Formula | C 36 H 53 N 7 O 6 |
| Molar mass | 679.85 g / mol |
///// Difelikefalin, CR845 , FE-202845, Phase III, PEPTIDES
CC (C) C [C @ H] (C (= O) N [C @ H] (CCCCN) C (= O) N1CCC (CC1) (C (= O) O) N) NC (= O) [ C @@ H] (Cc2ccccc2) NC (= O) [C @@ H] (Cc3ccccc3) N












































 .
.




















 DRUG APPROVALS BY DR ANTHONY MELVIN CRASTO …..
DRUG APPROVALS BY DR ANTHONY MELVIN CRASTO …..


 LIONEL MY SON
LIONEL MY SON